the second one in Weekly Contest 198.
Difficulty : Medium
Related Topics : DFS、BFS
Given a tree (i.e. a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of
nnodes numbered from0ton - 1and exactlyn - 1edges. The root of the tree is the node0, and each node of the tree has a label which is a lower-case character given in the stringlabels(i.e. The node with the numberihas the labellabels[i]).The
edgesarray is given on the formedges[i] = [ai, bi], which means there is an edge between nodesaiandbiin the tree.Return an array of size
nwhereans[i]is the number of nodes in the subtree of theithnode which have the same label as nodei.A subtree of a tree
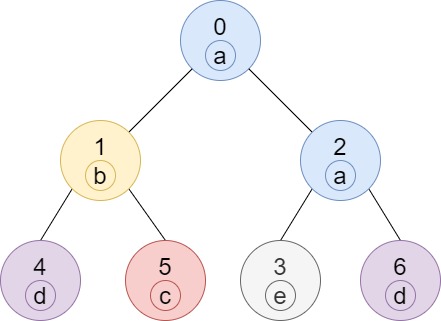
Tis the tree consisting of a node inTand all of its descendant nodes.Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], labels = "abaedcd" Output: [2,1,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: Node 0 has label 'a' and its sub-tree has node 2 with label 'a' as well, thus the answer is 2. Notice that any node is part of its sub-tree. Node 1 has a label 'b'. The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1,4 and 5, as nodes 4 and 5 have different labels than node 1, the answer is just 1 (the node itself).Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,3]], labels = "bbbb" Output: [4,2,1,1] Explanation: The sub-tree of node 2 contains only node 2, so the answer is 1. The sub-tree of node 3 contains only node 3, so the answer is 1. The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1 and 2, both have label 'b', thus the answer is 2. The sub-tree of node 0 contains nodes 0, 1, 2 and 3, all with label 'b', thus the answer is 4.Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[0,4]], labels = "aabab" Output: [3,2,1,1,1]Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[3,4],[4,5]], labels = "cbabaa" Output: [1,2,1,1,2,1]Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6]], labels = "aaabaaa" Output: [6,5,4,1,3,2,1]
1 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bilabels.length == nlabelsis consisting of only of lower-case English letters.
- mine
- Java
- Build Tree & DFS
Runtime: 119 ms, faster than 77.77%, Memory Usage: 207.5 MB, less than 100.00% of Java online submissions//O(N)time //O(N)space public int[] countSubTrees(int n, int[][] edges, String labels) { int[] res = new int[n]; Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); Node root = new Node(0); map.put(0, root); for (int[] e : edges) { if (!map.containsKey(e[0])) { Node t = new Node(e[0]); map.put(e[0], t); map.get(e[1]).nexts.add(t); } else { Node t = new Node(e[1]); map.put(e[1], t); map.get(e[0]).nexts.add(t); } } char[] arr = labels.toCharArray(); dfs(root, arr, res); return res; } int[] dfs(Node node, char[] arr, int[] res) { if (node == null) { return null; } if (node.nexts.size() == 0) { int[] record = new int[26]; record[arr[node.id] - 'a']++; res[node.id] = record[arr[node.id] - 'a']; return record; } int[] r = new int[26]; for (Node n : node.nexts) { int[] t = dfs(n, arr, res); for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) { r[i] += t[i]; } } r[arr[node.id] - 'a']++; res[node.id] = r[arr[node.id] - 'a']; return r; } class Node{ List<Node> nexts; int id; public Node(int id){ nexts = new ArrayList<>(); this.id = id; } }
- Build Tree & DFS
- Java
- the most votes
Runtime: 143 ms, faster than 66.98%, Memory Usage: 106.1 MB, less than 100.00% of Java online submissions//O(N)time //O(N)space public int[] countSubTrees(int n, int[][] edges, String labels) { Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g = new HashMap<>(); for (int[] e : edges) { g.computeIfAbsent(e[0], l -> new ArrayList<>()).add(e[1]); g.computeIfAbsent(e[1], l -> new ArrayList<>()).add(e[0]); } int[] ans = new int[n]; dfs(g, 0, -1, labels, ans); return ans; } private int[] dfs(Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g, int node, int parent, String labels, int[] ans) { int[] cnt = new int[26]; char c = labels.charAt(node); for (int child : g.getOrDefault(node, Collections.emptyList())) { if (child != parent) { int[] sub = dfs(g, child, node, labels, ans); for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) { cnt[i] += sub[i]; } } } ++cnt[c - 'a']; ans[node] = cnt[c - 'a']; return cnt; }