You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
#ifndef _CHANNEL_H_
#define _CHANNEL_H_
#include "pv.h"
typedef struct
{
int count; // allocate count
int used; // used count
int cursor; // current position to rcv
int last; // current position to send
int valsize; // each element size
void *data; // data memory ptr
mutex_t lock; // mutex lock
} channel_t;
channel_t *new_chan(int valsize);
// send val to channel
// if channel is full, expand it, the expand strategy is old_size * 2
int chan_send(channel_t *chan, void *val);
// recv value from channel
// return !0 if channel empty
// otherwise return 0 and update the element params
int chan_rcv(channel_t *chan, void *ele);
// free queue data
// free channel
void free_chan(channel_t *chan);
#endif
channel.c:
接口实现
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "channel.h"
channel_t *new_chan(int valsize)
{
channel_t *ch = malloc(sizeof(channel_t));
if (!ch) {
return NULL;
}
ch->count = 1;
ch->valsize = valsize;
ch->cursor = 0;
ch->last = 0;
ch->used = 0;
ch->data = malloc(valsize);
mutex_init(ch->lock);
return ch;
}
// send val to channel
int chan_send(channel_t *chan, void *val)
{
if (!chan) {
return -1;
}
P(chan->lock);
if (chan->used == chan->count)
{
int old = chan->count;
int newcount = old * 2;
chan->data = realloc(chan->data, chan->valsize * newcount);
if (!chan->data)
{
V(chan->lock);
return -2;
}
// reconstruct queue
// supporse that the old channel is data[1,2,3,4,5]
// the cursor pointer is 3, the last pointer is 2.
// after expand, the channel is data[1,2,3,4,5,0,0,0,0...]
// it should be data[0,0,3,4,5,1,2,0,0,0...]
// the last pointer should be cursor + old_queue_size
memcpy(chan->data + old * chan->valsize, chan->data, chan->cursor * chan->valsize);
chan->count = newcount;
chan->last = chan->cursor + old;
}
memcpy(chan->data + chan->last * chan->valsize, val, chan->valsize);
chan->last = (chan->last + 1);
if (chan->last == chan->count)
chan->last = 0;
chan->used += 1;
V(chan->lock);
return 0;
}
// recv value from channel
int chan_rcv(channel_t *chan, void *ele)
{
P(chan->lock);
if (chan->used == 0)
{
V(chan->lock);
return -1;
}
memcpy(ele, chan->data + chan->cursor * chan->valsize, chan->valsize);
chan->used -= 1;
chan->cursor += 1;
if (chan->cursor == chan->count)
{ // cursor move the begin of the queue
chan->cursor = 0;
}
V(chan->lock);
return 0;
}
// free channel
void free_chan(channel_t *chan)
{
mutex_destroy(chan->lock);
free(chan->data);
free(chan);
}
// reconstruct queue
// supporse that the old channel is data[1,2,3,4,5]
// the cursor pointer is 3, the last pointer is 2.
// after expand, the channel is data[1,2,3,4,5,0,0,0,0...]
// it should be data[0,0,3,4,5,1,2,0,0,0...]
// the last pointer should be cursor + old_queue_size
memcpy(chan->data + old * chan->valsize, chan->data, chan->cursor * chan->valsize);
chan->count = newcount;
chan->last = chan->cursor + old;
总的来说很小巧,不难,又有意思,适合无聊逛github的时候看看。
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
最近看到一段用c实现的channel,感觉挺小巧精妙的,就好好研究了下。
包含两个基本操作:1、往channel发送数据;2、从channel中读取数据
本质上是用一段内存来实现一个环形队列。用两个游标来指向队头和队尾。每次要发送时,往队尾加数据,要读取时,从队头游标获取数据,当内存块不足时进行扩容,扩容机制采用的是原来内存块*2的方式。针对并发操作,用锁来保证同一时刻环形队列只有一个线程操作。
下面是具体代码,代码量很少。
channel.h:
定义基本数据结构以及接口
channel.c:
接口实现
pv.h:
锁操作的包裹函数
接下来用图片显示具体每个操作之后内存状态。
初始化
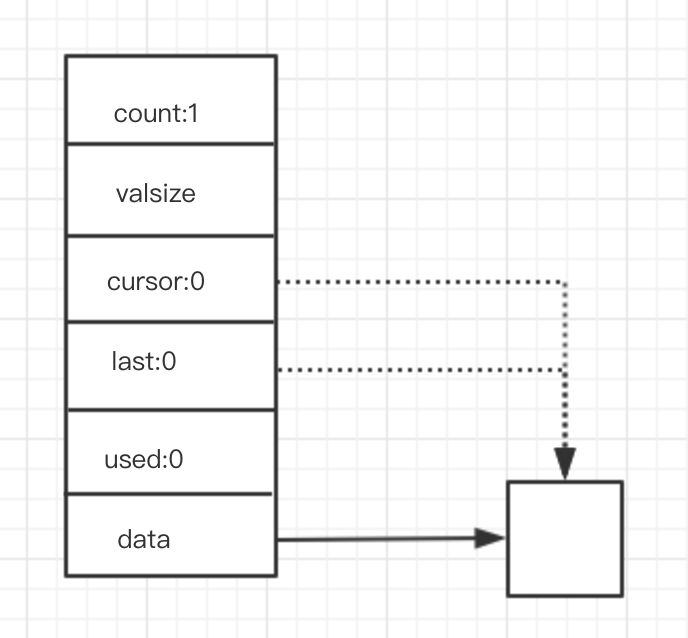
分配一个元素的空间
chan_send p1
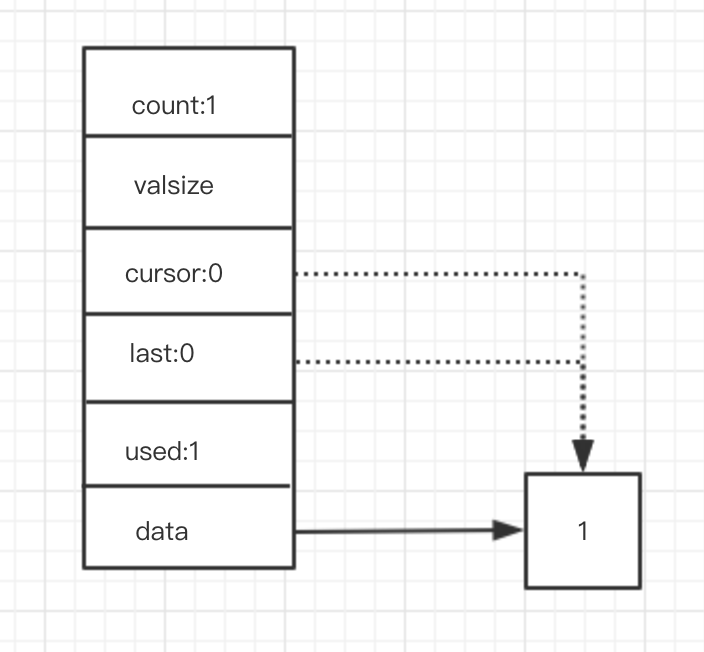
不需要扩容,直接附加到last即可
chan_send p2
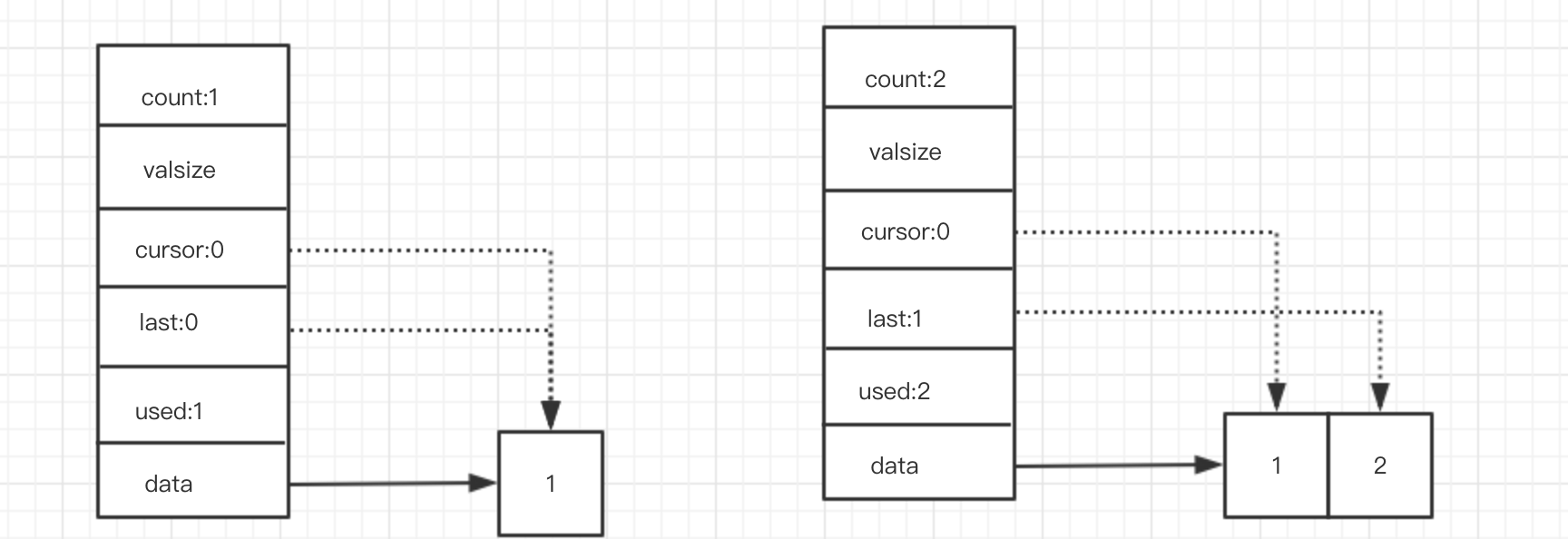
send p1之后,data指向的内存块已被占用完。需要进行扩容,然后再附加到last
接下来如果继续send,仅仅是重复上面两个过程,容量充足,则附加到last,不足,扩容再附加。
但是通常不会出现一直send的情况,会在send和rcv之间交替进行。
假设 send p1和send p2之后执行recv操作。
稍稍有点奇怪,但是也还算正常,这时候如果再 send p3, send p4。
这里挺巧妙的,需要琢磨一下,为了保证先进先出,需要将cursor之前的数据,也就是后进的数据移动到后面。代码当中也写了很长一段注释说明。
总的来说很小巧,不难,又有意思,适合无聊逛github的时候看看。
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: