-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 77
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
E32 433T30D transmission not received #57
Comments
|
Unplug the 1 watt units from your teensy immediately. These units can easily consume more power that the onboard regulator can supply. I've burned up some NANO's forgetting about power consumptions. I'm surprised the regulator survived this long. These units really don't like 5v0 power supply. 3v3 is their recommend input voltage. I hope the voltage / heat issue did not damage the EBYTES Do you have the antennas connected? The settings look like they match on both units. These should send/receive. |
|
Hi Kris, what do you recommend I power the Ebytes with, should I get another one just to be safe? |
|
I power all of mine with DC to DC buck converters there’s a wide variety of them on Amazon some have fixed output voltages some are variable. I’ve used several different types just as long as you’re out putting 3.3 V you should be good and at least one amp. Hard to see if your unit is fried. Do you have antennas installed? |
|
Yep, I have antennas installed, What else could be causing the problems? I believe the current and voltage requirements are being fulfilled with my setup |
|
Can you indicate exactly what you’re wearing connections are? |
|
I seriously doubt it will matter between a 3.2 and a 4.0 since they’re both 32 bit but each my pack that struct differently Try sending just one bite |
|
I’ll knock this up sometime this weekend and see if there are differences between how three point twos and 4.0’s interact |
|
I think I see what this issue is... I tried your exact code and mine did not work either. I noticed your receiver code does not have the Transceiver.SaveParameters(PERMANENT); Call I just tried the following (with the Transceiver.SaveParameters(PERMANENT); call) Teensy LC -> Teensy 4.0 Mine works, transmits and receives.. Try this... in your receiver code just after add the line Transceiver.SaveParameters(PERMANENT); This should get things working. |
|
You only need the library to program these units, let's skip the library completely and just use the serial port. If this does not work, i'd say your units are defective. // transmitter // create the transceiver object, passing in the serial and pins void setup() { digitalWrite(PIN_MO, LOW); Serial.begin(9600); while (!Serial) {} ESerial.begin(9600); Serial.println("Starting Sender"); } void loop() { ESerial.print(9); Serial.print("Sending"); delay(1000); } //////////////////////////////////////// #define ESerial Serial1 //note serial1 is pin 0 and 1 in the MCU, EBYTE Rx connects to pin 1, EBYTE Tx connects to pin 0 void setup() { digitalWrite(PIN_MO, LOW); while (!Serial) {} ESerial.begin(9600); Serial.println("Starting Reader"); } void loop() { if ESerial.available()) { } } } |
|
I would check the data sheet for an acceptable range of supply voltages |
|
one last thing, put a delay(10) in the receiver loop just before the available() call. I noticed my Teensy 4.0 sometimes can't ready the serial port from my GPS sensor, |
|
Alright Kris! I'll try that, would you mind if I close this issue once I get the new Ebyte (should be in 2 days) and test it? |
|
That is great news. I find these units very reliable even if loss of power, they start right up and continue working. I have these in a home automation setting (remote garage door and outside temp monitoring) and have been working for about 2 years with no issues. If you find yourself wanting to communicate between 2 different MCU (a Teensy and NANO), the structure will probably pack differently and become garbled up on the receive, attribute (packed)_ may help, or use the EasyTransfer library. |
|
Ok Kris, will keep that in mind! |
|
Hi Kris, one last thing, the datasheet recommends using this module with 5V, would it be ok to power it with 5V @ 3A (using an AP63300 to stepdown 7.4V to 5V, 7.4V comes from a 2s Li-Po). |
|
If that’s what the data sheet says… I’ve always powered mine with 3.3 they seem to get warm at 5 V. However before you connect your RX and TX lines I would measure the output voltage and make sure there’s still 3.3 if you power from 5 volts TEensy 4 are not 5 V tolerant. I’m not sure about that specific buck converter but that’s all I use.
Thanks.
Kris Kasprzak
… On Oct 12, 2022, at 11:53 AM, moonman ***@***.***> wrote:
Hi Kris, one last thing, the datasheet recommends using this module with 5V, would it be ok to power it with 5V @ 3A (using an AP63300 to stepdown 7.4V to 5V, 7.4V comes from a 2s Li-Po).
—
Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub, or unsubscribe.
You are receiving this because you modified the open/close state.
|







Hi Kris, firstly thanks for making this library! I'm having some problems with receiving data packets.
I'm using the E32 433T30D 1W module and a Teensy 4.0 with the transmitter and Teensy 3.2 with the receiver. I tried powering the transmitter E32 with a Panasonic NCR18650PF 3c 2900mAh Li-Ion battery, but the E32 was got extremely hot, so I'm currently powering both with the onboard teensy vregs.
This is the Transmitter code:-
This is the receiver's code:
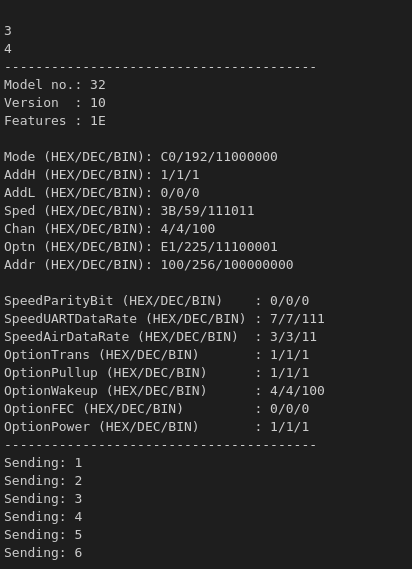
Here's all the transmitter's parameters:
The receiver's parameters:
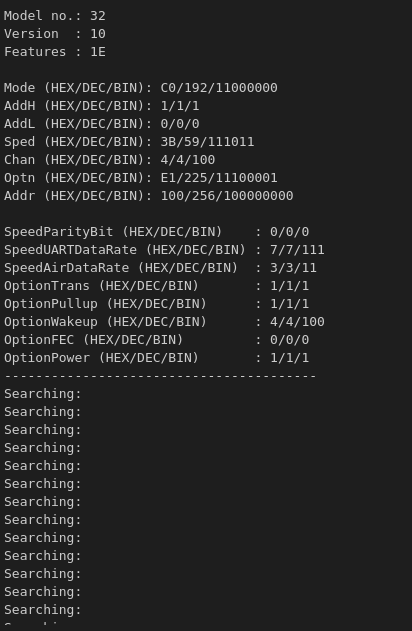
As you can see in the screenshots above, the transmitter has successfully sent data packets yet the receiver is still searching. Could you help me with this?
Thanks,
moonman
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: