Shivani kulkarni
Introduction of machine learning:-
Basically, ml is a machine which is a branch of AI.also it already has its own program which is then modified and put forward to make a real model.basically it's a pattern based language in which pattern is consists of clusters(collection of similar things) Key terminologies involved are: • converting data into information • solving problem • implementing the problem.Now, let's have a look on different types of ML through one tree diagram

- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
- Reinforcement learning
So now our main agenda is to learn about unsupervised machine learning
What is unsupervised machine learning?
- Labels/targets are unknown
- Finding hidden pattern in unlabeled data
- Problem itself is ambiguous
In unsupervised algorithm we kind of don't know what we are looking for so problem itself is ambiguous
Let's have a look on following diagram for understanding unsupervised ML in simple way
So basically unsupervised learning can be taught of as self learning where there is no teacher and the algorithm confined previously unknown pattern in dataset that does not have any sort of labels Let's take one real life exampleSuppose you and your friends want to watch the cricket match but you don't know what cricket is but for your friend you say yes then you reach home and start watching the match you don't really have an idea what's happening but looking at your friends you analyze the screen and come to some conclusion like • There are two teams India and Australia • Different kinds of players such as ballers,batters • Ball hits wicket or is caught batsman is out • Cheer when India score a 4 or 6 From knowing nothing to knowing everything about cricket you can enjoy the match now So basically you have materials and you learn everything by yourself so these is the principal that exactly unsupervised algorithm follows
Now we will see why unsupervised learning is important for real world solving problem ?
- They find pattern which are previously unknown
- Patterns help in categorization or finding association
- They can detect anomalies & detects in the data
- They work on unlabeled data which makes our work easier
Application of unsupervised learning :-
- Dimension reduction
- Image compression
- Anomaly detection
Let's give ans to following question to get to know how much you understand till now Quiz:- In which of the following scenario you would most likely use an unsupervised ML algorithm?
- a set of images are given to you in which you are interested in grouping the ones which are similar
- Given training data about user preferences you are interested in knowing whether they would like/dislike a movie
- Given a set of 1000 features you are interested in finding features that captures max variance in data
So ans could be 1&3 because in 2nd the training data is already provided. Let's see how clustering works on unsupervised ML algorithm
What is Clustering ?
We group similar items together,if our data is unlabeled we need to calculate similarity measures.
In these case over here we are not given any information about fruits. Now unsupervised learning algorithm trying to find hidden patterns in these data and then it will trying to classify things into different buckets without any prior information So in the above image we all can see how clustering works and set a group of fruits in a way that fruits having same color,shapes falls into one group having same pattern(clusters) Now let's understand clustering in detailedSimilarity measures are directly proportional to features.
# Clusturing approach how you would approach clustering problem let's have a look:- Now we have data sets like everything is black now our job is to color some of these as red and some of these as green And to do that initially you can obviously look at the things and color some of them as red and some as green and cluster those two things so what do you need for clustering let's have a look
# Proximity measure So 1st we need to do is to calculate proximity measure, it is the vector distance between two clusters, One of the method used for proximity is euclidean distance it is calculated as, D=√((x1-x2)^2+(y1-y2)^2)
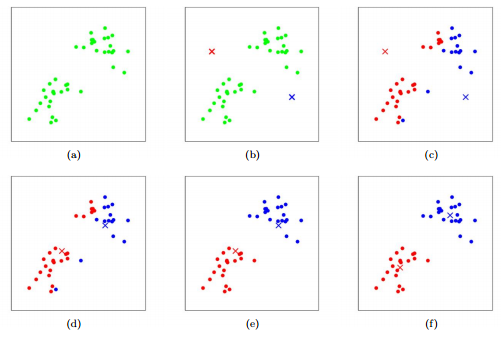
# Evaluation criteria 2)second thing you also need is now once yow create cluster you also need to see what a good cluster looks like and so there are some measures called evaluation criteria these will tell us how far two clusters are or how close points of one cluster are. So that's how you would approach cluster problem. # k-means To decide whether we get good results of clusters k-means plays an important role # k-means algorithm:- Now we are going to study one such approach to clustering which is called as k-means it's one of the famous algorithm for clustering Now, these points are not labeled eventually they look separate afterwards it performs many iteration on dataset and eventually come up with good ans,
Let's have a look on steps involved in implementation of k-means algorithm
Initializing the k value
So k-means is nothing but it comes with k centroids of the clusters so by looking the above example we assume that there are two clusters so let's say k=2 so we have two controllers of cluster.so there may be one question arises in everyone's mind,thats how we'll selects that two centroids, so initially we selects it randomly
Assignment step
so what k-means gonna do next it will find distance of all data points from the centroid and then which points are closest to say(red cluster) it marked itself as red & these step is called as assignment step as each point is assigned itself to a particular cluster
Equidistant case
Now there is also one case arrived as what about that points which are equidistant from say (red cluster) as well from centroid indeed in that case the pseudo code is applied as follows,
If { (I am closest to red) || (no) } Else if{ ( distance from red>=something ) ||(no) print(one cluster) Else if{ (distance<something) print(another cluster) } Else { (assign point to blue) }
So in these that "no" catches all in the Equality Case so machine will randomly assign itself to one cluster in case if they are equidistant
Move Centroid Step
In this step, we will calculating the mean of all data points in a particular cluster and move the centroid of that cluster to that mean position. We will repeat the above two steps once one of the following conditions is true: • Our centroids stop changing their positions. • Maximum number of iterations are reached. Our data is now arranged into clusters.
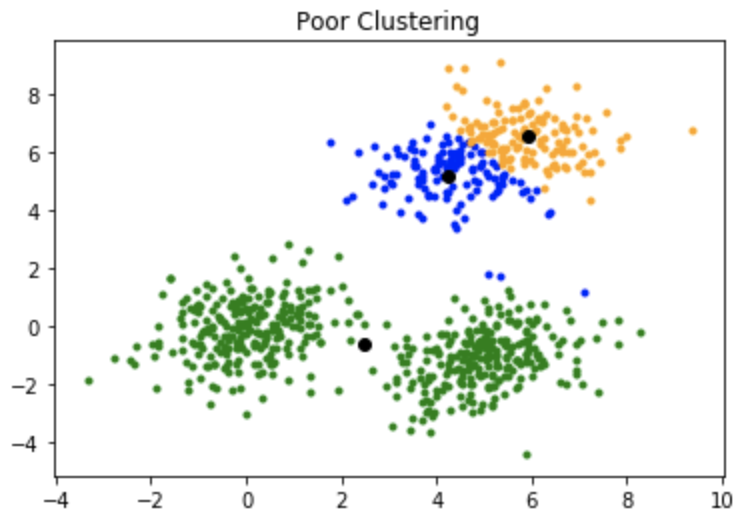
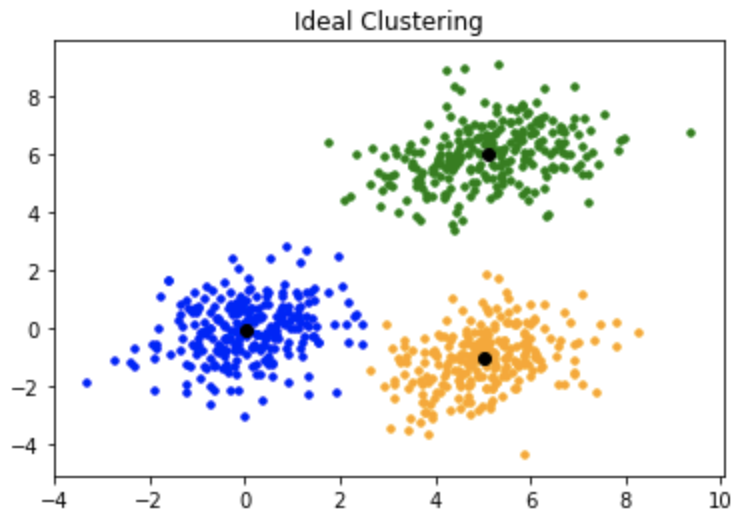
So finally after aplication of k-means we got final cluster as,
Let's discuss the flow chart in detailed
Steps involved
-
Select the number of clusters to be identified for eg:-select k=3 in above case
-
Measure the distance between the 1st point & selected 3 clusters
-
Assign the first point to nearest cluster(red in this case)
-
Calculate the centroid value including the new point for red cluster
-
Find to which does point 2 belongs and how? • Repeat the same above procedure but measure the distance of 2nd point from mean position • Calculate the cluster mean including new point
-
Repeat the procedure for points in 1st cluster.
-
Do the iteration until the data points within each cluster don't have space for moving
In case of graph we perform the same procedure the only difference is distance is calculated as euclidean distance in 2D it's nothing but a simple Pythagoras theorem.
Let's have one quiz:- Calculate distortion of clustering algorithm for following values £(data xi-centroid x) ^2 + (data yi-centroid y) ^2
Data x Data y Centroid x Centroid y
5 3 3 3
2 3
how to decide centroids But main question arises here Is that how do you go about deciding how many centroids to take over here just to explain we take two clusters but by even looking at the data we know there are 2 clusters only but how about when you are in higher dimensions like when you have 1000 features we can't even visualize that but approach is gonna same you have to use hit and trail method initializing from k=1
- K=1 is the worst case scenario >it will have 20different clusters for. 20 different data points
- K=2 is still better than k=1 it compares the total variation with k=1
- K=3 is even better in this total variation is less than that of k=2
Each time you increase the clusters the total variation decreases if, number of cluster=number of data points then in that case variation=0
number of clusters is inversely proportional to total variation.
Finally we plot reduction in variance,for per value of k on that basis we plot one graph in which on x axis there is reduction in variance and on y axis there is no of clusters that method is called as elbow method
Let's understand elbow method through above image
Initially we start with 1 cluster and we will see that distortion is 3.5 ok now let's do k-means once more say number of cluster at 2 & distortion is 1.5 after a point you will get elbow like structure so you select the point which is at elbow location which is at around 3 and reason behind that is after this we are getting some incrementally better results so you are not getting significant improvement in your distortion so it doesn't make any sense.these is what elbow method is used to determine how many number of clusters we should choose. on x axis we have no of k and on y axis we have distortion, So now by looking above graph we are going to choose point which looks like elbow and which is 3 it will show that we have 3 clusters i.e k=3 In these way k-means algorithm works
Coming to the next algorithm let's see hierarchical clustering algorithm in detail
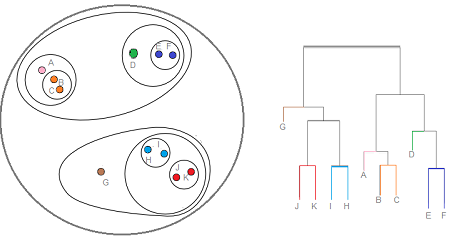
What is hierarchical clustering? It is separating data into different groups based on some measures of similarity. Let's consider we have 5 letters a,b,c,d,e in which a,b are closed and c,d are close to each other and e is a little bit far away from c and d so a,b form one cluster c,d forms one cluster c,d,e comines and form one cluster and finally all comines and form cluster consisting of a,b,c,d,e In these way hierarchical clustering goes. **types involved are** Agglomerative clustering:-it is a bottom up approach it combines the clusters and form one cluster Divisive clustering:-it is a top down approach it splits the clusters into subclusters.Let's understand the types one by one
Agglomerative clusters Let's consider we have few points on plane having x and y axis We are going to start by measuring the distance between each data point so we need to figure it out
remember each data point is a cluster of its own.
Now by going from bottom up agglomerative then we have each point being it's own cluster we try to find out the least distance between two data points to form a cluster and once by finding those points we start clustering of multiple points these tree like structure is called dendogram.
How to measure distance between two data points?
Distance measure will determine similarity between two elements and it will influence shape of cluster
4 ways to determine distance are as follows Euclidean distance:-playing with triangle shape Square euclidean distance:-playing with square shape Manhattan distance Cosine distance:-similarity measure angle between two vector.
Let's understand agglomerative clustering through three questions How do we represent cluster of more than one point? Steps:- We make use of centroid which is the argument of its points Once we made centroid of two clusters we find out which another is close to it then we make new point centroid Combine the clusters.
When do we stop combining clusters? approaches involved are:- Pick a no of clusters k upfront
we decide the cluster required in the beginning and we terminate when we reach the value k for ex:if we start with 2 clusters we have to terminate it when we left with 2 clusters Clusters are going to Stop when the next merge would create a cluster having low cohesion we keep clustering till next merge of clusters create a bad cluster/low cohesion How is cohesion define:- diameter of cluster=maximum distance between any pair of points in the cluster we stop it when diameter of new cluster exceeds threshold we don't want 2 clusters overlap.we stop before overlapping.
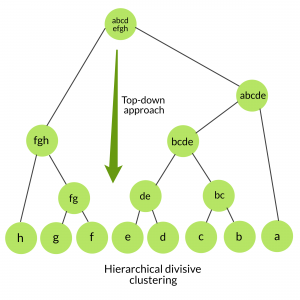
divisibe clustering What is divisive clustering:- We start with a single cluster consisting of all data points We separate it into different clusters
separation can be done using monothetic divisive method
monothetic divisive method Let's understand it through one example
Suppose we have 6 points a,b,c,d,e,f now we are going to apply top down approach so, Obtain all possible splits into two clusters For each split compute cluster sum of squares Bj12=n1(xj1-xj) ^2 +n2(xj2-xj) ^2
Where, Bj=between clusters 1&2 Xj1/2=mean of clusters n=no of member in cluster Xj=total mean We always selects cluster with largest sum of square distances
Let's have a look on steps involved in hierarchical clustering algorithm Import dataset Create a scatter plot Normalize the data Calculate euclidean distance Create a dendogram
Well we'll see how it's gonna implement in HOW section.
So at the end we all can see how we start to explore data & we start to see things where things are grouped together in a ways we might not have seen before and there is good start for giving advice for ex: city developement & many more.
do visit me 👇
thanks for reading ❤️