-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 10
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
JS源码片段 #46
Comments
函数工具记忆函数function memorize(func) {
const cache = new Map()
return (...args) => {
const key = JSON.stringify(args)
if (cache.has(key)) {
return cache.get(key)
}
const result = func(...args)
cache.set(key, result)
return result
}
} |
自定义字典对字符串进行加解密源自: https://github.com/wheatup/hexie-encode const _dict = ['富强', '民主', '文明', '和谐', '自由', '平等', '公正', '法治', '爱国', '敬业', '诚信', '友善'];
const encode = (src, dict = _dict) => {
dict = [...new Set(Array.isArray(dict) ? dict : [...dict])];
const decimal = dict.length - 1;
const codes = src.toString().split('').map(e => {
const code = e.charCodeAt(0);
const digits = [code % decimal];
let remainder = code;
while ((remainder /= decimal) >= 1) {
digits.unshift(remainder % decimal ^ 0);
}
return digits;
});
const result = [...codes].map((c, i) => c.map(d => dict[d]).join('') + (i < codes.length - 1 ? dict[dict.length - 1] : '')).join('');
return result;
}
const decode = (src, dict = _dict) => {
dict = [...new Set(Array.isArray(dict) ? dict : [...dict])];
const raw = dict.reduce((acc, key, index) =>
acc.replace(new RegExp(key, 'gm'), index === dict.length - 1 ? ',' : `{${index}}`), src);
const result = raw.split(',')
.map(e => /{(.+?)}/g[Symbol.match](e)
.map(e => +e.replace(/[\{\}]/g, ''))
.reduce((acc, cur, i, arr) => acc + cur * ((dict.length - 1) ** (arr.length - i - 1)), 0)
).map(e => String.fromCharCode(e)).join('');
return result
}
if (typeof module !== 'undefined') {
module.exports = {
encode,
decode
};
} |
实现函数的 bind, call, applybind 函数Function.prototype.myBind = function (ctx, ...args) {
const fn = this;
// 返回一个新的函数
return (...newArgs) => {
// 在新函数内部手动设置上下文,并调用原始函数
return fn.apply(ctx, [...args, ...newArgs]);
};
}call 函数Function.prototype.myCall = function (ctx, ...args) {
// 如果未传递context,则默认为全局对象
ctx = ctx === null || ctx === undefined ? globalThis : Object(ctx);
// 生成唯一的键,防止冲突
const key = Symbol();
// 将函数添加到ctx对象上,并设置为不可枚举
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
value: this,
enumerable: false,
});
const result = ctx[key](...args);
// 删除添加的函数属性
delete ctx[key];
return result;
};apply 函数Function.prototype.myApply = function (ctx, args) {
ctx = ctx === null || ctx === undefined ? globalThis : Object(ctx);
const key = Symbol();
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
value: this,
enumerable: false,
});
const result = ctx[key](...args);
delete ctx[key];
return result;
} |
Promise的实现finallyPromise.prototype.finally = function (callback) {
return this.then(
(value) => Promise.resolve(callback()).then(() => value),
(reason) =>
Promise.resolve(callback()).then(() => {
throw reason;
})
);
} |
函数式柯里化
柯里化是将接受多个参数的函数变换成接受一个单参 (最初函数的第一个参数) 的函数,并且返回一个接受剩余参数的新函数。
const add = function (x) {
return function (y) {
return x + y;
};
};
const increment = add(1);
increment(10); // 11通用的 柯里化 函数: function currying(func, ...args1) {
const length = func.length;
return function (...args2) {
const newArgs = [...args1, ...args2];
if (newArgs.length >= length) {
return func(...newArgs);
} else {
return currying(func, ...newArgs);
}
};
}函数组合
函数组合是指将代表各个动作的多个函数合并成一个函数。
函数 compose 的代码如下: const compose = (f, g) => x => f(g(x))
const f = x => x + 1;
const g = x => x * 2;
const fg = compose(f, g);
fg(1) //3我们可以看到 compose 就实现了一个简单的功能:形成了一个全新的函数,而这个函数就是一条从 compose(f, compose(g, t)) = compose(compose(f, g), t) = f(g(t(x)))只要其顺序一致,最后的结果是一致的。
通用的 compose 函数: function compose(...fns) {
return function (...args) {
return fns.reduceRight((arg, fn) => fn.apply(this, [].concat(arg)), args);
};
}函子
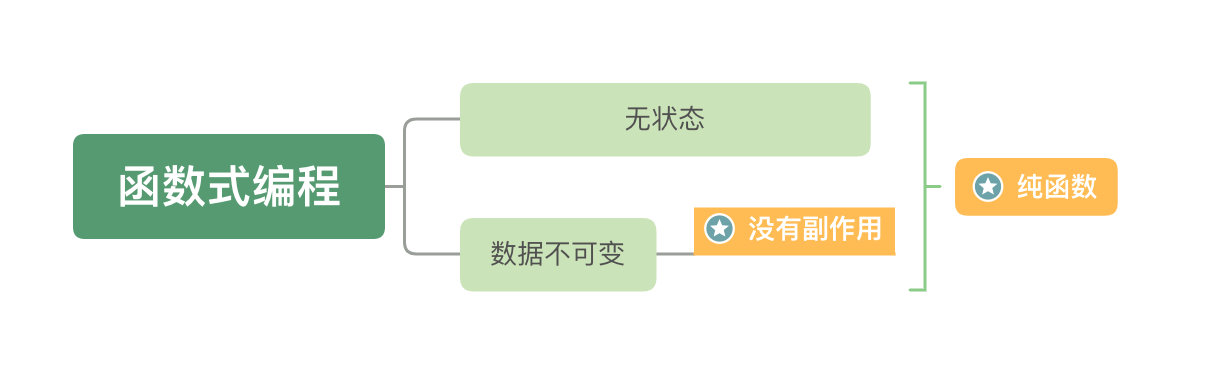
在函数式编程中,`函子 (Functor)`是一种具有特定行为和约定的对象或数据结构。它通过定义了 `map` 方法来支持函数的组合和转换,并遵循一定的规则。
函子具有以下特点:
函子通过 下面是一个示例展示一个简单的函子的实现: // 定义一个简单的函子
class Functor {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
}
// 定义 map 函数,用于将函数应用于容器中的值
map(fn) {
return new Functor(fn(this.value));
}
// 定义静态方法, 去掉调用时使用`new`
static of(value) {
return new Functor(value);
}
}
// 使用 map 方法应用函数到函子容器中的值
cosnt result = Functor.of(1).map(add4).map(multiply4)
console.log(result.value) // 20函子遵循一些法则,可以使得函数式编程更方便可靠。比如 const func = Functor.of(1)
func.map(x => f(g(x))) = func.map(g).map(f)函子的概念是函数式编程中的核心概念之一,它能够使我们以一种声明式的方式操作和组合数据。函子的应用可以帮助我们减少副作用和提高代码的可读性和可维护性。 |
斐波那契数列循环实现斐波那契数列function fibonacciWithLoop(n) {
if (n <= 1) return n
let [a, b] = [0, 1]
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
[a, b] = [b, a + b]
}
return b
}递归实现斐波那契数列function fibonacci(n) {
if (n <= 1) return n
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
}递归实现斐波那契数列(缓存)function fibonacciWithMemo(n, memo = {}) {
if (n in memo) return memo[n]
if (n <= 1) return n
memo[n] = fibonacci(n-1, memo) + fibonacci(n-2, memo)
return memo[n]
}递归实现斐波那契数列 (尾递归)/**
* 使用尾递归计算斐波那契数列的第 n 个数
*
* @param {number} n - 斐波那契数列的索引 (n >= 0)
* @param {number} [acc1=0] - 斐波那契数列的第 n-2 个数 (默认值为 0)
* @param {number} [acc2=1] - 斐波那契数列的第 n-1 个数 (默认值为 1)
* @return {number} 斐波那契数列的第 n 个数
*/
function fibonacciWithTail(n, acc1 = 0, acc2 = 1) {
if (n === 0) return acc1;
if (n === 1) return acc2;
return fibonacci(n - 1, acc2, acc1 + acc2);
} |
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment
No description provided.
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: