Adversarial Deep Domain Adaptation-Based Diagnosis of COVID-19 from Lung CT Scans Using Triplet Embeddings.
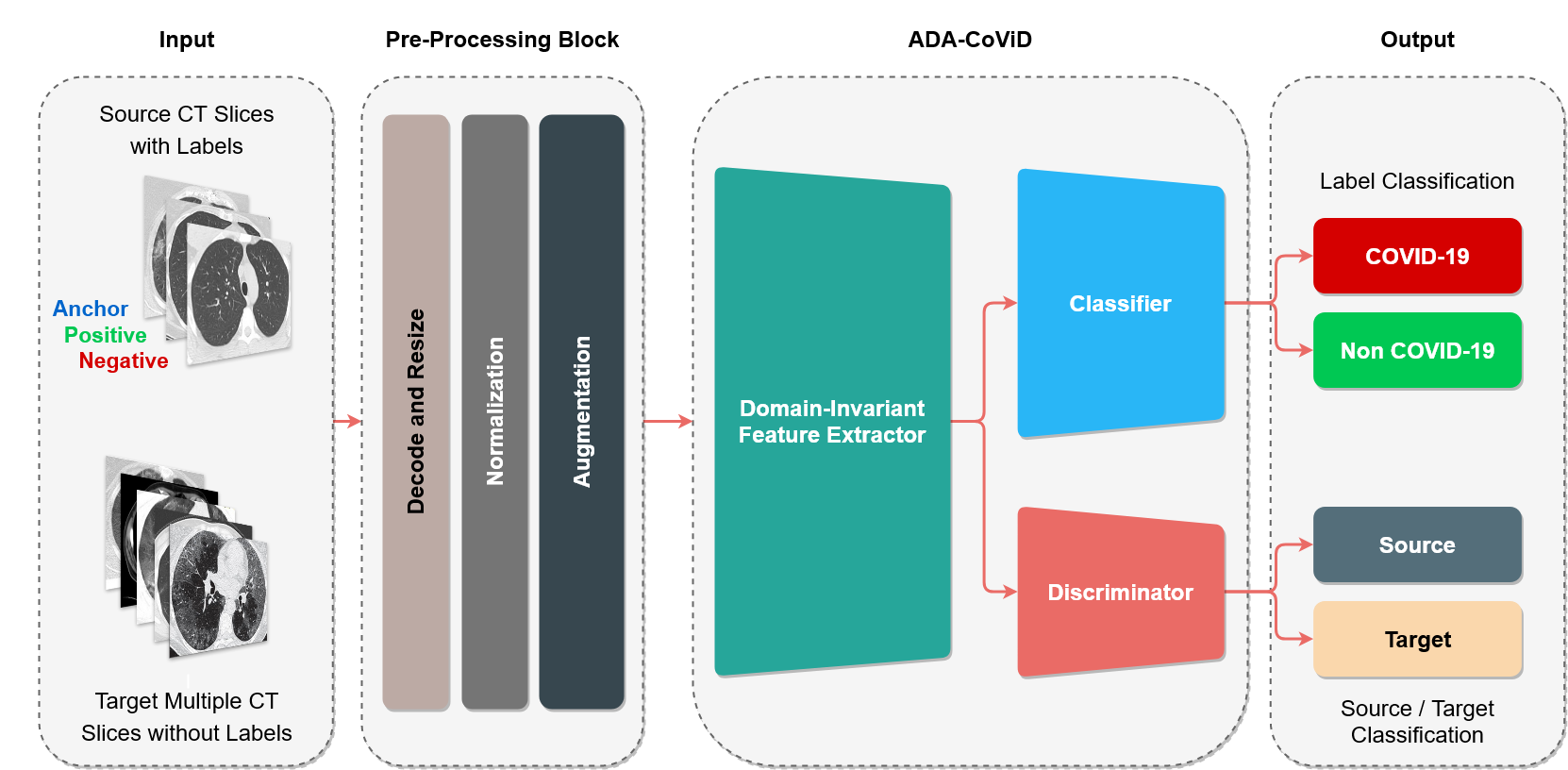
Rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 with high reliability is essential in the early stages. To this end, recent research often uses medical imaging combined with machine vision methods to diagnose COVID-19. However, the scarcity of medical images and the inherent differences in existing datasets that arise from different medical imaging tools, methods, and specialists may affect the generalization of machine learning-based methods. Also, most of these methods are trained and tested on the same dataset, reducing the generalizability and causing low reliability of the obtained model in real-world applications. This paper introduces an adversarial deep domain adaptation-based approach for diagnosing COVID-19 from lung CT scan images, termed ADA-COVID. Domain adaptation-based training process receives multiple datasets with different input domains to generate domain-invariant representations for medical images. Also, due to the excessive structural similarity of medical images compared to other image data in machine vision tasks, we use the triplet loss function to generate similar representations for samples of the same class (infected cases). The performance of ADA-COVID is evaluated and compared with other state-of-the-art COVID-19 diagnosis algorithms. The obtained results indicate that ADA-COVID achieves classification improvements of at least 3%, 20%, 20%, and 11% in accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score, respectively, compared to the best results of competitors, even without directly training on the same data.
Use ADA-COVID.py
# Example
python ADA-COVID.py --source_path "/source.txt" --target_path "/target.txt" --batch_size 32Parameters:
--number_of_gpus: Number of gpus to run. | default = '1'--network_name: Name of the feature extractor network. | default = 'ResNet50'--dataset_name: Name of the source dataset. | default = 'COVID'--dropout_classifier: Dropout ratio for classifier. | default = 0.25--dropout_discriminator: Dropout ratio for discriminator. | default = 0.25--source_path: default = Path to source dataset. | 'Source.txt'--target_path: default = Path to target dataset. | 'Target.txt'--lr_classifier: Learning rate for classifier model. | default = 0.0001--b1_classifier: Exponential decay rate of first moment. | default = 0.9--b2_classifier: Exponential decay rate of second moment for classifier model optimizer. | default = 0.999--lr_discriminator: Learning rate for discriminator model. | default = 0.00001--b1_discriminator: Exponential decay rate of first moment for discriminator optimizer. | default = 0.9--b2_discriminator: Exponential decay rate of second moment for discriminator optimizer. | default = 0.999--lr_combined: Learning rate for combined model. | default = 0.00001--b1_combined: Exponential decay rate of first moment for combined model optimizer. | default = 0.9--b2_combined: Exponential decay rate of second moment for combined model optimizer. | default = 0.999--classifier_loss_weight: Classifier loss weight. | default = 4--discriminator_loss_weight: Discriminator loss weight. | default = 1--batch_size: Batch size for training. | default = 32--test_interval: Gap between two successive test phases. | default = 30--num_iterations: Number of iterations. | default = 12000--snapshot_interval: Minimum gap between saving outputs. | default = 30--output_dir: Directory for saving outputs. | default = 'Models'
-
The paper (Open Access): ADA-COVID: Adversarial Deep Domain Adaptation-Based Diagnosis of COVID-19 from Lung CT Scans Using Triplet Embeddings
-
The dataset is accessible via Kaggle.
Aria, M., et al. "COVID-19 Lung CT Scans: A large dataset of lung CT scans for COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) detection." Kaggle. doi: https://doi.org/10.34740/kaggle/dsv/1875670. [accessed 2021-04-20] (2021).
- The model is not publicly available at this moment.
- Please cite the following paper:
Mehrad Aria, Esmaeil Nourani, Amin Golzari Oskouei,
"ADA-COVID: Adversarial Deep Domain Adaptation-Based Diagnosis of COVID-19 from Lung CT Scans Using Triplet Embeddings",
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, vol. 2022, Article ID 2564022, 17 pages, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2564022
- Please do not distribute the database or source codes to others without author authorization.
Authors’ Email:
mehrad.aria[at]shirazu.ac.ir(M. Aria).