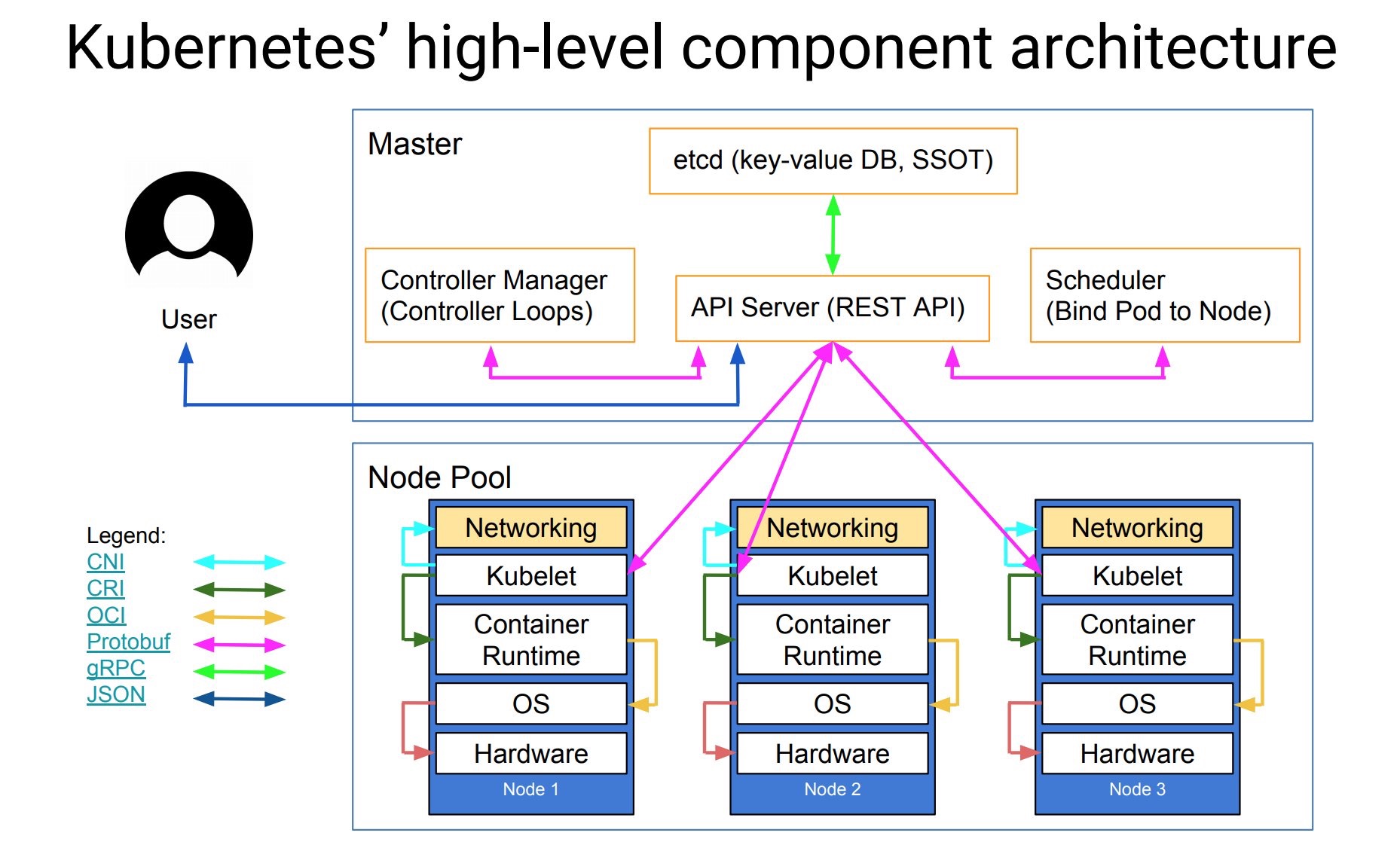
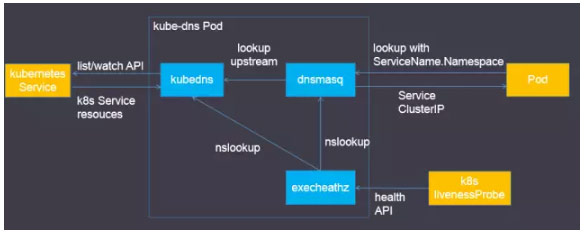
[TOC]
kubeadm 是官方提供的工具,用于快速安装一个最小运行的 Cluster,因此安装过程中不会安装相关的 addons,同时也不会安装相关的网络组件,主要我们自己调用 kubectl apply 命令进行安装兼容 CNI 标准的组件,例如 flannel。参考文档:
- Using kubeadm to Create a Cluster 介绍了使用 kubeadm 建立一个集群的主要步骤
- Overview of kubeadm 详细介绍了工具的使用细节
通过 kubeadm 工具安装 Cluster,有点类似于 Ceph 的安装方式。
在k8s 1.9.x 版本中,kubeadm整体特性已经为Beta版本,预计在2018年将会General Availability (GA)。
关于安装过程中的镜像问题:
kubeadm 中默认的镜像源是 Google Could的地址,因此在国内安装如果不能翻墙的话,可以参考一下文档:Running kubeadm without an internet connection, HA 方式可以参考 [kubeadm-highavailiability 1.7.x],离线安装过程中需要的镜像列表:
Image Name v1.8 release branch version v1.9 release branch version k8s.gcr.io/kube-apiserver-${ARCH} v1.8.x v1.9.x k8s.gcr.io/kube-controller-manager-${ARCH} v1.8.x v1.9.x k8s.gcr.io/kube-scheduler-${ARCH} v1.8.x v1.9.x k8s.gcr.io/kube-proxy-${ARCH} v1.8.x v1.9.x k8s.gcr.io/etcd-${ARCH} 3.0.17 3.1.10 k8s.gcr.io/pause-${ARCH} 3.0 3.0 k8s.gcr.io/k8s-dns-sidecar-${ARCH} 1.14.5 1.14.7 k8s.gcr.io/k8s-dns-kube-dns-${ARCH} 1.14.5 1.14.7 k8s.gcr.io/k8s-dns-dnsmasq-nanny-${ARCH} 1.14.5 1.14.7
如果在阿里云上安装,也可以采用阿里云提供的镜像,可能镜像同步会有滞后:阿里云快速部署Kubernetes - VPC环境 阿里云 kubernetes yum 仓库镜像
本地安装K8S可以通过 Minikube 与 Kubeadm,Minikube 使用虚拟机的方式,非常方便,但是只能安装单节点的集群,对于最新的 K8S 版本支持有点滞后,因此如果使用最新版本的话 Kubeadm 更加方便。
使用 VMWare Fusion 安装 Centos7 虚拟机两台,网络采用NAT方式,网段为 172.16.132.0/24
172.16.132.10 master node1
172.16.132.11 node2
**required ports **
Master node(s)
| Protocol | Direction | Port Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | Inbound | 6443* | Kubernetes API server |
| TCP | Inbound | 2379-2380 | etcd server client API |
| TCP | Inbound | 10250 | Kubelet API |
| TCP | Inbound | 10251 | kube-scheduler |
| TCP | Inbound | 10252 | kube-controller-manager |
| TCP | Inbound | 10255 | Read-only Kubelet API |
Worker node(s) kubernetes 简介: kubelet 和 pod
| Protocol | Direction | Port Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | Inbound | 10250 | Kubelet API |
| TCP | Inbound | 10255 | Read-only Kubelet API http://xxx:10255/pods or /spec/ or /stats |
| TCP | Inbound | 4194 | cAdvisor, 配置成0,则禁用 |
| TCP | Inbound | 10248 | localhost healthz endpoint |
| TCP | Inbound | 30000-32767 | NodePort Services |
在 Master 主机上设置相关指令:
# 设置时区
$ timedatectl list-timezones
$ timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
# 安装 lsb 工具
$ yum install redhat-lsb -y
$ lsb_release -a
LSB Version: :core-4.1-amd64:core-4.1-noarch:cxx-4.1-amd64:cxx-4.1-noarch:desktop-4.1-amd64:desktop-4.1-noarch:languages-4.1-amd64:languages-4.1-noarch:printing-4.1-amd64:printing-4.1-noarch
Distributor ID: CentOS
Description: CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core)
Release: 7.4.1708
Codename: Core
# 配置静态IP地址
$ vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
TYPE="Ethernet"
BOOTPROTO="static" # 修改 dhcp -> static
IPADDR=172.16.132.10
GATEWAY=172.16.132.2
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
DNS1=172.16.132.2
DEFROUTE="yes"
PEERDNS="yes"
PEERROUTES="yes"
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
NAME="ens33"
UUID="018249e8-2e66-41ec-8974-032e1ca47244"
DEVICE="ens33"
ONBOOT="yes"
# 重启网卡生效
$ systemctl restart network
# 设置DNS
$ vim /etc/resolv.conf
# Generated by NetworkManager
nameserver 172.16.132.2 # vmware 虚拟机
# 关闭防火墙
$ systemctl status firewalld
$ systemctl stop firewalld
$ systemctl disable firewalld
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
# 从Mac机器上添加证书
$ ssh-copy-id root@172.16.132.10
The authenticity of host '172.16.132.10 (172.16.132.10)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:4vwrFA2u0DwO8G0jCN+rqp3A3ZVf1oTIDb+LNG9M334.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/local/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/local/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@172.16.132.10's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@172.16.132.10'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
# 禁用 selinux
$ setenforce 0
$ vim /etc/selinux/config
SELINUX=disabled
$ cat /etc/hosts
172.16.132.10 node1
172.16.132.11 node2需要禁用 IPv6,防止后续的操作碰到IPv6的地址:
$ ifconfig -a | grep inet6
inet6 fe80::211:aff:fe6a:9de4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10[host]
# add /etc/sysctl.conf
$ cat /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
$ sysctl -p使用Centos 7中自带docker版本
$ yum install -y docker
$ systemctl enable docker && systemctl start docker
$ docker version
Client:
Version: 1.12.6
API version: 1.24
Package version: docker-1.12.6-68.gitec8512b.el7.centos.x86_64
Go version: go1.8.3
Git commit: ec8512b/1.12.6
Built: Mon Dec 11 16:08:42 2017
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
$ docker info
Containers: 0
Running: 0
Paused: 0
Stopped: 0
Images: 0
Server Version: 1.12.6
Storage Driver: devicemapper
Pool Name: docker-8:3-34809708-pool
Pool Blocksize: 65.54 kB
Base Device Size: 10.74 GB
Backing Filesystem: xfs
Data file: /dev/loop0
Metadata file: /dev/loop1
Data Space Used: 11.8 MB
Data Space Total: 107.4 GB
Data Space Available: 14.57 GB
Metadata Space Used: 581.6 kB
Metadata Space Total: 2.147 GB
Metadata Space Available: 2.147 GB
Thin Pool Minimum Free Space: 10.74 GB
Udev Sync Supported: true
Deferred Removal Enabled: true
Deferred Deletion Enabled: true
Deferred Deleted Device Count: 0
Data loop file: /var/lib/docker/devicemapper/devicemapper/data
WARNING: Usage of loopback devices is strongly discouraged for production use. Use `--storage-opt dm.thinpooldev` to specify a custom block storage device.
Metadata loop file: /var/lib/docker/devicemapper/devicemapper/metadata
Library Version: 1.02.140-RHEL7 (2017-05-03)
Logging Driver: journald
Cgroup Driver: systemd # 默认为systemd,不需要单独设置,否则在/etc/docker/daemon.json中设置
Plugins:
Volume: local
Network: host bridge overlay null
Swarm: inactive
Runtimes: docker-runc runc
Default Runtime: docker-runc
Security Options: seccomp selinux
Kernel Version: 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64
Operating System: CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
OSType: linux
Architecture: x86_64
Number of Docker Hooks: 3
CPUs: 1
Total Memory: 976.3 MiB
Name: master
ID: W4NY:E6NL:NV37:46ME:GYTH:Q3P7:VQKC:ONYH:YOIR:4TRK:6CAO:XBRB
Docker Root Dir: /var/lib/docker
Debug Mode (client): false
Debug Mode (server): false
Registry: https://index.docker.io/v1/
Insecure Registries:
127.0.0.0/8
Registries: docker.io (secure)On each of your machines, install Docker. Version v1.12 is recommended, but v1.11, v1.13 and 17.03 are known to work as well. Versions 17.06+ might work, but have not yet been tested and verified by the Kubernetes node team.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/independent/install-kubeadm/
可选: 安装 Docker CE版本 一般用于最新版本验证
$ yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
# 添加 repo
$ yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
$ yum list docker-ce.x86_64 --showduplicates |sort -r
* updates: mirrors.163.com
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
docker-ce.x86_64 17.12.0.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable
docker-ce.x86_64 17.09.1.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable
docker-ce.x86_64 17.09.0.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable
docker-ce.x86_64 17.06.2.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable
docker-ce.x86_64 17.06.1.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable
docker-ce.x86_64 17.06.0.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable
docker-ce.x86_64 17.03.2.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable
docker-ce.x86_64 17.03.1.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable
docker-ce.x86_64 17.03.0.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
Available Packages
# 安装 docker-ce-17.03.2 或者 使用 centos 默认支持的版本
# $ yum makecache fast
#$ yum install -y --setopt=obsoletes=0 \
# docker-ce-17.03.2.ce-1.el7.centos \
# docker-ce-selinux-17.03.2.ce-1.el7.centos
# docker 1.12.6 中,不需要设置该参数 cmd 中已经包含
# 使用系统默认支持的方法
# Note: Make sure that the cgroup driver used by kubelet is the same as the one used by Docker. # To ensure compatability you can either update Docker, like so:
$ mkdir -p /etc/docker/
$ cat << EOF > /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"]
}
EOF
$ cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
sysctl --system
设置官方 Repo
$ cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
setenforce 0
$ yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl安装 kubelete 和 kubeadm
安装 kubeadm/kubectl/kubernetes-cni 三个主要程序,安装两个依赖包kubernetes-cni 和 socat
由于 socat 安装不需要翻墙,如果翻墙了还可能存在安装的问题,建议先安装 socat 后再翻墙
$ yum install -y socat以下过程需要科学上网
$ yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.163.com
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package kubeadm.x86_64 0:1.9.1-0 will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: kubernetes-cni for package: kubeadm-1.9.1-0.x86_64
---> Package kubectl.x86_64 0:1.9.1-0 will be installed
---> Package kubelet.x86_64 0:1.9.1-0 will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: socat for package: kubelet-1.9.1-0.x86_64
--> Running transaction check
---> Package kubernetes-cni.x86_64 0:0.6.0-0 will be installed
---> Package socat.x86_64 0:1.7.3.2-2.el7 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
Package Arch Version Repository Size
=========================================================
Installing:
kubeadm x86_64 1.9.1-0 kubernetes 16 M
kubectl x86_64 1.9.1-0 kubernetes 8.9 M
kubelet x86_64 1.9.1-0 kubernetes 17 M
Installing for dependencies:
kubernetes-cni x86_64 0.6.0-0 kubernetes 8.6 M
socat x86_64 1.7.3.2-2.el7 base 290 k
Transaction Summary
=========================================================
Install 3 Packages (+2 Dependent packages)
Total size: 51 M
Installed size: 274 M
Downloading packages:
warning: /var/cache/yum/x86_64/7/kubernetes/packages/cec192f6a1a3a90321f0458d336dd56ccbe78f2a47b33bfd6e8fd78151fa3326-kubelet-1.9.1-0.x86_64.rpm: Header V4 RSA/SHA1 Signature, key ID 3e1ba8d5: NOKEY
Retrieving key from https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg
Importing GPG key 0xA7317B0F:
Userid : "Google Cloud Packages Automatic Signing Key <gc-team@google.com>"
Fingerprint: d0bc 747f d8ca f711 7500 d6fa 3746 c208 a731 7b0f
From : https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg
Retrieving key from https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
Importing GPG key 0x3E1BA8D5:
Userid : "Google Cloud Packages RPM Signing Key <gc-team@google.com>"
Fingerprint: 3749 e1ba 95a8 6ce0 5454 6ed2 f09c 394c 3e1b a8d5
From : https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : kubectl-1.9.1-0.x86_64 1/5
Installing : socat-1.7.3.2-2.el7.x86_64 2/5
Installing : kubernetes-cni-0.6.0-0.x86_64 3/5
Installing : kubelet-1.9.1-0.x86_64 4/5
Installing : kubeadm-1.9.1-0.x86_64 5/5
Verifying : kubelet-1.9.1-0.x86_64 1/5
Verifying : kubernetes-cni-0.6.0-0.x86_64 2/5
Verifying : socat-1.7.3.2-2.el7.x86_64 3/5
Verifying : kubeadm-1.9.1-0.x86_64 4/5
Verifying : kubectl-1.9.1-0.x86_64 5/5
Installed:
kubeadm.x86_64 0:1.9.1-0
kubectl.x86_64 0:1.9.1-0
kubelet.x86_64 0:1.9.1-0
Dependency Installed:
kubernetes-cni.x86_64 0:0.6.0-0
socat.x86_64 0:1.7.3.2-2.el7
Complete!使用 kubeadm验证一下版本信息:
$ kubeadm version
kubeadm version: &version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"9", GitVersion:"v1.9.1", GitCommit:"3a1c9449a956b6026f075fa3134ff92f7d55f812", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2018-01-04T11:40:06Z", GoVersion:"go1.9.2", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
$ systemctl enable kubelet
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/kubelet.service to /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service
# RHEL/CentOS 7 have reported issues with traffic being routed incorrectly due to iptables being bypassed
$ cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
# 不开启 IPv6,因此注释掉
# net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
# 配置生效
$ sysctl --system由于还未采用kubeam进行集群初始化,因此现在启动 kubelet 服务会报错,可以使用命令 systemctl status kubelet 和 tail -f /var/log/messages查看,目前为止可以忽略报错信息,大致错误如下:
.....
error: unable to load client CA file /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt: open /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt: no such file or directory**
.....设置 Kubelete Swap 选项
Kubernetes 1.8开始要求关闭系统的Swap,如果不关闭,默认配置下kubelet将无法启动。可以通过kubelet的启动参数--fail-swap-on=false更改这个限制。
全局关闭: 关闭系统的Swap方法如下:
swapoff -a修改 /etc/fstab 文件,注释掉 SWAP 的自动挂载,使用
free -m确认swap已经关闭。 > swappiness参数调整,修改/etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf添加下面一行:vm.swappiness=0执行
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf使修改生效。
因为测试主机上还运行其他服务,关闭swap可能会对其他服务产生影响,所以这里修改kubelet的启动参数 --fail-swap-on=false 去掉这个限制。修改 /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf,加入:
Environment="KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=--fail-swap-on=false"
$ systemctl daemon-reloadkubelete 的配置文件全部内容如下:
$ cat /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf
[Service]
Environment="KUBELET_KUBECONFIG_ARGS=--bootstrap-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.conf --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf"
Environment="KUBELET_SYSTEM_PODS_ARGS=--pod-manifest-path=/etc/kubernetes/manifests --allow-privileged=true"
Environment="KUBELET_NETWORK_ARGS=--network-plugin=cni --cni-conf-dir=/etc/cni/net.d --cni-bin-dir=/opt/cni/bin"
Environment="KUBELET_DNS_ARGS=--cluster-dns=10.96.0.10 --cluster-domain=cluster.local"
Environment="KUBELET_AUTHZ_ARGS=--authorization-mode=Webhook --client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt"
Environment="KUBELET_CADVISOR_ARGS=--cadvisor-port=0"
Environment="KUBELET_CGROUP_ARGS=--cgroup-driver=systemd"
Environment="KUBELET_CERTIFICATE_ARGS=--rotate-certificates=true --cert-dir=/var/lib/kubelet/pki"
# add for this time ==================================
Environment="KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=--fail-swap-on=false"
ExecStart=
ExecStart=/usr/bin/kubelet $KUBELET_KUBECONFIG_ARGS $KUBELET_SYSTEM_PODS_ARGS $KUBELET_NETWORK_ARGS $KUBELET_DNS_ARGS $KUBELET_AUTHZ_ARGS $KUBELET_CADVISOR_ARGS $KUBELET_CGROUP_ARGS $KUBELET_CERTIFICATE_ARGS $KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS
启动 Kubelete 服务
$ systemctl daemon-reload
$ systemctl start kubelet以上操作完成后,可以使用 Vmware 的 Take Snapshot 创建一个快照,然后关闭虚拟机使用 Create Full Clone 功能将我们安装虚拟机 Clone 成 Node 节点,然后根据需要修改IP地址等信息即可;在阿里云的环境中我们一般是将这个具备了一定环境的系统保存为镜像,以后扩容的时候可以方便使用,不再需要从头安装。
Kubernetes 1.8开始要求关闭系统的Swap,如果不关闭,默认配置下kubelet将无法启动,本安装过程中我们会采用先忽略后面再设置的方法,所以采用参数 --ignore-preflight-errors=Swap 忽略这个错误。对于 POD Network 我们采用 Flannel,Flannel 默认设置的网段为 10.244.0.0./16,因此我们在 init 命令中使用 --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 来指定。当然 kubeadm init 命令行中的参数也可以使用配置文件来配置,参见 Configureation file 章节。
init 过程中需要科学上网,(不需要翻墙安装方式见本文的第一章节)如果顺利的话,则可以看到以下输出:
$ kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.9.1 --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 --apiserver-advertise-address=172.16.132.10 --ignore-preflight-errors=Swap > install.log 2>&1 # 安装的信息
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.9.1
[init] Using Authorization modes: [Node RBAC]
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks.
[WARNING Swap]: running with swap on is not supported. Please disable swap
[WARNING FileExisting-crictl]: crictl not found in system path
[preflight] Starting the kubelet service
[certificates] Generated ca certificate and key.
[certificates] Generated apiserver certificate and key.
[certificates] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [node1 kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 172.16.132.10]
[certificates] Generated apiserver-kubelet-client certificate and key.
[certificates] Generated sa key and public key.
[certificates] Generated front-proxy-ca certificate and key.
[certificates] Generated front-proxy-client certificate and key.
[certificates] Valid certificates and keys now exist in "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[kubeconfig] Wrote KubeConfig file to disk: "admin.conf"
[kubeconfig] Wrote KubeConfig file to disk: "kubelet.conf"
[kubeconfig] Wrote KubeConfig file to disk: "controller-manager.conf"
[kubeconfig] Wrote KubeConfig file to disk: "scheduler.conf"
[controlplane] Wrote Static Pod manifest for component kube-apiserver to "/etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml"
[controlplane] Wrote Static Pod manifest for component kube-controller-manager to "/etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml"
[controlplane] Wrote Static Pod manifest for component kube-scheduler to "/etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-scheduler.yaml"
[etcd] Wrote Static Pod manifest for a local etcd instance to "/etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd.yaml"
[init] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as Static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests".
[init] This might take a minute or longer if the control plane images have to be pulled.
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 31.501968 seconds
[uploadconfig] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[markmaster] Will mark node node1 as master by adding a label and a taint
[markmaster] Master node1 tainted and labelled with key/value: node-role.kubernetes.io/master=""
[bootstraptoken] Using token: 047b97.bf92a2b4e89d9e0b
[bootstraptoken] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstraptoken] Configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstraptoken] Configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstraptoken] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-dns
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes master has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of machines by running the following on each node
as root:
kubeadm join --token 047b97.bf92a2b4e89d9e0b 172.16.132.10:6443 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f24acbcecbfa71ca8cae8367d4ad807d472107a8fca0280ff0624f503b7f93f9
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
gcr.io/google_containers/kube-apiserver-amd64 v1.9.1 e313a3e9d78d 10 days ago 210.4 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/kube-scheduler-amd64 v1.9.1 677911f7ae8f 10 days ago 62.7 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/kube-controller-manager-amd64 v1.9.1 4978f9a64966 10 days ago 137.8 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/kube-proxy-amd64 v1.9.1 e470f20528f9 10 days ago 109.1 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/etcd-amd64 3.1.10 1406502a6459 4 months ago 192.7 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/pause-amd64 3.0 99e59f495ffa 20 months ago 746.9 kB
安装中遇到的两个问题解释:
[WARNING Swap]: running with swap on is not supported. Please disable swap
---- 我们前面已经通过 kubelet 的命令行来指定
[WARNING FileExisting-crictl]: crictl not found in system path
---- crictl 工具是go开发的工具包,需要单独安装,但是安装成功后也遇到了不能解决的问题,因此可以忽略这个错误如果按照过程中遇到了其他问题,可以使用 kubeadm reset进行清除。
设置用户的 kubectl 环境
# 如果为 root 用户
$ export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
# 如果是非root用户
$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
$ cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
$ chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
# 设置 kubectl补全
$ kubectl completion bash > ~/.kube/completion.bash.inc
$ cat ~/.bash_profile
.....
source ~/.kube/completion.bash.inc
.....
$ source ~/.bash_profile获取集群的状态
$ kubectl get cs
NAME STATUS MESSAGE ERROR
scheduler Healthy ok
controller-manager Healthy ok
etcd-0 Healthy {"health": "true"}
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -o wide默认情况下 Master 节点不进行 Pod 调度,为了方便测试,我们可以通过以下命令让 Master 参与调度:
$ kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/master-更多问题排查参见:Troubleshooting kubeadm
The network must be deployed before any applications. Also, kube-dns, an internal helper service, will not start up before a network is installed. kubeadm only supports Container Network Interface (CNI) based networks (and does not support kubenet).
— From https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/independent/create-cluster-kubeadm/
本文选择 Flannel 作为 Pod Network,默认网段已经通过 init 参数 --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16指定。由于 kube-flannel.yml 中以 DaemonSet 方式运行的,能够保证每个新加如 Node 自动运行 Flannel, 因此只需要在 Master 节点上运行即可。
$ mkdir -p ~/k8s/
$ cd ~/k8s
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
$ kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
clusterrole "flannel" created
clusterrolebinding "flannel" created
serviceaccount "flannel" created
configmap "kube-flannel-cfg" created
daemonset "kube-flannel-ds" created安装完成后会创建 cni0 与 flannel.1 两个设备:
6: flannel.1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/ether 9e:a4:0e:29:5c:cf brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.244.0.0/32 scope global flannel.1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::9ca4:eff:fe29:5ccf/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
7: cni0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc noqueue state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 0a:58:0a:f4:00:01 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.244.0.1/24 scope global cni0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::c83d:76ff:fe49:6232/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
$ brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
cni0 8000.0a580af40001 no veth7f53d148
docker0 8000.0242eed2f41f no
virbr0 8000.52540096686f yes virbr0-nic
如果过程中遇到问题可以使用以下命令清除设置的相关网络设备与运行时候的配置文件:
$ ifconfig cni0 down
$ ip link delete cni0
$ ifconfig flannel.1 down
$ ip link delete flannel.1
$ rm -rf /var/lib/cni/测试 dns 和 nginx
# curl 工具,不需要翻墙
$ kubectl run curl --image=radial/busyboxplus:curl -i --tty
$ nslookup kubernetes.default
Server: 10.96.0.10
Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
Name: kubernetes.default
Address 1: 10.96.0.1 kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local
$ cat nginx-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2 # for versions before 1.8.0 use apps/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 2 # tells deployment to run 2 pods matching the template
template: # create pods using pod definition in this template
metadata:
# unlike pod-nginx.yaml, the name is not included in the meta data as a unique name is
# generated from the deployment name
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.7.9
ports:
- containerPort: 80
$ kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
# 导出服务
$ kubectl expose deployment nginx-deployment --port=80 --target-port=80
和 master node 上一样设置 kubele 相关参数(KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=--fail-swap-on=false);
保持科学上网:
$ kubeadm join --token 047b97.bf92a2b4e89d9e0b 172.16.132.10:6443 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f24acbcecbfa71ca8cae8367d4ad807d472107a8fca0280ff0624f503b7f93f9 --ignore-preflight-errors=Swap
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks.
[WARNING FileExisting-crictl]: crictl not found in system path
[discovery] Trying to connect to API Server "172.16.132.10:6443"
[discovery] Created cluster-info discovery client, requesting info from "https://172.16.132.10:6443"
[discovery] Requesting info from "https://172.16.132.10:6443" again to validate TLS against the pinned public key
[discovery] Cluster info signature and contents are valid and TLS certificate validates against pinned roots, will use API Server "172.16.132.10:6443"
[discovery] Successfully established connection with API Server "172.16.132.10:6443"
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to master and a response
was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the master to see this node join the cluster.
在 Master 节点上参看 Node 状态:
# join 的过程,需要下载镜像等准备工作,需要一定时间
$ kubectl get nodes在 Master 节点上产生证书并Copy Config到Node节点上:
$ ssh-keygen # 一路回车
$ ssh-copy-id root@172.16.132.11
# copy 配置文件到 node2上
$ scp /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf root@172.16.132.11:/root/.kube/config移除 Node
$ kubectl drain node2 --delete-local-data --force --ignore-daemonsets
$ kubectl delete node node2
# 清理
$ kubeadm reset
$ ifconfig cni0 down
$ ip link delete cni0
$ ifconfig flannel.1 down
$ ip link delete flannel.1
$ rm -rf /var/lib/cni/$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v1.8.1/src/deploy/recommended/kubernetes-dashboard.yaml
spec:
type: NodePort # add to nodeport
ports:
- port: 8443
targetPort: 8443
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
$ kubectl create -f kubernetes-dashboard.yaml
$ cat kubernetes-dashboard-admin.rbac.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard-admin
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: kubernetes-dashboard-admin
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: kubernetes-dashboard-admin
namespace: kube-system
# kubernetes-dashboard.yaml文件中的ServiceAccount kubernetes-dashboard只有相对较小的权限,因此
# 创建一个kubernetes-dashboard-admin的ServiceAccount并授予集群admin的权限
$ kubectl create -f kubernetes-dashboard-admin.rbac.yaml
serviceaccount "kubernetes-dashboard-admin" created
clusterrolebinding "kubernetes-dashboard-admin" created
$ kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep kubernetes-dashboard-admin
kubernetes-dashboard-admin-token-tszj5 kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 20s
$ kubectl describe -n kube-system secret/kubernetes-dashboard-admin-token-tszj5
kubectl describe -n kube-system secret/kubernetes-dashboard-admin-token-tszj5
Name: kubernetes-dashboard-admin-token-tszj5
Namespace: kube-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name=kubernetes-dashboard-admin
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid=dd1a582a-f9cd-11e7-85ec-000c2975be81
Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
Data
====
ca.crt: 1025 bytes
namespace: 11 bytes
token: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJrdWJlLXN5c3RlbSIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VjcmV0Lm5hbWUiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzLWRhc2hib2FyZC1hZG1pbi10b2tlbi10c3pqNSIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50Lm5hbWUiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzLWRhc2hib2FyZC1hZG1pbiIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50LnVpZCI6ImRkMWE1ODJhLWY5Y2QtMTFlNy04NWVjLTAwMGMyOTc1YmU4MSIsInN1YiI6InN5c3RlbTpzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudDprdWJlLXN5c3RlbTprdWJlcm5ldGVzLWRhc2hib2FyZC1hZG1pbiJ9.iuqjGsXy9zohzCDLSCpd4RqUyFptSZ_Al8qEpGb_D46Gfscb8DvV24qLR6QF5ejZKh_3Oe4g42GRROLsy_he8Exlxs86YDA5505QptNMDcNOqJqvlk6y8hovLl8gIu6K70ND4q_i9pIxWLDOOUuYLuDO1re3Z0rUa0jZimXiayBXUjuzbJJYYlHL9SREIjxr4y1FTsFFnbZESCYmMNKcQSwhYyTrSyPA8XiiUm_k4aYVtvWqo84nRyxreZ7DH6Zg7YT57oy8DqXHC-GNXFGj7tmDFWzih1GFvTuFp0zqhkjtS1ZAFsSNLIvIwBhg7Aj-6LyDBE4RSUOJg5UiH2trYA查询 dashboard 暴露出来的 NodePort,并使用上图的 token 信息输入:
$ kubectl get service -n kube-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP 2h
kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.111.165.62 <none> 443:31290/TCP 5m
在浏览器上输入 https://172.16.132.10:31290, 选择忽略证书,然后输入 Token 既可以访问。
Heapster为集群添加使用统计和监控功能,为Dashboard添加仪表盘。 使用InfluxDB做为Heapster的后端存储。
$ mkdir -p ~/k8s/heapster
$ cd ~/k8s/heapster
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/heapster/master/deploy/kube-config/influxdb/grafana.yaml
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/heapster/master/deploy/kube-config/rbac/heapster-rbac.yaml
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/heapster/master/deploy/kube-config/influxdb/heapster.yaml
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/heapster/master/deploy/kube-config/influxdb/influxdb.yaml
# 修改 grafana 导出的 service
$ cat grafana.yaml
....
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 3000
selector:
k8s-app: grafana
.....
$ kubectl create -f ./
$ kubectl get service -n kube-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
....
monitoring-grafana NodePort 10.103.229.66 <none> 80:32447/TCP 18m
...使用 http://172.16.132.10:32447/?orgId=1 则可以看到 Grafana 的界面,可以通过📈来查看集群中的各类资源信息。
Weaveworks 公司开源的四大组件,简化容器和微服务的部署、监控和管理,包括:
- Weave Net:创建了一个虚拟的覆盖网,它连接跨多个主机的Docker容器,模拟一个完整的两层网络,使应用可以像容器全部接入同一网络交换机一样来使用网络,不必配置端口映射、大使或挎斗(ambassadors/sidecar )容器或链路。
- Weave Scope:Weave Scope为容器调度器(比如Kubernetes)内正在运行的容器自动化地生成一个实时映射,这使人工操作可视化、可监控,并检查网络通信和相关的度量。
- Weave Flux:使容器镜像的持续交付成为可能。Weave Flux可以查询容器调度器部署的当前状态和容器镜像的上一个版本,并且,如果检测到新的版本将执行自动化部署。
- Weave Cortex:是一个兼容 Prometheus 容器监控实现的API,它原生支持多租户和水平扩展的集群。
Weave Scope为容器调度器(比如Kubernetes)内正在运行的容器自动化地生成一个实时映射,这使人工操作可视化、可监控,并检查网络通信和相关的度量。Weave Scope提供了一个个体应用容器以及整个基础设施的视图,它可以让你更轻松地诊断分布式集装箱内应用的潜在问题。
From: Weaveworks增加发布自动化和事件管理
From: https://www.weave.works/docs/scope/latest/installing/#k8s
Without Weave Cloud (run Scope in standalone mode)
$ kubectl apply --namespace weave -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/scope.yaml?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')"
$ kubectl port-forward -n weave "$(kubectl get -n weave pod --selector=weave-scope-component=app -o jsonpath='{.items..metadata.name}')" 9090
# 或者直接修改 Service,暴露出 NodePortcrictl not found in system path https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/cri-tools,需要自己编译安装
$ wget https://dl.google.com/go/go1.9.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.9.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
$ go version
go version go1.9.2 linux/amd64
$ yum install git -y
$ mkdir -p $HOME/go/src
$ export GOPATH=$HOME/go
$ go get github.com/kubernetes-incubator/cri-tools
$ cd $GOAPTH/src/github.com/kubernetes-incubator/cri-toolscri-tools/ && make
$ cp $GOPATH/bin/crictl /usr/local/bin$ kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.9.1 --pod-network-cidr=10.0.0.0/16 --apiserver-advertise-address=172.16.132.10
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.9.1
[init] Using Authorization modes: [Node RBAC]
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks.
[preflight] Some fatal errors occurred:
[ERROR Swap]: running with swap on is not supported. Please disable swap
[ERROR CRI]: unable to check if the container runtime at "/var/run/dockershim.sock" is running: exit status 1
[preflight] If you know what you are doing, you can make a check non-fatal with `--ignore-preflight-errors=...`
如果安装了 crictl,可能会报一下错误 参见 kubernetes-sigs/cri-tools#153
$ kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.9.1 --pod-network-cidr=10.0.0.0/16 --apiserver-advertise-address=172.16.132.10 --ignore-preflight-errors=Swap
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.9.1
[init] Using Authorization modes: [Node RBAC]
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks.
[preflight] Some fatal errors occurred:
[ERROR CRI]: unable to check if the container runtime at "/var/run/dockershim.sock" is running: exit status 1
[preflight] If you know what you are doing, you can make a check non-fatal with `--ignore-preflight-errors=...`
$ crictl ps
2018/01/10 11:16:54 grpc: addrConn.resetTransport failed to create client transport: connection error: desc = "transport: dial unix /var/run/dockershim.sock: connect: no such file or directory"; Reconnecting to {/var/run/dockershim.sock <nil>}
FATA[0000] listing containers failed: rpc error: code = Unavailable desc = grpc: the connection is unavailable
$ crictl --version
crictl version 1.0.0-alpha.0
From kubernetes-sigs/cri-tools#153
CRI is complaining about the lack of the shim sock, which gets checked during
kubeadm initpreflight:[ERROR CRI]: unable to check if the container runtime at "/var/run/dockershim.sock" is running: exit status 1. I don't think this is crictl because kubeadm still complains about it even without crictl installed. FYI, CRI is a kubelet concept which is exposed as a JSON API, crictl/cri-tools is just a CLI to access kubelet's CRI API.Also, kubeadm only warns with the lack of crictl, but doesn't require it. So, the additional dependencies only come into play when you want to use a different container runtime interface other than the dockershim that ships with kubelet. This is where you might use cri-o (formerly ocid), which must be manually built and additionally depends on runc.
Aside: on centos 7, runc v1.0.0 is available via extras, so a
yum install runcshould do the trick. i'm not sure about other centos versions or distros.
一个警告信息是 crictl not found in system path,另一个错误信息是 running with swap on is not supported. Please disable swap。因为我们前面已经修改了kubelet的启动参数,所以重新添加 –ignore-preflight-errors=Swap 参数忽略这个错误,重新运行。或者使用 swapoff -a 临时全局关闭,可能会影响运行的服务。
$ kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.9.1 --pod-network-cidr=10.0.0.0/16 --apiserver-advertise-address=172.16.132.10 --ignore-preflight-errors=Swap错误排查:
$ systemctl status docker.service -l
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Tue 2018-01-09 17:50:56 CST; 31s ago
Docs: http://docs.docker.com
Process: 41393 ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd-current --add-runtime docker-runc=/usr/libexec/docker/docker-runc-current --default-runtime=docker-runc --exec-opt native.cgroupdriver=systemd --userland-proxy-path=/usr/libexec/docker/docker-proxy-current $OPTIONS $DOCKER_STORAGE_OPTIONS $DOCKER_NETWORK_OPTIONS $ADD_REGISTRY $BLOCK_REGISTRY $INSECURE_REGISTRY $REGISTRIES (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Main PID: 41393 (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Jan 09 17:50:56 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting Docker Application Container Engine...
Jan 09 17:50:56 localhost.localdomain dockerd-current[41393]: time="2018-01-09T17:50:56+08:00" level=fatal msg="unable to configure the Docker daemon with file /etc/docker/daemon.json: the following directives are specified both as a flag and in the configuration file: exec-opts: (from flag: [native.cgroupdriver=systemd], from file: [native.cgroupdriver=systemd])\n"
Jan 09 17:50:56 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: docker.service: main process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
Jan 09 17:50:56 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Failed to start Docker Application Container Engine.
Jan 09 17:50:56 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Unit docker.service entered failed state.
Jan 09 17:50:56 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: docker.service failed.不能访问 API-Server 遇到 system:anonymous" cannot get path:
{
kind: "Status",
apiVersion: "v1",
metadata: { },
status: "Failure",
message: "forbidden: User "system:anonymous" cannot get path "/"",
reason: "Forbidden",
details: { },
code: 403
}解决方式1:
$ kubectl proxy --address='0.0.0.0' --port=30099 --accept-hosts='^*$'
$ http://172.16.132.100:30099/api/v1/proxy/nodes/node1/metrics解决方式2:
参见 Kubernetes集群安全:Api Server认证
添加 ServiceAccount,参考 在Kubernetes Pod中使用Service Account访问API Server
ServiceAccount 是一种账号,但是不是为集群用户(管理员、运维人员等)使用的,而是给运行在集群中的 Pod 里面的进程使用的。
留作备注,暂时不用
$ kubectl get serviceaccount --all-namespaces
$ kubectl describe serviceaccount/default -n kube-system
Name: default
Namespace: kube-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Image pull secrets: <none>
Mountable secrets: default-token-vpq4x
Tokens: default-token-vpq4x
Events: <none>
$ kubectl get secret/default-token-vpq4x -n kube-system
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
default-token-vpq4x kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 22h
$ kubectl get secret/default-token-vpq4x -o yaml -n kube-system
kubectl get secret/default-token-vpq4x -n kube-system -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
ca.crt: {{ base64 encoded }}
namespace: a3ViZS1zeXN0ZW0= # echo -n "a3ViZS1zeXN0ZW0="|base64 = kube-system
token: {{ base64 encoded }}
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: default
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: 1bd3a7d0-fa85-11e7-9d32-000c2975be81
creationTimestamp: 2018-01-16T06:18:46Z
name: default-token-vpq4x
namespace: kube-system
resourceVersion: "313"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/secrets/default-token-vpq4x
uid: 1be19e7c-fa85-11e7-9d32-000c2975be81
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-tokengcr.io/google_containers/kube-apiserver-amd64:v1.9.1 210.4 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/kube-scheduler-amd64:v1.9.1 62.7 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/kube-proxy-amd64:v1.9.1 109.1 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/kube-controller-manager-amd64:v1.9.1 137.8 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/kubernetes-dashboard-amd64:v1.8.1 120.7 MB
quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.9.1-amd64 51.31 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/k8s-dns-sidecar-amd64:1.14.7 42.03 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/k8s-dns-kube-dns-amd64:1.14.7 50.27 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/k8s-dns-dnsmasq-nanny-amd64:1.14.7 40.95 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/etcd-amd64:3.1.10 192.7 MB
gcr.io/google_containers/pause-amd64:3.0 746.9 kB
k8s.gcr.io/heapster-influxdb-amd64:v1.3.3 12.55 MB
k8s.gcr.io/heapster-grafana-amd64:v4.4.3 151.5 MB
k8s.gcr.io/heapster-amd64:v1.4.2 73.4 MB
docker.io/radial/busyboxplus:curl 4.212 MB补充:
用户证书登录与授权分别参见:Kubernetes集群安全:Api Server认证 生成用户证书和Using RBAC Authorization
$ cd /etc/kubernetes/pki/
# 查看根证书
$ openssl x509 -noout -text -in ca.crt
# 验证证书
$ openssl verify -CAfile ca.crt apiserver.crt
$ openssl genrsa -out diwh.key 2048
$ openssl req -new -key diwh.key -subj "/CN=diwh/O=kube-user" -out diwh.csr
$ openssl x509 -req -in diwh.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -out diwh.crt -days 3650
$ sz ca.crt diwh.key diwh.crt
# 设置 pod-reader role
$ cat pod-reader.yaml
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
# 绑定 role 到 user diwh
$ cat roleBinding_diwh.yaml
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: User
name: diwh
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: pod-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
# 连接使用
# 不具备 configmap,期望失败
$ kubectl --server=https://172.16.132.100:6443 --certificate-authority=ca.crt --client-certificate=diwh.crt --client-key=diwh.key get configmap
Error from server (Forbidden): configmaps is forbidden: User "diwh" cannot list configmaps in the namespace "default"
# 访问 pod,期望成功
$ kubectl --server=https://172.16.132.100:6443 --certificate-authority=ca.crt --client-certificate=diwh.crt --client-key=diwh.key get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
curl-545bbf5f9c-g28fr 1/1 Running 0 1d
nginx-deployment-6c54bd5869-8t2xt 1/1 Running 0 1d
nginx-deployment-6c54bd5869-hh2ft 1/1 Running 2 1d
- 使用kubeadm安装Kubernetes 1.9
- kubeadm部署k8s1.9高可用集群--4部署master节点
- Issues 40969
- Using kubeadm to Create a Cluster
- Kubernetes集群Dashboard插件安装
- k8s network
- Cluster Networking
- Four ways to connect a docker container to a local network
- Docker container networking
- Bridge the docker containers to external network
- Docker - Create a Bridge and Shared Network
- Build your own bridge
- Customize the docker0 bridge
- CentOS / RHEL 7 : How to disable IPv6
- k8s 中文网站
- 升级Dashboard
- 最新实践 | 将Docker网络方案进行到底