In NLP, Machine Reading Comprehension is the problem of reading and "comprehending" a given text passage, and then answering questions based on it. A Reader is a model that can do this. We can also refer to this task by talking about Extractive Question Answering: given a question and a context, the model selects the best span from the context, which answers the question.
How to get such a model, using Transformers?
Language Models are neural networks implementing the Transformer architecture. They are trained on huge linguistic corpora, to predict some masked words given the context. During the training, they leverage the attention mechanism to learn a rich, context-aware representation of language.
These models achieve state of the art in countless NLP tasks.
Once trained, a Language Model can encode an input text into a set of word vectors.
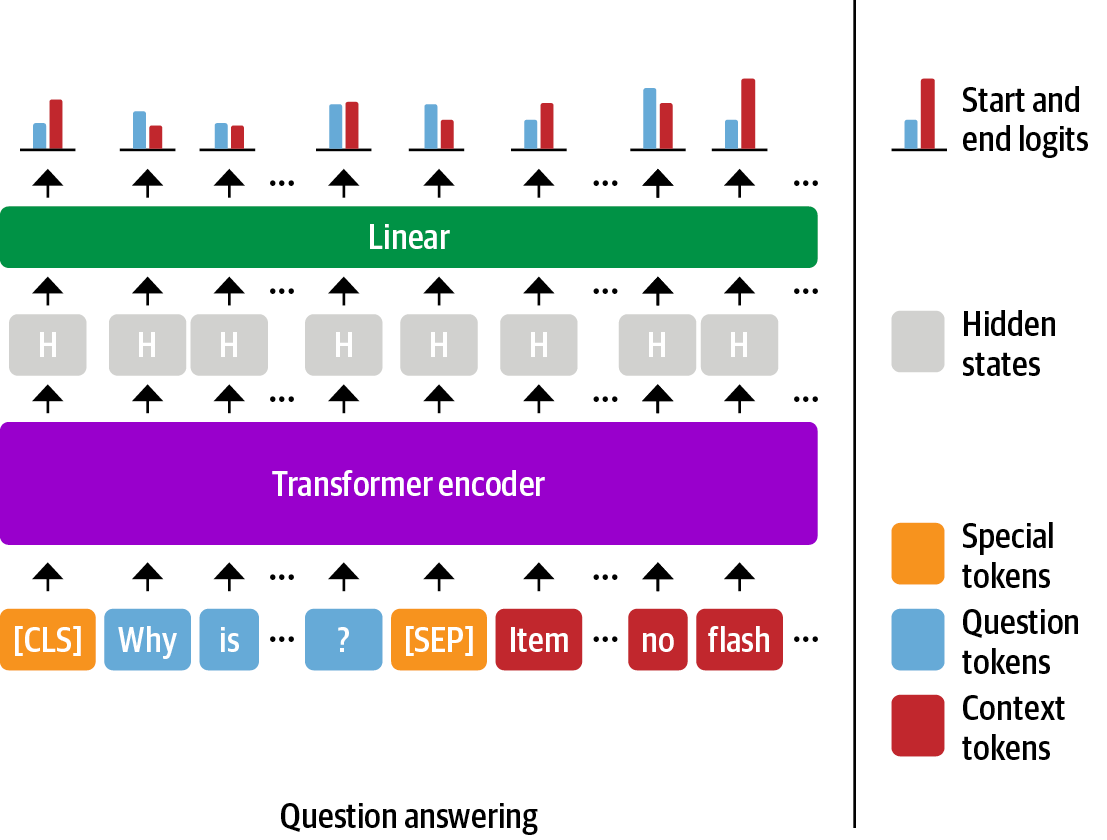 (Image from the "Natural Language Processing with Transformers" by Lewis Tunstall, Leandro von Werra, and Thomas Wolf)
(Image from the "Natural Language Processing with Transformers" by Lewis Tunstall, Leandro von Werra, and Thomas Wolf)
The Extractive Question Answering problem can be thought of as a token classification task (similar to Named Entity Extraction). Our model should assign each context token a probability 📊 of being the start or end token of the correct answer.
To fit a Language Model for this task, we add a Question Answering prediction head (a linear layer) on top of it and fine-tune the LM using a QA dataset (such as SQuAD). A Language Model usually returns vectors that contain rich linguistic knowledge (in the image, these vectors correspond to the gray hidden states). In practice, in this step, we are teaching our LM to use/update its linguistic knowledge to identify the correct answers.
We also usually adopt some strategies:
- to make the model return a "no answer" prediction if the context does not contain a valid answer.
- for tackling long passages that exceed the maximum context size of a model.
- From Language Model to Haystack Reader: simple explanation from the deepset Haystack documentation
- Modern Question Answering Systems Explained: in-depth blogpost by deepset, diving into Reader models.
- Chapter 7 of "Natural Language Processing with Transformers" by Lewis Tunstall, Leandro von Werra and Thomas Wolf - Free download