This is the base code for our work on leveraging the road plane geometry for solving self-supervised relative pose estimation using only a single pose network. Currently you will need to supply your own dataloader, option parsing and logging functionality. We developed using PyTorch and PyTorch-Lightning.
We propose a self-supervised method for relative pose estimation for road scenes. By exploiting the approximate planarity of the local ground plane, we can extract a self-supervision signal via cross-projection between images using a homography derived from estimated ground-relative pose. We augment cross-projected perceptual loss by including classical image alignment in the network training loop. We use pretrained semantic segmentation and optical flow to extract ground plane correspondences between approximately aligned images and RANSAC to find the best fitting homography. By decomposing to ground-relative pose, we obtain pseudo labels that can be used for direct supervision. We show that this extremely simple geometric model is competitive for visual odometry with much more complex self-supervised methods that must learn depth estimation in conjunction with relative pose.
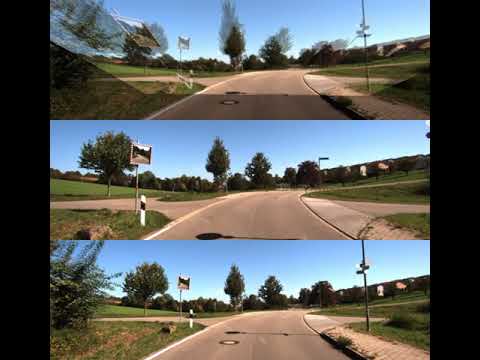
The following video illustrates our performance on KITTI VO sequence 09. The second and third rows show the input images for that scene. The first row shows a composition of the second input image with the first input image warped into the persective of the second by leveraging ground-plane cross projection. This provides us with a self-supervision signal without needing any explicit depth estimation. In this case we use a frame separation of five between input images.
The following video illustrates with a much larger frame separation which we did not train with but still achieve viable visual odometry overall.