A solidity library for verifying Ethereum message multi-signatures.
These utilities make it simple to interact with Ethereum signed messages based on EIP 191 and ERC 1077. They are a building block for Cleargraph's open and decentralized identity system, and can be used for many other purposes in decentralized applications.
You can sign a transaction/message using your private key by calling web3.personal.sign() using MetaMask, Toshi, or another compatible web3 runtime. All signatures are 65 bytes long with the format {bytes32 r}{bytes32 s}{uint8 v}. Multiple signatures are stored densely (no padding) by concatenating them.
API Reference · Read the announcement. · See tests for examples.
Signed messages are an increasingly important tool used by decentralized applications. They enable complex access management and delegation patterns and have greater flexibility than raw transactions. Wallet applications such as MetaMask and Toshi support signing transactions via their web3 provider which contracts can verify using ecrecover().
In the context of identity management, signed messages play a crucial role in building more secure and accessible wallets. Conventionally, anyone with a user's private key has full control over their wallet. This is a security vulnerability: any malicious actor with access to the user's private key can steal all funds.
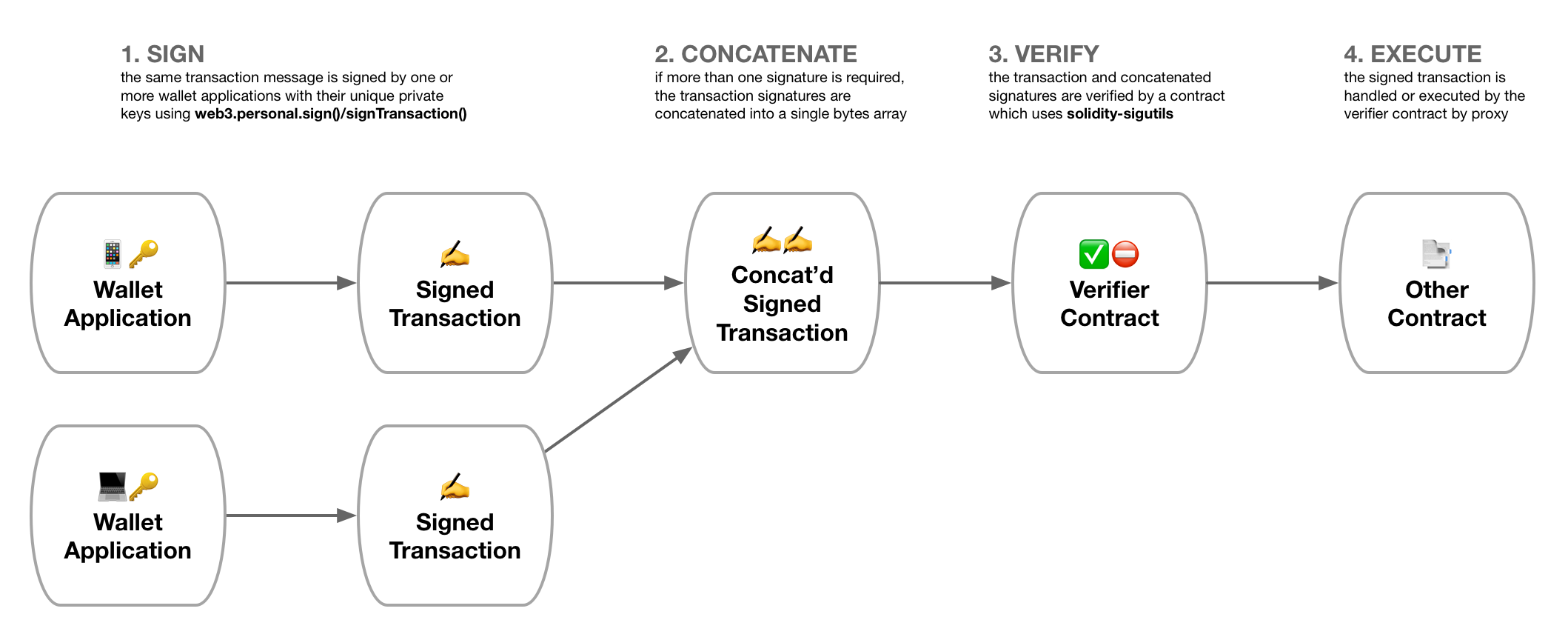
To improve security, it makes sense to require multi-factor approval from more than one device for some or all transactions. A so-called "multisig identity" often involves a proxy contract that accepts signed transactions from a whitelist of keys. To perform a multisig transaction:
- Sign: The user signs a transaction message with their private key from multiple devices.
- Concatenate: The user concatenates the message signatures into a single multi-signature.
- Verify: The user sends the transaction message and concatenated signatures to their proxy verifier contract, which verifies that enough valid signatures have been provided using solidity-sigutils.
- Execute: The proxy contract forwards the transaction to the designated contract.
Signed messages inherit the security of Ethereum's web3.personal.sign() and ecrecover(). One important benefit over raw transactions is that users can work with trust-less intermediaries without sharing their private keys. For example, signed messages enable complex transaction funding strategies like gas relays which pay for transaction costs on a user's behalf. Additionally, identity contracts may choose to use signed messages to implement advanced functionalities such as account recovery logic that does not rely on centralized authorities.
Install using npm:
$ npm install --save solidity-sigutils
Then, in your solidity file, use the library:
import "solidity-sigutils/contracts/SignatureUtils.sol";
contract MyContract {
using SignatureUtils for *; // optional
function myFunction(
string _personalMessage,
bytes _signatures
) public returns (address[]) {
// Generate the message hash according to EIP 191
bytes32 hash = SignatureUtils.toEthPersonalSignedMessageHash(_personalMessage);
// Returns the array of addresses which signed hash using their private key
return SignatureUtils.recoverAddresses(hash, _signatures);
// or use SignatureUtils.recoverAddress(hash, _signatures, 0) for only one signature
}
}PRs welcome. To install dependencies and start the local development server:
$ npm install
$ npm run migrate
$ npm start
$ npm test
$ npm run watch # requires watchman: brew install watchman
$ npm run gen-docs
$ make install-mythril
$ make myth
Licensed under Apache 2.0. Started at ETHBuenosAires.