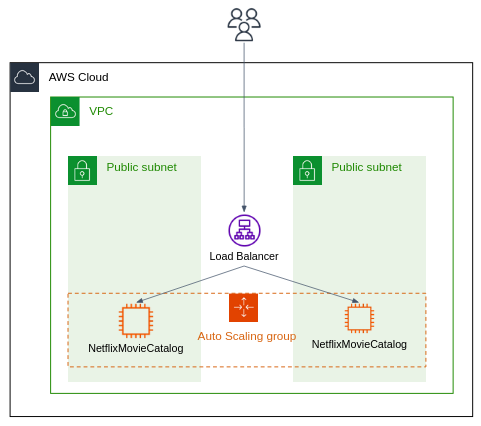
In the below tutorial you are going to deploy the NetflixMovieCatalog service in different EC2 instances. The traffic would be distributed among different instance using an Elastic Load Balancer. The service could be auto-scaled according to the traffic load.
-
Open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/.
-
In the left navigation pane, under Load Balancing, choose Target Groups.
-
Choose Create target group.
-
In the Basic configuration section, set the following parameters:
-
For Choose a target type, select Instance to specify targets by instance ID
-
For Target group name, enter a name for the target group.
-
Set the Port and Protocol to HTTP 8080 (the protocol and port on the NetflixMovieCatalog.
-
For VPC, select your virtual private cloud (VPC)
-
For Protocol version, select HTTP1.
-
-
In the Health checks section, modify the default settings as needed to perform a health checks to the NetflixMovieCatalog webserver at the
/statusendpoint. -
Choose Next.
-
In the Register targets page, no need to add targets as instances will be registered automatically by Auto Scaling Group.
-
Choose Create target group.
-
In the navigation pane, under Load Balancing, choose Load Balancers.
-
Choose Create Load Balancer.
-
Under Application Load Balancer, choose Create.
-
Basic configuration
-
For Load balancer name, enter a name for your load balancer.
-
For Scheme, choose Internet-facing.
Note: We want the ALB to be public to allow also end-users to talk with the NetflixMovieCatalog API, not only the NetflixFrontend (which is located in the same VPC). -
For IP address type, choose IPv4.
-
-
Network mapping
-
For VPC, select the VPC that you used for your EC2 instances. As you selected Internet-facing for Scheme, only VPCs with an internet gateway are available for selection.
-
For Mappings, select two or more Availability Zones and corresponding subnets. Enabling multiple Availability Zones increases the fault tolerance of your applications.
-
-
For Security groups, select an existing security group, or create a new one. The rules in this Security Group would be applied to the Load Balancer itself (not to your instances).
-
For Listeners and routing, the default listener accepts HTTP traffic on port 8080.
-
Review your configuration, and choose Create load balancer.
A launch template is a reusable configuration for Amazon EC2 instances, specifying instance parameters such as AMI, instance type, key pair, security groups, and more. Configure a launch template once, deploy the many instances according to your template.
-
Open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/.
-
On the navigation pane, under Instances, choose Launch Templates.
-
Choose Create launch template. Enter a name and provide a description for the initial version of the launch template.
-
Under Auto Scaling guidance, select the check box to have Amazon EC2 provide guidance to help create a template to use with Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling.
-
Under Launch template contents, fill out each required field and any optional fields as needed.
-
Application and OS Images (Amazon Machine Image): Choose the Ubuntu AMI.
-
For Instance type, choose some
t[2|3].microtype. -
Key pair (login): For Key pair name, choose your existing key pair.
-
Network settings: For Firewall (security groups), use one of your security groups used to allow traffic to the NetflixMovieCatalog app (port
8080), or create one if needed. -
For Resource tags, specify tags to identify your instances.
-
-
In Advanced settings, under User Data specify a bash script that installs Docker and runs your NetflixMovieCatalog image, as follows:
#!/bin/bash apt-get update apt-get install ca-certificates curl -y install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc # Add the repository to Apt sources: echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null apt-get update # Install docker apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin -y usermod -aG docker ubuntu docker run -d -p 8080:8080 <your-image-name>
Change
<your-image-name>accordingly. -
Choose Create launch template.
-
On the EC2 service navigation bar, choose Auto Scaling Group.
-
Choose Create an Auto Scaling group.
-
On the Choose launch template or configuration page, do the following:
-
For Auto Scaling group name, enter a name for your Auto Scaling group.
-
For Launch template, choose an existing launch template.
-
For Launch template version, choose whether the Auto Scaling group uses the default, the latest, or a specific version of the launch template when scaling out.
-
Verify that your launch template supports all of the options that you are planning to use, and then choose Next.
-
-
On the Choose instance launch options page, under Network, for VPC, choose a VPC. The Auto Scaling group must be created in the same VPC as the security group you specified in your launch template.
-
For Availability Zones and subnets, choose the availability zones according to your load balancer AZs.
-
Choose Next to continue to the next step.
-
On the Configure advanced options page, choose Attach to an existing load balancer.
-
Under Existing load balancer target groups, choose your target group.
-
Check the Turn on Elastic Load Balancing health checks, then click Next.
-
On the Configure group size and scaling policies page, configure the following options, and then choose Next:
- For Desired capacity, enter the initial number of instances to launch: 1.
- For Scaling limits choose Min desired capacity of 1 and Max desired capacity of 2.
- Choose Target tracking scaling policy and choose a scaling threshold of 50% CPU utilization.
-
On the Review page, choose Create Auto Scaling group.
Note
When done, don't forget to configure the min and desired capacity of your ASG to 0 to avoid additional charges!
-
Configure your NetflixFrontend to talk with the NetflixMovieCatalog via the LB (by changing the
MOVIE_CATALOG_SERVICEenv var to the load balancer's domain name). -
We will use the
locustPython package to perform a load test.Locust is an easy to use, scriptable and scalable performance testing tool.
From our course repo virtual env, install it by
pip install locust. -
Take a look on the
locust.pyfile underhttp_load_test, it specify the app endpoint that will be requested during the load test. -
Launch the locust test UI by:
cd http_load_test locust -
Open http://localhost:8089.
-
Provide the host name of your service (the IP address or the domain of your Nginx). You can start by 2-3 number of concurrent users and increase the value as your instances handle the load.
-
Try it out! the CHARTS tab can graphically visualize your system performance under load.
We would like our load balancers to listen on HTTPS protocol for clients connection. In order to achieve that, we need to create and sign a digital certificate.
In order to create your own SSL certificate, perform the following in your local machine (openssl required):
- Generate private key as private.pem
openssl genrsa -out private.pem 2048 - Generate public key as public.pem
openssl rsa -in private.pem -outform PEM -pubout -out public.pem - Create a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) as certificate.csr
openssl req -new -key private.pem -out certificate.csr - Create a Self-signed certificate as certificate.crt
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in certificate.csr -signkey private.pem -out certificate.crt
IAM securely encrypts your private keys and stores the encrypted version in IAM SSL certificate storage. You cannot manage your certificates from the IAM Console.
- To upload a server certificate to IAM (make sure your local aws cli is configured with the proper credentials)
aws iam upload-server-certificate --server-certificate-name <your-cert-name> --certificate-body file://certificate.crt --private-key file://private.pem
-
On the navigation pane, under Load Balancing, choose Load Balancers.
-
Select a load balancer, and choose Listeners, Add listener.
-
For Protocol : port, choose HTTPS and keep the default port or enter a different port.
-
For Default actions, choose Add action, Forward to and choose a target group.
-
For Security policy, we recommend that you keep the default security policy.
-
For Default SSL certificate, choose From IAM and choose the certificate that you uploaded.
-
Choose Save.
-
Test your load balancer over HTTPS.
Sticky session is a load balancing technique commonly used in web applications that require maintaining user session state. It ensures that all requests from a particular user are routed to the same instance that initially handled their request, allowing the server to maintain session data and provide a consistent user experience. This is particularly useful for applications that rely on session-specific information or personalized settings.
-
On the navigation pane, under Load Balancing, choose Target Groups.
-
Choose the name of the target group to open its details page.
-
On the Group details tab, in the Attributes section, choose Edit.
-
On the Edit attributes page, do the following:
-
Select Stickiness.
-
For Stickiness type, select Load balancer generated cookie.
-
For Stickiness duration, specify a value between 1 second and 7 days.
-
Choose Save changes.
-
-
Make sure stickiness is applied by requesting the URL multiple times and validating that you always communicate with the same instance.