| title | lock |
|---|---|
第18章:数据类型转换工厂设计实现 |
need |
作者:小傅哥
博客:https://bugstack.cn
星球:https://articles.zsxq.com/id_d0cpbs31880x.html
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄
- 类型转换机制设计 @Rechie
- Spring 全核心类图总结 @NibNait
- 逐渐完善Spring全体系流程图 @Alex
- 类型转换也就是数据转换,从 String 转为 Integer、String 转为 Date、Double 转为 Long 都是很常用的功能 @水中捞月
值得的,总是在精雕细琢!
在你写的程序开发中,你有为一个类名、方法名、属性名,反复斟酌吗?代码格式间隔大小、编写方式、注释描述不断的提升吗?你有为一个功能逻辑的实现不断的重构吗?我有,我一直都有,为了能写好一块代码,甚至会忘记时间从上午到下午,当能实现完成后,会欣赏似的看待自己的代码,也根本不舍得把他交给别人!
如果你也是这样的工程师,其实在你不去刻意追求大厂、高薪、好职位的时候,也会把你送到那个位置上去。想不被这个已经有些内卷的行业打下去,那么基本就需要选择一条能沉淀下来核心知识的路径来提升自己,做好长期规划,让以后你的30岁有30岁的能力,35岁有35岁的经历!
其实实现到本章节,关于IOC、AOP在日常使用和面试中高频出现的技术点都该涵盖了。那么为了补全整个框架内容的结构,方便读者后续在阅读 Spring 时不至于对类型转换的知识体系陌生,这里再添加一些关于此类知识的实现。
类型转换也可以叫做数据转换,比如从String到Integer、从String到Date、从Dubbo到Long等等,但这些操作不能在已经使用框架的情况下还需要手动处理,所以我们要把这样的功能扩展到Spring框架中。
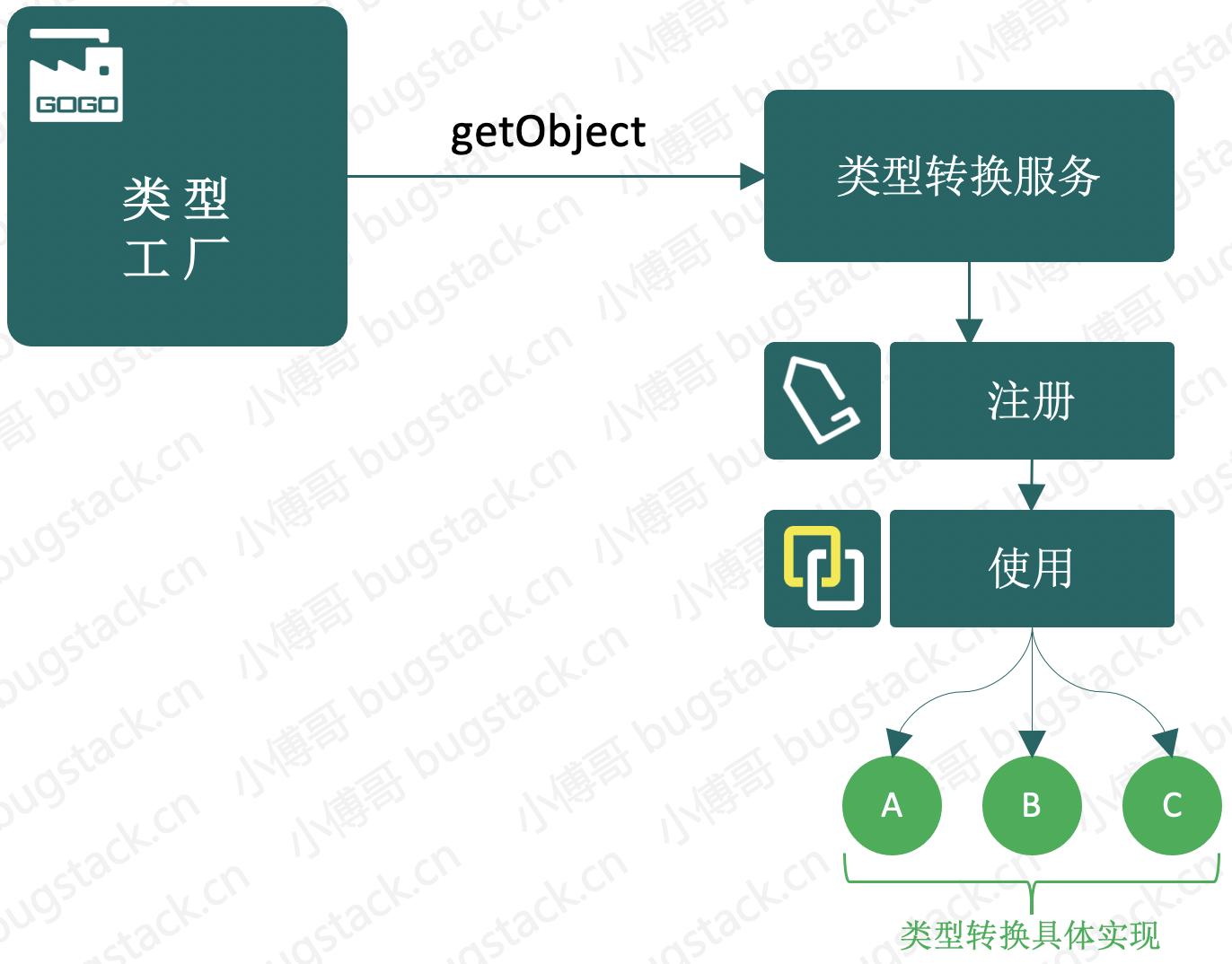
如果我们来把只是看上去一个简单的类型转换操作抽象成框架,那么它就需要一个标准的接口,谁实现这个接口就具备类型转换的具体实现,提供类型转换的能力。那么在有了这样接口后,还需要类型转换服务的注册、工厂等内容,才可以把类型转换抽象成一个组件服务。整体设计结构如下图:
- 首先从工厂出发我们需要实现一个
ConversionServiceFactoryBean来对类型转换服务进行操作。 - 而实现类型转换的服务,需要定义
Converter转换类型、ConverterRegistry注册类型转换功能,另外转换类型的操作较多,所以这里也会需要定义一个类型转换工厂ConverterFactory各个具体的转换操作来实现这个工厂接口。
small-spring-step-17
└── src
├── main
│ └── java
│ └── cn.bugstack.springframework
│ ├── aop
│ │ ├── aspectj
│ │ │ └── AspectJExpressionPointcut.java
│ │ │ └── AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor.java
│ │ ├── framework
│ │ │ ├── adapter
│ │ │ │ └── MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.java
│ │ │ ├── autoproxy
│ │ │ │ └── MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.java
│ │ │ ├── AopProxy.java
│ │ │ ├── Cglib2AopProxy.java
│ │ │ ├── JdkDynamicAopProxy.java
│ │ │ ├── ProxyFactory.java
│ │ │ └── ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java
│ │ ├── AdvisedSupport.java
│ │ ├── Advisor.java
│ │ ├── BeforeAdvice.java
│ │ ├── ClassFilter.java
│ │ ├── MethodBeforeAdvice.java
│ │ ├── MethodMatcher.java
│ │ ├── Pointcut.java
│ │ ├── PointcutAdvisor.java
│ │ └── TargetSource.java
│ ├── beans
│ │ ├── factory
│ │ │ ├── annotation
│ │ │ │ ├── Autowired.java
│ │ │ │ ├── AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java
│ │ │ │ ├── Qualifier.java
│ │ │ │ └── Value.java
│ │ │ ├── config
│ │ │ │ ├── AutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ │ ├── BeanDefinition.java
│ │ │ │ ├── BeanFactoryPostProcessor.java
│ │ │ │ ├── BeanPostProcessor.java
│ │ │ │ ├── BeanReference.java
│ │ │ │ ├── ConfigurableBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ │ ├── InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.java
│ │ │ │ └── SingletonBeanRegistry.java
│ │ │ ├── support
│ │ │ │ ├── AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ │ ├── AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java
│ │ │ │ ├── AbstractBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ │ ├── BeanDefinitionReader.java
│ │ │ │ ├── BeanDefinitionRegistry.java
│ │ │ │ ├── CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy.java
│ │ │ │ ├── DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ │ ├── DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java
│ │ │ │ ├── DisposableBeanAdapter.java
│ │ │ │ ├── FactoryBeanRegistrySupport.java
│ │ │ │ ├── InstantiationStrategy.java
│ │ │ │ └── SimpleInstantiationStrategy.java
│ │ │ ├── support
│ │ │ │ └── XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
│ │ │ ├── Aware.java
│ │ │ ├── BeanClassLoaderAware.java
│ │ │ ├── BeanFactory.java
│ │ │ ├── BeanFactoryAware.java
│ │ │ ├── BeanNameAware.java
│ │ │ ├── ConfigurableListableBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ ├── DisposableBean.java
│ │ │ ├── FactoryBean.java
│ │ │ ├── HierarchicalBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ ├── InitializingBean.java
│ │ │ ├── ListableBeanFactory.java
│ │ │ ├── ObjectFactory.java
│ │ │ └── PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.java
│ │ ├── BeansException.java
│ │ ├── PropertyValue.java
│ │ └── PropertyValues.java
│ ├── context
│ │ ├── annotation
│ │ │ ├── ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner.java
│ │ │ ├── ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.java
│ │ │ └── Scope.java
│ │ ├── event
│ │ │ ├── AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.java
│ │ │ ├── ApplicationContextEvent.java
│ │ │ ├── ApplicationEventMulticaster.java
│ │ │ ├── ContextClosedEvent.java
│ │ │ ├── ContextRefreshedEvent.java
│ │ │ └── SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java
│ │ ├── support
│ │ │ ├── AbstractApplicationContext.java
│ │ │ ├── AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
│ │ │ ├── AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
│ │ │ ├── ApplicationContextAwareProcessor.java
│ │ │ ├── ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java
│ │ │ └── ConversionServiceFactoryBean.java
│ │ ├── ApplicationContext.java
│ │ ├── ApplicationContextAware.java
│ │ ├── ApplicationEvent.java
│ │ ├── ApplicationEventPublisher.java
│ │ ├── ApplicationListener.java
│ │ └── ConfigurableApplicationContext.java
│ ├── core
│ │ ├── convert
│ │ │ ├── converter
│ │ │ │ ├── Converter.java
│ │ │ │ ├── ConverterFactory.java
│ │ │ │ ├── ConverterRegistry.java
│ │ │ │ └── GenericConverter.java
│ │ │ ├── support
│ │ │ │ ├── DefaultConversionService.java
│ │ │ │ ├── GenericConversionService.java
│ │ │ │ └── StringToNumberConverterFactory.java
│ │ │ └── ConversionService.java
│ │ └── io
│ │ ├── ClassPathResource.java
│ │ ├── DefaultResourceLoader.java
│ │ ├── FileSystemResource.java
│ │ ├── Resource.java
│ │ ├── ResourceLoader.java
│ │ └── UrlResource.java
│ ├── stereotype
│ │ └── Component.java
│ └── utils
│ ├── ClassUtils.java
│ └── StringValueResolver.java
└── test
└── java
└── cn.bugstack.springframework.test
├── bean
│ └── Husband.java
├── bean
│ ├── ConvertersFactoryBean.java
│ ├── StringToIntegerConverter.java
│ └── StringToLocalDateConverter.java
└── ApiTest.java工程源码:公众号「bugstack虫洞栈」,回复:Spring 专栏,获取完整源码
包:cn.bugstack.springframework.core.convert.converter
类型转换处理接口
public interface Converter<S, T> {
/** Convert the source object of type {@code S} to target type {@code T}. */
T convert(S source);
}类型转换工厂
public interface ConverterFactory<S, R>{
/**
* Get the converter to convert from S to target type T, where T is also an instance of R.
* @param <T> the target type
* @param targetType the target type to convert to
* @return a converter from S to T
*/
<T extends R> Converter<S, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType);
}类型转换注册接口
public interface ConverterRegistry {
/**
* Add a plain converter to this registry.
* The convertible source/target type pair is derived from the Converter's parameterized types.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the parameterized types could not be resolved
*/
void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter);
/**
* Add a generic converter to this registry.
*/
void addConverter(GenericConverter converter);
/**
* Add a ranged converter factory to this registry.
* The convertible source/target type pair is derived from the ConverterFactory's parameterized types.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the parameterized types could not be resolved
*/
void addConverterFactory(ConverterFactory<?, ?> converterFactory);
}- Converter、ConverterFactory、ConverterRegistry,都是用于定义类型转换操作的相关接口,后续所有的实现都需要围绕这些接口来实现,具体的代码功能可以进行调试验证。
cn.bugstack.springframework.core.convert.support.DefaultConversionService
public class DefaultConversionService extends GenericConversionService{
public DefaultConversionService() {
addDefaultConverters(this);
}
public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
// 添加各类类型转换工厂
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new StringToNumberConverterFactory());
}
}- DefaultConversionService 是继承 GenericConversionService 的实现类,而 GenericConversionService 实现了 ConversionService, ConverterRegistry 两个接口,用于 canConvert 判断和转换接口 convert 操作。
cn.bugstack.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean
public class ConversionServiceFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<ConversionService>, InitializingBean {
@Nullable
private Set<?> converters;
@Nullable
private GenericConversionService conversionService;
@Override
public ConversionService getObject() throws Exception {
return conversionService;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return conversionService.getClass();
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
this.conversionService = new DefaultConversionService();
registerConverters(converters, conversionService);
}
private void registerConverters(Set<?> converters, ConverterRegistry registry) {
if (converters != null) {
for (Object converter : converters) {
if (converter instanceof GenericConverter) {
registry.addConverter((GenericConverter) converter);
} else if (converter instanceof Converter<?, ?>) {
registry.addConverter((Converter<?, ?>) converter);
} else if (converter instanceof ConverterFactory<?, ?>) {
registry.addConverterFactory((ConverterFactory<?, ?>) converter);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Each converter object must implement one of the " +
"Converter, ConverterFactory, or GenericConverter interfaces");
}
}
}
}
public void setConverters(Set<?> converters) {
this.converters = converters;
}
}- 有了 FactoryBean 的实现就可以完成工程对象的操作,可以提供出转换对象的服务 GenericConversionService,另外在 afterPropertiesSet 中调用了注册转换操作的类。最终这个类会被配置到 spring.xml 中在启动的过程加载。
cn.bugstack.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, Object bean, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
try {
PropertyValues propertyValues = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValues.getPropertyValues()) {
String name = propertyValue.getName();
Object value = propertyValue.getValue();
if (value instanceof BeanReference) {
// A 依赖 B,获取 B 的实例化
BeanReference beanReference = (BeanReference) value;
value = getBean(beanReference.getBeanName());
}
// 类型转换
else {
Class<?> sourceType = value.getClass();
Class<?> targetType = (Class<?>) TypeUtil.getFieldType(bean.getClass(), name);
ConversionService conversionService = getConversionService();
if (conversionService != null) {
if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceType, targetType)) {
value = conversionService.convert(value, targetType);
}
}
}
// 反射设置属性填充
BeanUtil.setFieldValue(bean, name, value);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeansException("Error setting property values:" + beanName + " message:" + e);
}
}- 在 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyPropertyValues 填充属性的操作中,具体使用了类型转换的功能。
- 在 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues 也有同样的属性类型转换操作。
public class Husband {
private String wifiName;
private Date marriageDate; // 添加一个日期类的转换操作
// ... get/set
} 转换时间的操作类
public class StringToLocalDateConverter implements Converter<String, LocalDate> {
private final DateTimeFormatter DATE_TIME_FORMATTER;
public StringToLocalDateConverter(String pattern) {
DATE_TIME_FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(pattern);
}
@Override
public LocalDate convert(String source) {
return LocalDate.parse(source, DATE_TIME_FORMATTER);
}
}- Husband 是一个基础对象类设置了时间属性,之后再添加一个类型转换的操作用于转换时间信息。
spring.xml
<bean id="husband" class="cn.bugstack.springframework.test.bean.Husband">
<property name="wifiName" value="你猜"/>
<property name="marriageDate" value="2021-08-08"/>
</bean>
<bean id="conversionService" class="cn.bugstack.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters" ref="converters"/>
</bean>
<bean id="converters" class="cn.bugstack.springframework.test.converter.ConvertersFactoryBean"/>- 配置基础Bean对象,设置属性的日期,同时再添加类型转换的服务和自己实现的
ConvertersFactoryBean
@Test
public void test_convert() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml");
Husband husband = applicationContext.getBean("husband", Husband.class);
System.out.println("测试结果:" + husband);
}
@Test
public void test_StringToIntegerConverter() {
StringToIntegerConverter converter = new StringToIntegerConverter();
Integer num = converter.convert("1234");
System.out.println("测试结果:" + num);
}
@Test
public void test_StringToNumberConverterFactory() {
StringToNumberConverterFactory converterFactory = new StringToNumberConverterFactory();
Converter<String, Integer> stringToIntegerConverter = converterFactory.getConverter(Integer.class);
System.out.println("测试结果:" + stringToIntegerConverter.convert("1234"));
Converter<String, Long> stringToLongConverter = converterFactory.getConverter(Long.class);
System.out.println("测试结果:" + stringToLongConverter.convert("1234"));
}测试结果
测试结果:Husband{wifiName='你猜', marriageDate=Sun Aug 08 00:00:00 CST 2021}
Process finished with exit code 0- 这个测试内容还是比较简单的,可以自行验证结果,虽然最终的结果看上去比较简单,但整个框架结构实现设计还是蛮复杂的,把这么一个转换操作抽象为接口适配、工厂模型等方式,还是很值得借鉴的。
- 本章节实现的类型转换操作如果只是功能性的开发,就像你自己承接的需求那样,可能只是简单的if判断就搞定了,但放在一个成熟的框架要中要考虑的是可复用性、可扩展性,所以会看到接口的定义、工厂的使用等等设计模式在这里体现。
- 最后非常感谢你能坚持学习到这个章节,如果你在学习的过程也是每一个章节都是对着文章、写着代码代码、调试着bug,感悟着设计,那么你一定会在这个过程中得到很多很多,以后再阅读Spring的源码也就不会感觉那么难了。