[toc]
https://missing.csail.mit.edu/ ,介绍了如何利用工具提升效率
- shell:空格分割输入,
~is short for "home",.表示当前文件夹.在UNIX系统的遗留问题
- environment variable:
echo $PATH;vim ~/.zshrc$PATH可以作为输入
- connecting programs:
- <和>:rewire the input and output streams; >>可append
cat < hello.txt > hello2.txt- wire:
ls -l | tail -n1,`` curl --head --silent baidu.com | grep --ignore-case content-length | cut -f2 -d ' '
- sudo: super user,linux系统可改/sys下面的sysfs
echo 1 | sudo tee /sys/class/leds/input6::scrolllock/brightness
- foo=bar, $foo 注意等号前后不能有space,否则被当成参数
- 单引号和双引号的区别:同样套在$foo上,前者是literal meaning,而" "会替换成变量值
- shell scripting也有if、case、while、for、function特性
- source mcd.sh后即可使用。cd如果在function内部使用,针对的是子shell,不影响外部,因此直接用./mcd.sh不合适
#!/bin/bash
mcd(){
mkdir -p "$1"
cd "$1"
}- if else
- for特性的实用例子
POLICIES=("FIFO" "LRU" "OPT" "UNOPT" "RAND" "CLOCK")
for policy in "${POLICIES[@]}"
do
for i in 1 2 3 4
do
./paging-policy.py -c -f ./vpn.txt -p " <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=policy%22%20-C%20%22" alt="policy" -C "" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> i"
done
echo ""
done- case-esac 语句的使用
while [ "$#" -gt 0 ]; do
case $1 in
-c | --clang)
clang=1
;;
-g | --gcc)
gcc=1
;;
--lto)
lto=1
;;
--thinlto)
thinlto=1
;;
esac
shift
doneset -e:遇到错误,shell script 直接退出shift: 含义是<img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=0%60%20%E4%B8%8D%E7%A7%BB%E5%8A%A8%EF%BC%8C%E5%B0%86%20%60" alt="0不移动,将" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> 1起始的若干参数干掉
$0- Name of the script<img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=1%20to%20%5C" alt="1 to \" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> 9- Arguments to the script. $1 is the first argument and so on.$@- All the arguments$*同义,区别是它在“”包围下会当成一个参数
$#- Number of arguments- 最后一个参数:
${!#}
- 最后一个参数:
$?- Return code of the previous command$$- Process Identification number for the current script!!- Entire last command, including arguments. A common pattern is to execute a command only for it to fail due to missing permissions, then you can quickly execute it with sudo by doing sudo !!$_- Last argument from the last command. If you are in an interactive shell, you can also quickly get this value by typing Esc followed by .$!- last backgrounded job- ||和&& operator:机制和 error code 联系,true 和 false 命令返回固定的error code
- linux中,&和&&, |和|| ,&> 与 >的区别
false || sleep 10s固定error code为零
false || echo "Oops, fail"
# Oops, fail
true || echo "Will not be printed"
#
true && echo "Things went well"
# Things went well
false && echo "Will not be printed"
#
false ; echo "This will always run"
# This will always run
percent=${PERCENT:-50}- variable substitution:
<img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=var%2C%20" alt="var, " class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> {var} - command substitution:
for file in <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=%28ls%29%60%EF%BC%8C%E5%8F%AF%E4%BB%A5%E7%94%A8%60%27%20%27%60%E4%BB%A3%E6%9B%BF%60" alt="(ls),可以用' '代替" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> ( ),但后者辨识度更高 - process substitution: 生成返回temporary file,
diff <(ls foo) <(ls bar)
#!/bin/bash
echo "Starting program at $(date)" # Date will be substituted
echo "Running program <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=0%20with%20" alt="0 with " class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> # arguments with pid $$"
for file in $@; do
grep foobar $file > /dev/null 2> /dev/null
# When pattern is not found, grep has exit status 1
# We redirect STDOUT and STDERR to a null register since we do not care about them
if [[ $? -ne 0 ]]; then
echo "File $file does not have any foobar, adding one"
echo "# foobar" >> "$file"
fi
done
- 2>,重定向 stderr
- &> 或 >&,重定向到 stderr
&>word<=>>word 2>&1$command > result 2>&1,STDOUT、STDERR 均重定向到 result
-ne,更多的查看man test,比如-n 文件存在为真 -z 不存在为真- “test command”, [[和[的区别:http://mywiki.wooledge.org/BashFAQ/031 ,
[[是compound command,存在special parsing context,寻找reserved words or control operatorsif [[ -e <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=file%20%5D%5D%20%26%26%20%5B%5B%20" alt="file ]] && [[ " class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> var == true]]
--- to signify the end of command options
grep -- -v file
-
wildcard通配符:?和*
ls *.sh -
{}:
mv *{.py,.sh} folder,mv abc{000..120}* folder -
touch {foo,bar}/{a..h} -
利用shellcheck检查shell scripts的错误
-
shebangline 进行解释,可以利用env命令
#!/usr/bin/env python#!/usr/bin/env -S /usr/local/bin/php -n -q -dsafe_mode=0
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/146462733
最简单的方法就是单双引号交替
shell函数和scripts的区别:
- Functions have to be in the same language as the shell, while scripts can be written in any language. This is why including a shebang for scripts is important.
- Functions are loaded once when their definition is read. Scripts are loaded every time they are executed. This makes functions slightly faster to load but whenever you change them you will have to reload their definition.
- Functions are executed in the current shell environment whereas scripts execute in their own process. Thus, functions can modify environment variables, e.g. change your current directory, whereas scripts can’t. Scripts will be passed by value environment variables that have been exported using
export- 比如cd只能在function中影响到外界shell
- As with any programming language functions are a powerful construct to achieve modularity, code reuse and clarity of shell code. Often shell scripts will include their own function definitions.
-
alias ll='ls -aGhlt' -
marco记录directory,polo前往
#!/bin/bash
marco(){
foo=$(pwd)
export MARCO=$foo
}
polo(){
cd "$MARCO" || echo "cd error"
}- 实用小工具,比如可以抢实验室GPU(实现的功能相对原题有改动)
- 简化版:
mycount=0; while (( <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=mycount%20%3C%2015%20%29%29%3B%20do%20./my_script%3B%28%28mycount%3D" alt="mycount < 15 )); do ./my_script;((mycount=" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> mycount+1)); done;
- 简化版:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
debug(){
echo "start capture the program failure log"
cnt=-1
ret=0
while [[ $ret -eq 0 ]]; do
sh "$1" 2>&1
ret=$?
cnt=$((cnt+1))
# let cnt++
if [[ $# -eq 2 ]];then
sleep "$2"
fi
done
echo "succeed after ${cnt} times"
}-
fd -e html -0 | xargs -0 zip output.zip -
返回文件夹下最近修改的文件:
-
fd . -0 -t f | xargs -0 stat -f '%m%t%Sm %N' | sort -n | cut -f2- | tail -n 1(设成了我的fdrecent命令) -
find . -exec stat -f '%m%t%Sm %N' {} + | sort -n | cut -f2- | tail -n 1 -
find . -type f -print0 | xargs -0 stat -f '%m%t%Sm %N' | sort -n | cut -f2- | tail -n 1
-
-
import envs from main process
. <(xargs -0 bash -c 'printf "export %q\n" " <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=%40%22%27%20--%20%3C%20/proc/" alt="@"' -- < /proc/" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> {MAIN_PID}/environ)- 关于
%q,"causes printf to output the corresponding argument in a format that can be reused as shell input"- Prints
''for the null/empty string. - Prints the string normally if it has no spaces, using backslashes to escape shell-recognized characters like quotes or semicolons.
- Prints the string in single-quotes ("shell quoting") if it has spaces, using
'\''to escape single-quotes. - Prints the string in a
$'...'"ANSI C" style string, with backslashed-escaped command sequences, if it has special/non-printing characters like newlines.
- Prints
- 关于
帮助文档
- XX -h
- man XX
- :help 或 ? (interactive)
- tldr:比man好用!
shell中的查找
-
查找文件:find, fd, locate,见底部命令解释
-
查找代码:见【code-reading】笔记
-
查找shell指令
-
history | grep find -
zsh-history-substring-search: 键盘上下键寻找历史
-
zsh-autosuggestions:键盘右键快速键入
-
如果输入命令有leading space,不会记入历史数据;如果不慎记入,可修改
.bash_history或.zsh_history
-
-
查找目录
-
Shell编辑
-
Ctrl-a光标移动到行前 -
ESC进入Vim-mode,ESC-v进入Vim直接编辑
-
- oh-my-zsh
- zsh的10个优点,zsh介绍
- MacOS配置iTerm2+zsh+powerline
- autojump: j, jc, jo, jco, j A B
- zsh-autosuggestions
- zsh-history-substring-search
- zsh-completions: tab自动补全,比如输cd按tab会自动识别文件夹;输git add会自动识别需要add的文件
Aliases
- pyfind
- pyclean [dirs]
- pygrep <text>
What are other useful data wrangling tools?
Some of the data wrangling tools we did not have time to cover during the data wrangling lecture include jq or pup which are specialized parsers for JSON and HTML data respectively. The Perl programming language is another good tool for more advanced data wrangling pipelines. Another trick is the column -t command that can be used to convert whitespace text (not necessarily aligned) into properly column aligned text.
More generally a couple of more unconventional data wrangling tools are vim and Python. For some complex and multi-line transformations, vim macros can be a quite invaluable tools to use. You can just record a series of actions and repeat them as many times as you want, for instance in the editors lecture notes (and last year’s video) there is an example of converting a XML-formatted file into JSON just using vim macros.
For tabular data, often presented in CSVs, the pandas Python library is a great tool. Not only because it makes it quite easy to define complex operations like group by, join or filters; but also makes it quite easy to plot different properties of your data. It also supports exporting to many table formats including XLS, HTML or LaTeX. Alternatively the R programming language (an arguably bad programming language) has lots of functionality for computing statistics over data and can be quite useful as the last step of your pipeline. ggplot2 is a great plotting library in R.
杀进程
-
signals: software interrupts
-
Ctrl-C:SIGINT;Ctrl-\:SIGQUIT;kill -TERM PID:SIGTERM
#!/usr/bin/env python
import signal, time
def handler(signum, time):
print("\nI got a SIGINT, but I am not stopping")
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, handler)
i = 0
while True:
time.sleep(.1)
print("\r{}".format(i), end="")
i += 1Pausing and backgrounding processes
- 暂停并放入后台:
Ctrl-Z,SIGTSTP - 继续暂停的job:
fg和bg;jobs搭配pgrep $!- last backgrounded job- 命令行后缀
&在背景运行命令 - 关闭终端发出
SIGHUP信号,使子进程终止,解决方案:- 运行前
nohup - 运行后
disown tmux
- 运行前
SIGKILL和SIGSTOP都不能被相关的系统调用阻塞,因此SIGKILL不会触发父进程的清理部分,可能导致子进程成为孤儿进程;如果是SIGINT,可能会有handler处理资源,比如有些数据还在内存,需要刷新到磁盘上。
基于我的键位(配置文件)
-
Sessions - a session is an independent workspace with one or more windows
tmuxstarts a new session.tmux new -s NAMEstarts it with that name.tmux rename-session -t 0 database重命名tmux lslists the current sessions- Within
tmuxtyping<C-a> d/Ddetaches the current session tmux aattaches the last session. You can use-tflag to specify which
-
Windows
- Equivalent to tabs in editors or browsers, they are visually separate parts of the same session
<C-a> cCreates a new window. To close it you can just terminate the shells doing<C-d> / exit<C-a> NGo to the N th window. Note they are numbered<C-a> pGoes to the previous window<C-a> nGoes to the next window<C-a> ,Rename the current window<C-a> wList current windows
-
Panes
- Like vim splits, panes let you have multiple shells in the same visual display.
- 配置下可以用鼠标选取/缩放pane
<C-a> -Split the current pane horizontally<C-a> |Split the current pane vertically<Alt> <direction>Move to the pane in the specified direction. Direction here means arrow keys.<C-a> zmake a pane go full screen. Hit<C-a> zagain to shrink it back to its previous size<C-a> [Start scrollback. You can then press<space>to start a selection andenterto copy that selection.<C-a> <space>Cycle through pane arrangements.
-
其它操作
<C-a> rreload配置文件Shift + Command + c,配合iTerm2复制文件
-
For further reading, here is a quick tutorial on
tmuxand this has a more detailed explanation that covers the originalscreencommand. You might also want to familiarize yourself withscreen, since it comes installed in most UNIX systems. -
tmux是client-server的实现模式
alias ll可print出alias的对象unalias ll可解除alias
# alias base
alias v='vim'
alias ll='ls -aGhlt'
alias la='ls -a'
alias l='ls -CF'
alias cls='clear'
alias gs='git status'
alias gc='git commit'
alias gqa='git add .'
alias v="vim"
alias mv="mv -i" # -i prompts before overwrite
alias mkdir="mkdir -p" # -p make parent dirs as needed
alias df="df -h" # -h prints human readable format
alias vfzf='vim $(fzf)' #vim打开搜索到的结果文件
alias cdfzf='cd $(find * -type d | fzf)'
alias gitfzf='git checkout $(git branch -r | fzf)'
# alias docker
alias dkst="docker stats"
alias dkps="docker ps"
alias dklog="docker logs"
alias dkpsa="docker ps -a"
alias dkimgs="docker images"
alias dkcpup="docker-compose up -d"
alias dkcpdown="docker-compose down"
alias dkcpstart="docker-compose start"
alias dkcpstop="docker-compose stop"
e.g.
bash-~/.bashrc,~/.bash_profilegit-~/.gitconfigvim-~/.vimrcand the~/.vimfolderssh-~/.ssh/configtmux-~/.tmux.conf
管理方法:单独的文件夹,版本控制,symlinked into place using a script
-
用git的submodule
-
Easy installation: if you log in to a new machine, applying your customizations will only take a minute.
-
Portability: your tools will work the same way everywhere.
-
Synchronization: you can update your dotfiles anywhere and keep them all in sync.
-
Change tracking: you’re probably going to be maintaining your dotfiles for your entire programming career, and version history is nice to have for long-lived projects.
一些有用的构造代码块:
# $HOME/dotfiles
BASEDIR=" <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=%28cd%20%22" alt="(cd "" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> (dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}")" && pwd)"
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Linux" ]]; then {do_something}; fi
# Check before using shell-specific features
if [[ "$SHELL" == "zsh" ]]; then {do_something}; fi
# You can also make it machine-specific
if [[ "$(hostname)" == "myServer" ]]; then {do_something}; fi
# Test if ~/.aliases exists and source it
if [ -f ~/.aliases ]; then
source ~/.aliases
fi在~/.gitconfig里加
[include]
path = ~/.gitconfig_local
- 装虚拟机
sudo apt-get install --reinstall lightdm && sudo systemctl start lightdm图形界面Ctrl+Alt+A打开终端- 自动/手动设置共享文件夹:
sudo mkdir -p /media/sf_<FolderName> && sudo mount -t vboxsf -o rw,gid=vboxsf FolderName /media/sf_FolderName
- ssh可执行命令
ssh foobar@server ls | grep PATTERNls | ssh foobar@server grep PATTERN
- 用SSH连GitHub
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "huangrt01@163.com"
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
ssh-add -K ~/.ssh/id_rsa
pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub #适合MacOS , Linux用xclip
# 上github添加SSH Key
ssh -T git@github.com
ssh-keygen -y -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa- ssh agent及其forwarding特性
- ssh连虚拟机
ssh -p 2222 cs144@localhost
# ssh will look into .ssh/authorized_keys to determine which clients it should let in.
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub -p 2222 cs144@localhost
# or
cat .ssh/id_ed25519.pub | ssh foobar@remote 'cat >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys'- ssh传文件
ssh+tee, the simplest is to usesshcommand execution and STDIN input by doingcat localfile | ssh remote_server 'tee serverfile'. Recall thatteewrites the output from STDIN into a file.scpwhen copying large amounts of files/directories, the secure copyscpcommand is more convenient since it can easily recurse over paths. The syntax isscp -P 2075 -r path/to/local_file remote_host:path/to/remote_filersyncimproves uponscpby detecting identical files in local and remote, and preventing copying them again. It also provides more fine grained control over symlinks, permissions and has extra features like the--partialflag that can resume from a previously interrupted copy.rsynchas a similar syntax toscp.
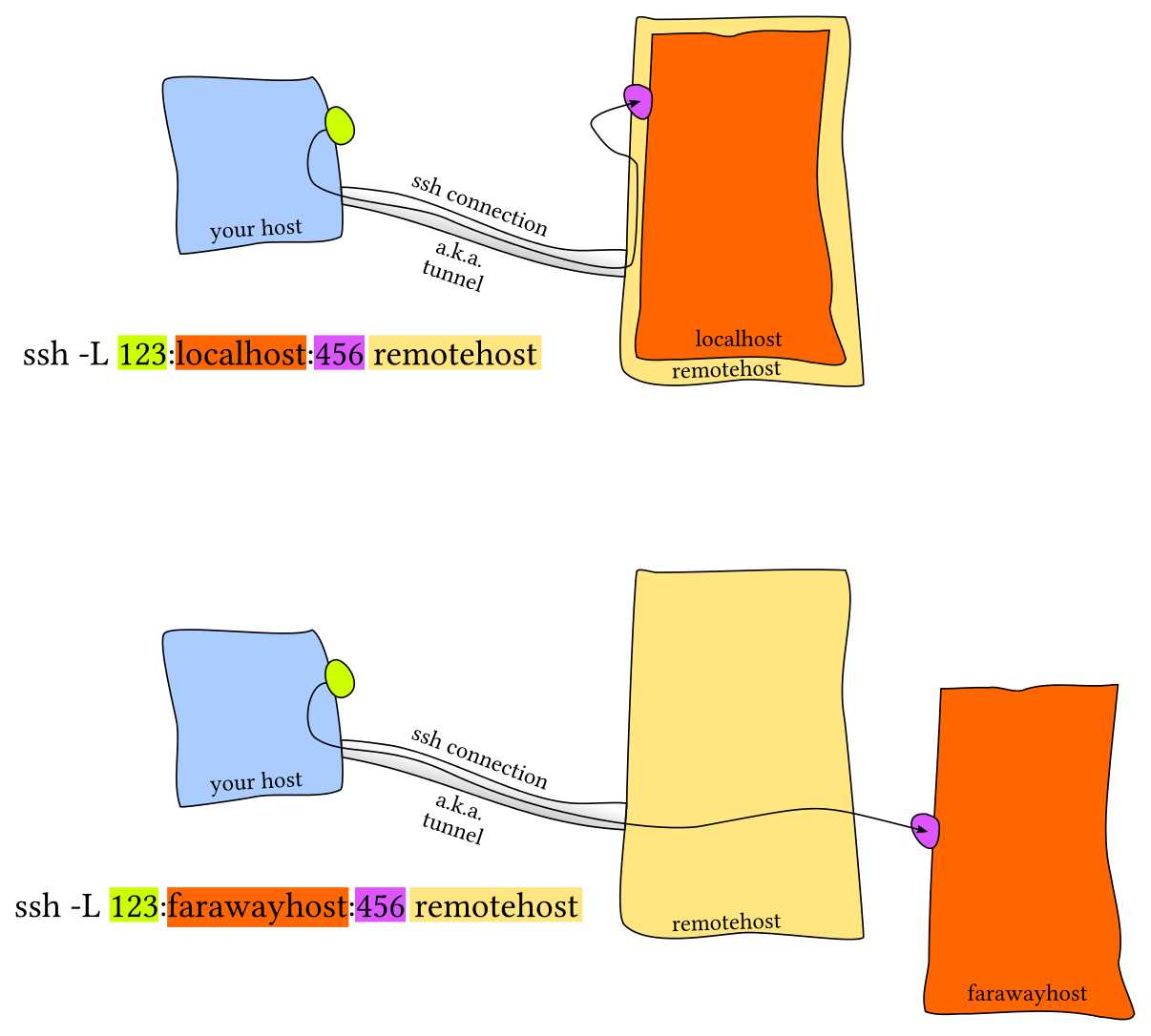
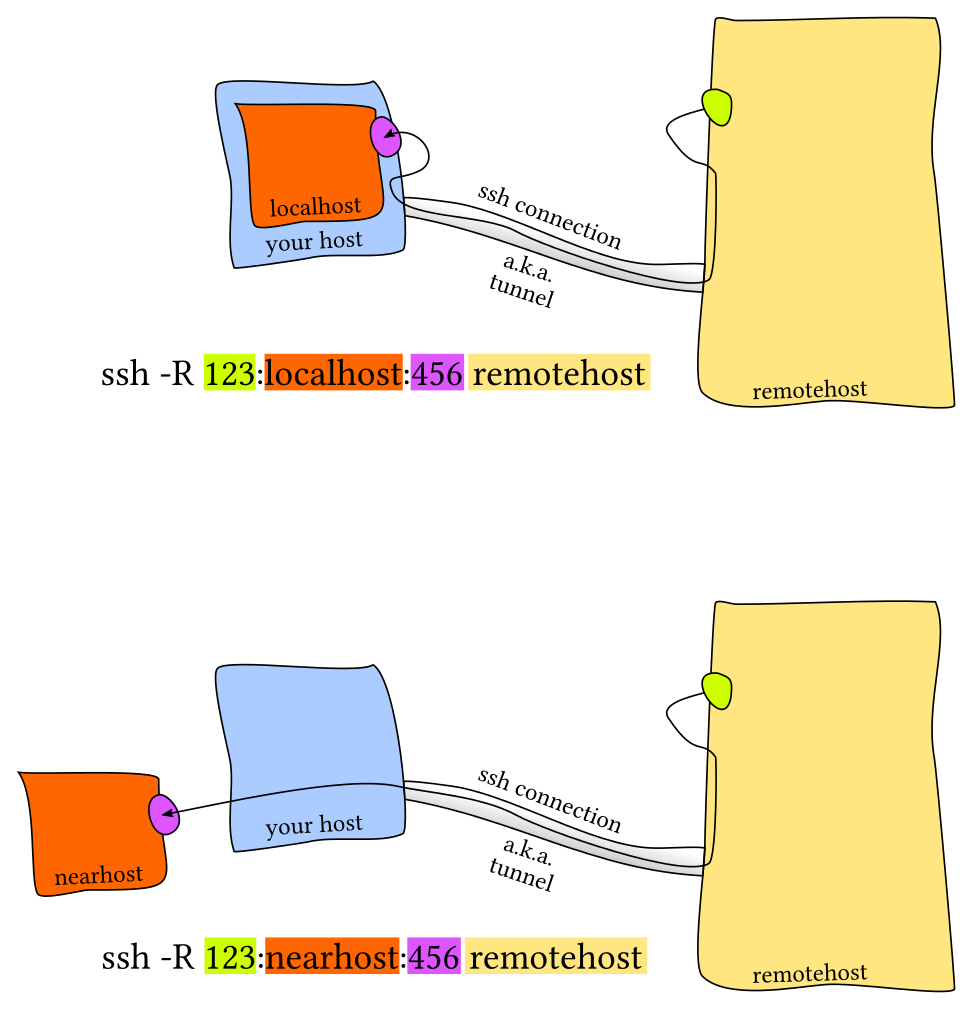
- Port Forwarding:
localhost:PORT or 127.0.0.1:PORT ssh -K: 穿越服务器,打开GSSAPIDelegateCredentials, 可转存tgt- ssh configuration:
~/.ssh/config,server side:/etc/ssh/sshd_config,调端口、X11 forwarding等
Host vm
User foobar
HostName 172.16.174.141
Port 2222
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
LocalForward 9999 localhost:8888
# Configs can also take wildcards
Host *.mit.edu
User foobaz- 其它
-
openconnect:
sudo openconnect --juniper https://sslvpn.tsinghua.edu.cn -u 2015010356 -
vscode remote-ssh中ssh_config的配置细节
-
Mosh, the mobile shell, improves upon ssh, allowing roaming connections, intermittent connectivity and providing intelligent local echo.
-
sshfs can mount a folder on a remote server locally, and then you can use a local editor.
-
zsh的新特性
- Smarter globbing,
**:**/README.md可递归地列出相应文件 - Inline globbing/wildcard expansion
- Spelling correction
- Better tab completion/selection (
XXX -加tab会列出说明,很贴心) - Path expansion (
cd /u/lo/bwill expand as/usr/local/bin)
重点:
- Font choice
- Color Scheme
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Tab/Pane support
- Scrollback configuration
- Performance (some newer terminals like Alacritty or kitty offer GPU acceleration).
Exercises
- pidwait,用于跨终端的控制
#!/bin/bash
pidwait(){
try=0
while [[ $try -eq 0 ]]; do
kill -0 "$1" || try=1
sleep 1
done
}ubuntu无sudo权限以及非root的用户apt安装软件
Mac-os karabiner,right command -> escape
-
e.g. sshd, systemd
systemctl --user status
-
Systemd can be interacted with the
systemctlcommand in order toenable,disable,start,stop,restartor check thestatusof services (those are thesystemctlcommands).- 如果出现端口占用,可以先stop再disable相关service
-
Systems Intro
- https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/systemd-understanding-and-administering/
- 特点:
- Aggressive parallelization capabilities
- Uses socket and D-Bus activation for starting services
- Offers on-demand starting of daemons, keeps track of processes using Linux cgroups
- Supports snapshotting and restoring of the system state
- Maintains mount and automount points
- Implements an elaborate transactional dependency-based service control logic.
-
运维操作
cd .config/systemd/user/
systemctl start/stop/restart/reload/condrestart(如果运行中则重新启动)/status/enable/disable/mask/is-enabled foosystemctl
systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
ls /lib/systemd/system/*.service /etc/systemd/system/*.service
ls /etc/systemd/system/*.wants/
systemctl list-dependencies graphical.target
# Used when you create a new service file or modify any configuration
systemctl daemon-reload
-
Modify service
-
systemctl edit httpd.service -
To replace an option that can be set multiple times, it must cleared first, otherwise the override file will add the option a second time.
-
systemctl restart httpd
-
[Service]
Restart=always
RestartSec=30
[Service]
ExecStart=
ExecStart=<new command>
systemctl restart httpd
# systemctl edit --full httpd.service
- create service
- /etc/systemd/system/foo.service
[Unit]
Description=My custom service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/bin/sleep infinity
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
-
Converting SysVinit services to systemd
-
man systemd.unit
-
Mapping runlevels to targets
FUSE (Filesystem in User Space)
- sshfs - Open locally remote files/folder through an SSH connection.
- rclone - Mount cloud storage services like Dropbox, GDrive, Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage and open data locally.
- gocryptfs - Encrypted overlay system. Files are stored encrypted but once the FS is mounted they appear as plaintext in the mountpoint.
- kbfs - Distributed filesystem with end-to-end encryption. You can have private, shared and public folders.
- borgbackup - Mount your deduplicated, compressed and encrypted backups for ease of browsing.
a copy of the data in the same disk is not a backup, because the disk is the single point of failure for all the data
Synchronization solutions are not backups
Some core features of good backups solutions are versioning, deduplication and security.
“OAuth” is a protocol you will often see used. At its heart, OAuth is a way to give you tokens that can “act as you” on a given service, and can only be used for particular purposes. Keep in mind that these tokens are secret, and anyone who gains access to your token can do whatever the token allows under your account!
IFTTT is a website and service centered around the idea of APIs — it provides integrations with tons of services, and lets you chain events from them in nearly arbitrary ways.
Command-line tools vary a lot, and you will often want to check out their man pages before using them. They often share some common features though that can be good to be aware of:
- Most tools support some kind of
--helpflag to display brief usage instructions for the tool. - Many tools that can cause irrevocable change support the notion of a “dry run” in which they only print what they would have done, but do not actually perform the change. Similarly, they often have an “interactive” flag that will prompt you for each destructive action.
- You can usually use
--versionor-Vto have the program print its own version (handy for reporting bugs!). - Almost all tools have a
--verboseor-vflag to produce more verbose output. You can usually include the flag multiple times (-vvv) to get more verbose output, which can be handy for debugging. Similarly, many tools have a--quietflag for making it only print something on error. - In many tools,
-in place of a file name means “standard input” or “standard output”, depending on the argument. - Possibly destructive tools are generally not recursive by default, but support a “recursive” flag (often
-r) to make them recurse. - Sometimes, you want to pass something that looks like a flag as a normal argument. For example, imagine you wanted to remove a file called
-r. Or you want to run one program “through” another, likessh machine foo, and you want to pass a flag to the “inner” program (foo). The special argument--makes a program stop processing flags and options (things starting with-) in what follows, letting you pass things that look like flags without them being interpreted as such:rm -- -rorssh machine --for-ssh -- foo --for-foo.
- Bind hotkeys to move windows to specific locations
- Create a menu bar button that automatically lays out windows in a specific layout
- Mute your speaker when you arrive in lab (by detecting the WiFi network)
- Show you a warning if you’ve accidentally taken your friend’s power supply
command + option + 方向键
resources:
- Learn Lua in Y minutes
- Getting Started with Hammerspoon
- Sample configurations
- Hammerspoon APIs
- Anish’s Hammerspoon config
When your machine boots up, before the operating system is loaded, the BIOS/UEFI initializes the system. During this process, you can press a specific key combination to configure this layer of software. For example, your computer may say something like “Press F9 to configure BIOS. Press F12 to enter boot menu.” during the boot process. You can configure all sorts of hardware-related settings in the BIOS menu. You can also enter the boot menu to boot from an alternate device instead of your hard drive.
Live USBs are USB flash drives containing an operating system. You can create one of these by downloading an operating system (e.g. a Linux distribution) and burning it to the flash drive. This process is a little bit more complicated than simply copying a .iso file to the disk. There are tools like UNetbootin to help you create live USBs.
Live USBs are useful for all sorts of purposes. Among other things, if you break your existing operating system installation so that it no longer boots, you can use a live USB to recover data or fix the operating system.
docker和VM的区别:docker运行的时候和host共享kernel,在Linux中用LXC机制,利用一系列isolation机制spin up a program that thinks it’s running on its own hardware but it’s actually sharing the hardware and kernel with the host
Vagrant is a tool that lets you describe machine configurations (operating system, services, packages, etc.) in code, and then instantiate VMs with a simple vagrant up. Docker is conceptually similar but it uses containers instead.
Popular services include Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, and DigitalOcean.
Notebook programming environments can be really handy for doing certain types of interactive or exploratory development. Perhaps the most popular notebook programming environment today is Jupyter, for Python (and several other languages). Wolfram Mathematica is another notebook programming environment that’s great for doing math-oriented programming.
/bin- Essential command binaries/sbin- Essential system binaries, usually to be run by root/dev- Device files, special files that often are interfaces to hardware devices/etc- Host-specific system-wide configuration files/home- Home directories for users in the system/lib- Common libraries for system programs/opt- Optional application software/sys- Contains information and configuration for the system (covered in the first lecture)/tmp- Temporary files (also/var/tmp). Usually deleted between reboots./usr/- Read only user data/usr/bin- Non-essential command binaries/usr/sbin- Non-essential system binaries, usually to be run by root/usr/local/bin- Binaries for user compiled programs
/var- Variable files like logs or caches
关于package manager的选择
- use the language-specific package manager whenever possible, and to use isolated environments (like Python’s virtualenv) to avoid polluting the global environment.
- Depending on the operating system and the hardware architecture, some of these packages might come with binaries or might need to be compiled. For instance, in ARM computers like the Raspberry Pi, using the system package manager can be better than the language specific one if the former comes in form of binaries and the later needs to be compiled. This is highly dependent on your specific setup.
- ag
- Flags 含义与 grep 相似
- http://conqueringthecommandline.com/book/ack_ag
- alias
alias pip3="python3 -m pip"- 非交互模式下启用 alias 扩展
shopt -s expand_aliases
shopt expand_aliases # show current status- apt
- 坑:krb5在docker中安装 https://askubuntu.com/questions/1017999/install-kerberos-client-without-interactive-session
- -y:静默模式
sudo apt update # 更新源
sudo apt dist-upgrage
sudo apt install
sudo apt remove
sudo apt autoremove- awk: 一种控制台编程工具,寻找和处理pattern
- 入门wiki
- 数据统计:
awk -F'[ ,]+' '{print <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=1%2C" alt="1," class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> 3, <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=5%2C" alt="5," class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> 7}' | awk '{ for (i=1; i<=NF; i++) { sum[i]+= $i }} END { for (i=1; i<=NF; i++) {printf "%.9f ", sum[i]/NR}}':算均值- ``-F'[]'
内空格和逗号都是分隔符,+`表示将连续分隔符视为一个
- ``-F'[]'
history | awk '{ <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=1%3D%22%22%3Bprint%20substr%28" alt="1="";print substr(" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> 0,2)}' | sort | uniq -c | sort -n | tail -n 10:得到使用频率最高的10个命令
awk ' <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=NF%21~/%5C.so/%7Bnext%7D%20%7B" alt="NF!~/\.so/{next} {" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> 0= <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=NF%7D%20%21a%5B" alt="NF} !a[" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> 0]++' /proc/1585728/maps$NF!~/\.so/{next}– If the last column doesn’t contain “.so“, we ignore it{ <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=0%3D" alt="0=" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> NF}- If the last column contains a shared library, we replace the line by the last column, which is the filename of the library*!a[$0]++*is an awk trick to remove duplicate lines
find . -name "*@to_be_deleted" | awk -F"@to_be_deleted" '{print "mv " <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=0%20%22%20%22%20" alt="0 " " " class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> 1}'|sh:将文件夹内文件名中的某个pattern删掉- 循环打印:
awk 'BEGIN { for (i=0; i<10; i++) printf("%02d ", i) }'
bash -x run.sh显示shell脚本执行过程中的实际命令- bg: resume后台暂停的命令
- cat
- cd
- chmod:
sudo chmod 777 -R文件修改为可执行Permissions 0644 for ‘~/.ssh/id_rsa’ are too open=>chmod 0600 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- chown: 用于设置文件所有者和文件关联组的命令
sudo chown root:root /usr/bin/rclone
HOST_PERM=" <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=%28id%20-u%29%3A" alt="(id -u):" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> (id -g)"
chown <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=HOST_PERMS%20" alt="HOST_PERMS " class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> file- cloc: 代码行数统计
- curl
- -I/--head: 只显示传输文档,经常用于测试连接本身
curl --head --silent baidu.com | grep --ignore-case content-length | cut -f2 -d ' ' - curl查询公网出口ip
curl cip.cc
- -I/--head: 只显示传输文档,经常用于测试连接本身
- cut
- 使用 -f 选项提取指定字段:
cut -f2,3 test.txt
- 使用 -f 选项提取指定字段:
- cp
- -H vs -L, 两者都是 follow symbolic links,区别在于 -r 时表现不同
- cron: a daemon your system already runs to perform scheduled tasks
- c++filt: demangle C++/Java symbols
-
d: zsh的特点,可显示最近10个目录,然后
cd -数字进入 -
date:日期
-
dd
-
you have very large devices to copy, so that experimenting to determine the best block-size is worthwhile.
-
you have to copy only part of a disk. You can specify
countto limit how many blocks are copied. -
you want to resume an interrupted copy. You can't do so with
cp, but you can try withdd, by using theseekandskipoptions. -
you want to pipe it to the standard input of something (admittedly,
catwill work here too):dd if=/dev/sda bs=10M | ssh host dd of=/dev/sdb -
ddusefulness is very well discussed in this Unix and Linux post: dd vs cat — is dd still relevant these days?
-
-
declare
declare -a NAMES=(
a \
b \
c \
d \
)-
df: disk情况
-
disown
-
diff:Linux中diff的渊源
diff -Naur比较两个文件夹
-
dmesg: kernel log
-
dpkg -i ***.deb -
du -h -d 1 $file
- echo: 输出输入,空格分割
- env: 进入环境
- 读man env,
#!/usr/bin/env -S /usr/local/bin/php -n -q -dsafe_mode=0,利用env来传参。(FreeBSD 6.0之后不能直接传参,解释器会把多个参数合成一个参数)
- 读man env,
- export
- fd:作为find的替代品
- colorized output, default regex matching, Unicode support, more intuitive syntax
- fg: Run jobs in foreground
- find:1)寻找文件; 2)机械式操作
- -iname:大小写不敏感
# Find all directories named/including src
find . -name src -type d
find . -name "*src*" -type d
# Find all python files that have a folder named test in their path
find . -path '**/test/**/*.py' -type f
# Find all files modified in the last day
find . -mtime -1
# Find all zip files with size in range 500k to 10M
find . -size +500k -size -10M -name '*.tar.gz'
# Delete all files with .tmp extension
find . -name '*.tmp' -exec rm {} \;
# Find all PNG files and convert them to JPG
find . -name '*.png' -exec convert {} {.}.jpg \;
find /tmp -maxdepth 1 -mmin +720 -name "tmp*" -delete
- fuck: 流行的纠正工具
- grep
# specify lines of trailing context
-A 10
# ignore cases
-i
# "NOT"筛选
grep -v "trash"
# “OR”筛选
grep -E "key1|key2"
# “AND”筛选
grep -E "key1.*key2"
# 颜色
--color
grep -o '^20120603 08:02:..' $file | sort | uniq -c
- gunzip
gunzip 1.gz
gunzip -v 1.gz
gunzip -v -S "mygz" 1.mygz # 按指定后缀名解压- icdiff: 分屏比较文档
icdiff button-{a,b}.css
- ifconfig
- jobs
- krb5
export DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive && apt-get update && apt-get install -y krb5-user- less
space / B翻页
- locate
- Most would agree that
findandfdare good but some of you might be wondering about the efficiency of looking for files every time versus compiling some sort of index or database for quickly searching. That is whatlocateis for.locateuses a database that is updated usingupdatedb. In most systemsupdatedbis updated daily viacron. Therefore one trade-off between the two is speed vs freshness. Moreoverfindand similar tools can also find files using attributes such as file size, modification time or file permissions whilelocatejust uses the name. A more in depth comparison can be found here.
- Most would agree that
- ls
- -l: long listing format; drwxr-xr-x,d代表文件夹,后面3*3代表owner、owning group、others的权限
- r:read,w:modify,x:execute
- -t: 按时间排序
- lsof: 查看文件占用
- 也可查看端口占用,接 grep 即可
- man: q退出
fork(2)->man 2 fork
- mkdir
- mv
- nc(netcat): TCP/IP 的瑞士军刀
- 端口测试:
nc localhost $port
- 端口测试:
- netstat
- nohup
# 将标准输出放到name.log中,并且记录该进程的pid到run.pid中
nohup python -u main.py > name.log 2>&1 & echo $! > run.pid
# 若存在run.pid文件,则加载它并杀掉该进程
[[ -f run.pid ]] && kill $(cat run.pid)- open:
- -n用来多开
open -a "sublime text" ~/temp.diff
-
pandoc test1.md -f markdown -t html -s -o test1.htmlpandoc -s --toc -c pandoc.css -A footer.html MANUAL.txt -o example3.html
-
pbcopy: 复制到剪贴板
pbcopy < file -
pgrep: 配合jobs
pgrep -f 100全命令行匹配
-
ping
-
pip
-
pip list
-
pip show requests
-
pip uninstall requests
-
pip freeze > requirements.txt -
python -m ensurepip --upgrade # 如果损坏 pip install /path/to/package #安装一个本地的Python包 pip install package== 显示可安装的版本 pip install -r requirements.txt #从requirements.txt文件中安装包 pip cache purge #清理缓存 pip install package_name==version_number #安装指定版本的包 pip install --upgrade package_name #升级已安装的包 pip install --user package_name #这将在用户的本地目录中安装该库 pip install --no-dependencies package_name #安装名为xx的Python包但忽略其依赖项 pip install --find-links=URL package_name #从指定的URL中找到并安装名为"myproject的Python包
-
-
pkill = pgrep + kill
pkill -9 -f 100
-
pmap: Displays the memory map of a process.
-
ps aux
-
pstree
-
pushd: 目录栈,方便切换目录
- 配合popd
-
pwd: print cwd
- rsync
rsync -avz /path/to/source/ user@remote:/path/to/destination/
- scp
scp <img src="https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=file%20user%40ip%3A/home/" alt="file user@ip:/home/" class="ee_img tr_noresize" eeimg="1"> folder
scp -r $folder-
script
- 记录终端操作记录,按
C-d退出 - 可用于demo演示终端操作
- 记录终端操作记录,按
-
sha1sum:
printf 'hello' | sha1sum -
sha256sum
-
source
# "." 等价于 source-
strings
-
https://www.howtogeek.com/427805/how-to-use-the-strings-command-on-linux/
-
sudo strings /dev/mem | less
-
- tac: 反向
- tar
- 报错可能需要sudo
tar cvzf 压缩文件名.tar.gz 被压缩文件夹 # gz文件
tar xvzf 压缩文件名.tar.gz -C 目标文件夹 # 否则解压到当前路径
tar xvf 压缩文件名.tar.xz-
tail
ls -l | tail -n1- -f:不断读最新内容,实时监视
-
tee: Read from standard input and write to standard output and files (or commands).
- 和
xargs有相似之处,都是转化stdin用于他用 echo "example" | tee /dev/tty | xargs printf "[%s]"
- 和
-
tig
- tig是一个基于ncurses的git文本模式接口。它的功能主要是作为一个Git存储库浏览器,但也可以帮助在块级别上分段提交更改,并充当各种Git命令输出的分页器
-
time
-
tmux
-
top
- -d 10: 10s采样
- -H: 显示线程
- -H -p $pid:显示指定进程下的线程
- 按 1 键显示 per cpu core 利用率
- 按 e/E 切换内存单位
- 按 f 键增加显示项目
VIRT:virtual memory usage 虚拟内存
1、进程“需要的”虚拟内存大小,包括进程使用的库、代码、数据等
2、假如进程申请100m的内存,但实际只使用了10m,那么它会增长100m,而不是实际的使用量
RES:resident memory usage 常驻内存
1、进程当前使用的内存大小,但不包括swap out
2、包含其他进程的共享
3、如果申请100m的内存,实际使用10m,它只增长10m,与VIRT相反
4、关于库占用内存的情况,它只统计加载的库文件所占内存大小
SHR:shared memory 共享内存
1、除了自身进程的共享内存,也包括其他进程的共享内存
2、虽然进程只使用了几个共享库的函数,但它包含了整个共享库的大小
3、计算某个进程所占的物理内存大小公式:RES – SHR
4、swap out后,它将会降下来
DATA
1、数据占用的内存。如果top没有显示,按f键可以显示出来。
2、真正的该程序要求的数据空间,是真正在运行中要使用的。
-
traceroute: -w 1
-
tree: 显示树形文件结构,
-L设置层数
uname -a查内核版本ulimit -aulimit -s xxx修改线程栈大小
-
wait:
wait pid,不加pid则等待所有进程 -
watch -n 5 $cmd -
wc: -l
- source code
- 这段代码只将连续的字母作为一个字,连续的数字等不作为word
- isword用来判断当前字符是否处于一个字,isword实现的功能不完善
- source code
-
which:找到程序路径
-
wget: 断点续传-c 后台-b
- xargs:解决命令的输入来源问题:命令参数有标准输入和命令行参数两大来源,有的命令只接受命令行参数,需要xargs来转换标准输入
- e.g.
ls | xargs rm -0: 分隔符用NULL
- e.g.
- youget
- 自动补全:
curl -fLo ~/.zplug/repos/zsh-users/zsh-completions/src/_youget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/soimort/you-get/develop/contrib/completion/_you-get
- 自动补全:
_arguments:450: _vim_files: function definition file not found
rm ~/.zcompdump*
rm ~/.zplug/zcompdump*
exec zsh