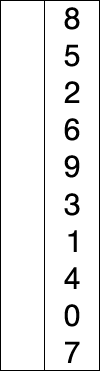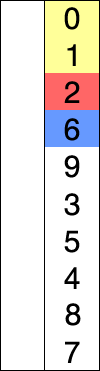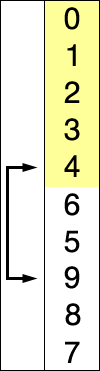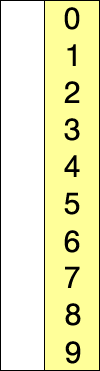
Select the minimum element and move it to its correct place in every pass
- Red is the current min.
- Yellow is the sorted list.
- Blue is the current item.
- Worst Case Complexity: O(n2) If we want to sort in ascending order and the array is in descending order then, the worst case occurs.
- Best Case Complexity: O(n2) It occurs when the array is already sorted
- Average Case Complexity: O(n2) It occurs when the elements of the array are in jumbled order (neither ascending nor descending).
- Space complexity is O(1) because an extra variable is used for swapping.
- Comparison Based
- Not Stable
- Inplace
- Basic idea for Heap Sort
- Less memory writes compared to Bubble Sort
- It is used when a small list is to be sorted
- If the cost of swapping does not matter
- If checking of all the elements is compulsory
- If the cost of writing to a memory matters like in flash memory (number of writes/swaps is O(n) as compared to O(n2) of bubble sort)
- Simple and easy to understand.
- Works well with small datasets.
- Selection sort has a time complexity of O(n2) in the worst and average case.
- Does not work well on large datasets.
- Does not preserve the relative order of items with equal keys which means it is not stable.