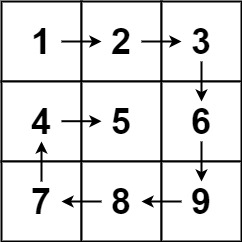
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]输入:matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
输出:[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]提示:
- m == matrix.length
- n == matrix[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 10
- -100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
思路: 这个问题可以通过模拟螺旋遍历的过程来解决。以下是算法的主要逻辑:
- 初始化:定义一个空数组order,用于存储最终的螺旋顺序元素。
- 边界控制:设置四个指针,left、right、top、bottom,分别表示矩阵的左边界、右边界、上边界和下边界。
- 循环条件:使用while循环,条件是左边界不大于右边界,且上边界不大于下边界。
- 添加顶部元素:从左边界到右边界,添加矩阵顶部的元素。
- 添加右侧元素:从上边界的下一个位置到下边界,添加矩阵右侧的元素。
- 添加底部元素(如果存在):如果左边界小于右边界,从右到左,添加矩阵底部的元素。
- 添加左侧元素(如果存在):如果上边界小于下边界,从下到上,添加矩阵左侧的元素。
- 更新边界:更新四个边界的位置,为下一轮循环做准备。
- 返回结果:循环结束后,返回order数组。
时间复杂度是O(m * n),其中m是矩阵的行数,n是矩阵的列数。这是因为算法需要访问矩阵中的每个元素一次。 空间复杂度是O(m * n),因为输出数组order的大小与矩阵的大小相同。
var spiralOrder = function (matrix) {
if (!matrix.length || !matrix[0].length) {
return [];
}
const rows = matrix.length,
columns = matrix[0].length;
const order = [];
let left = 0,
right = columns - 1,
top = 0,
bottom = rows - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
for (let column = left; column <= right; column++) {
order.push(matrix[top][column]);
}
for (let row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) {
order.push(matrix[row][right]);
}
if (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (let column = right - 1; column > left; column--) {
order.push(matrix[bottom][column]);
}
for (let row = bottom; row > top; row--) {
order.push(matrix[row][left]);
}
}
[left, right, top, bottom] = [left + 1, right - 1, top + 1, bottom - 1];
}
return order;
};