This repository uses the GitHub CI/CD pipeline to deploy applications on a Kubernetes cluster.
Instead of manually deploying the application via kubectl commands or terraform commands, the process can be automated with a CI/CD pipeline.
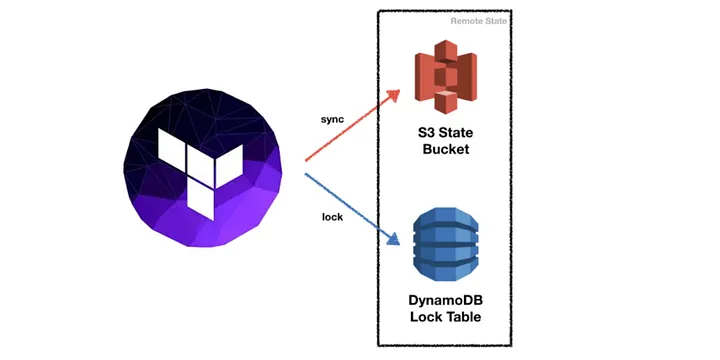
The Terraform backend uses S3 and DynamoDB with state locking.
The main.yml file handles the CD process. Its 'deploy' task contains several steps as follows.
-
aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1This provides AWS credentials for virtual environments hosted on GitHub (Runners). -
tale/kubectl-action@v1GitHub Action to manage a K8s cluster using kubectl -
actions/checkout@v2Checkout the code from Git repository -
hashicorp/setup-terraform@v2sets up Terraform CLI in workflow -
Terraform Initinitializes working directory -
Terraform Validatevalidate the configuration internally -
Terraform Plancreates the execution plan -
Terraform Applyexecutes the actions
By default, Terraform stores state locally in terraform.tfstate file. When working with Terraform in a team, use of a local file makes Terraform usage complicated because each user must make sure they always have the latest state data before running Terraform and make sure that nobody else runs Terraform at the same time.
With remote state, Terraform writes the state data to a remote data store (In this case S3), which can then be shared between all members of a team. With support of DynamoDB, Terraform will lock state for all operations. This prevents others from acquiring the lock and potentially corrupting state.