You are given a 0-indexed m x n binary matrix grid. You can move from a cell (row, col) to any of the cells (row + 1, col) or (row, col + 1).
Return true if there is a path from (0, 0) to (m - 1, n - 1) that visits an equal number of 0's and 1's. Otherwise return false.
Example 1:
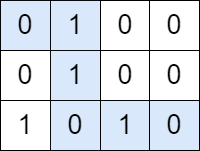
Input: grid = [[0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0],[1,0,1,0]] Output: true Explanation: The path colored in blue in the above diagram is a valid path because we have 3 cells with a value of 1 and 3 with a value of 0. Since there is a valid path, we return true.
Example 2:
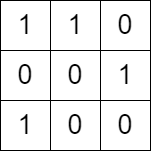
Input: grid = [[1,1,0],[0,0,1],[1,0,0]] Output: false Explanation: There is no path in this grid with an equal number of 0's and 1's.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 100grid[i][j]is either0or1.
Companies: Google
Related Topics:
Array, Dynamic Programming, Matrix
Similar Questions:
- Minimum Path Sum (Medium)
- Dungeon Game (Hard)
- Minimum Cost Homecoming of a Robot in a Grid (Medium)
- Paths in Matrix Whose Sum Is Divisible by K (Hard)
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/check-if-there-is-a-path-with-equal-number-of-0s-and-1s
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(MN * (M + N))
// Space: O(N * (M + N))
class Solution {
public:
bool isThereAPath(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size();
vector<bitset<200>> dp(N);
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) dp[j].set(A[i][j] ? 101 : 99);
else if (i == 0) dp[j] = A[i][j] ? (dp[j - 1] << 1) : (dp[j - 1] >> 1);
else if (j == 0) dp[j] = A[i][j] ? (dp[j] << 1) : (dp[j] >> 1);
else dp[j] = A[i][j] ? ((dp[j] << 1) | (dp[j - 1] << 1)) : ((dp[j] >> 1)
| (dp[j - 1] >> 1));
}
}
return dp[N - 1].test(100);
}
};Intuition: There exists a discretely continuous transformation between any pair of paths. Namely, given two paths p1 and p2 with sums s1 <= s2 respectively, there existsthere exists a path p with sum s for every s1 <= s <= s2.
For the simpliest case of 2x2 cells, A[0][0] and A[1][1] are shared between p1 and p2. The only difference is A[1][0] and A[0][1], and their difference is at most 1.
Now consider a 2x3 grid, p1 = (0,0) - (0,1) - (0,2) - (1,2), p2 = (0,0) - (0,1) - (1,1) - (1,2), and p3 = (0,0) - (1,0) - (1,1) - (1,2). We can see that the difference between p1 and p2 is at most 1, and the same for p2 and p3. So, the difference between p1 and p3 is at most 2, in which case p1, p2, p3 are continous.
We can generalize this to MxN grid, and see that the above intuition is true.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/check-if-there-is-a-path-with-equal-number-of-0s-and-1s
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(MN)
// Space: O(MN)
class Solution {
public:
bool isThereAPath(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size();
if ((M + N) % 2 == 0) return false;
vector<vector<int>> mn(M, vector<int>(N)), mx(M, vector<int>(N));
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) mn[i][j] = mx[i][j] = A[i][j];
else if (i == 0) mn[i][j] = mx[i][j] = mn[i][j - 1] + A[i][j];
else if (j == 0) mn[i][j] = mx[i][j] = mn[i - 1][j] + A[i][j];
else {
mn[i][j] = min(mn[i - 1][j], mn[i][j - 1]) + A[i][j];
mx[i][j] = max(mx[i - 1][j], mx[i][j - 1]) + A[i][j];
}
}
}
return mn[M - 1][N - 1] <= (M + N - 1) / 2 && (M + N - 1) / 2 <= mx[M - 1][N - 1];
}
};Since mx[i][j] only depends on mx[i][j - 1]and mx[i - 1][j], we can reduce the complexity from O(MN) to O(N).
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/check-if-there-is-a-path-with-equal-number-of-0s-and-1s
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(MN)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
bool isThereAPath(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size();
if ((M + N) % 2 == 0) return false;
vector<int> mn(N), mx(N);
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) mn[j] = mx[j] = A[i][j];
else if (i == 0) mn[j] = mx[j] = mn[j - 1] + A[i][j];
else if (j == 0) mn[j] = mx[j] = mn[j] + A[i][j];
else {
int prevMin = min(mn[j], mn[j - 1]), prevMax = max(mx[j], mx[j - 1]);
mn[j] = prevMin + A[i][j];
mx[j] = prevMax + A[i][j];
}
}
}
return mn[N - 1] <= (M + N - 1) / 2 && (M + N - 1) / 2 <= mx[N - 1];
}
};