-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 9.3k
Working Issues and PRs
With a fork cloned, a branch created, you just need some issues and start working!
As you find issues to work on, don't forget to check the wikis and DevDocs that may be available per project to get you started.
If looking for issues to work on, we have a verified set of issues available on the Community Backlog. These are all issues you can work for the Magento 2 Open Source repo.
Claim issues from the following columns:
-
Ready for Dev: Issues that were Confirmed (label
Issue: Confirmed) and ready for development and Pull Request creation. All issues in this column are available and free to claim and work. - Good First Issue: Issues that are great for beginners new to Magento or contributing.
Need a bit of help understanding the backlog? See the backlog guide. If you have any questions understanding the issues, join us in #beginners Slack chat (or self join).
Interested in a special project? Heard about PWA, MSI, GraphQL, Asynchronous API, B2B, Adobe integrations, etc and want to join?
We have a great list!
-
Japanese Localization - Wiki | Repo | #japanese-localization
-
All localizations project - Repo | ZenHub | CrowdIn | #translations
-
DevDocs - Repo | Contributing | #devdocs
-
Magento Architecture - Wiki | Repo | #appdesign | Architecture Services Isolation #service-isolation
-
Coding Standards - Wiki | Repo | #coding-standard
-
Magento Functional Testing Framework - Wiki | Repo | Test Conversions | #mftf
Create your branch and start coding. While providing your contribution to the Magento code base it is important to accompany it with a meaningful commit message. A meaningful commit message is important to:
- Help speed up the reviewing process
- Help us write a good release note
- Help future developers understand why a particular change was made
We recommend including the GitHub issue number and title, as well as some additional comments that you feel are relevant. Adding the GitHub issue, your commit is automatically linked to this issue. Everyone can quickly see your commited work and the issue associated to it in GitHub.
magento/magento2#<issue-number>: <issue-title>
- <additional comment>
For example:
magento/magento2#8618: Apply coupon code button issue on checkout
- fixed issue with assigning coupon_code value from totals
- If it feels hard to summarize what your commit is, then try splitting it into multiple commits.
- If there is no GitHub issue, you can skip adding
magento/magento2#<issue-number>:and just add a meaningful title. - If you are working on a community project, please update the issue part as appropriate. For example, Import Export work should be
magento-engcom/import-export-improvements#<issue-number>:.
More information: https://github.com/magento/magento2/wiki/Commit-Message-Formatting
Don't forget about testing your code. The best way to test your code, is to consider how you write your code. We recommend reading the following:
You can search and find info in the Magento DevDocs to help you write and test your code!
To run all the unit tests via the command line you can use the following snippet from the Magento root directory:
./vendor/bin/phpunit -c dev/tests/unit/phpunit.xml.dist
Though you can also run specific directories or even specific test files by appending the information to the end of the command:
./vendor/bin/phpunit -c dev/tests/unit/phpunit.xml.dist app/code/Example/Module/Test/Unit
./vendor/bin/phpunit -c dev/tests/unit/phpunit.xml.dist app/code/Example/Module/Test/Unit/SampleTest.php
More information: https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.3/test/unit/unit_test_execution.html
Before you can use the Magento integration test framework, you must prepare the test environment. Prerequisites for the test environment include the following:
- A dedicated integration test database
- The test framework database configuration
- The PHPUnit configuration matches the purpose of the integration test execution
Using the following MySQL you can create a database for your integration tests. Please replace the example database, username, and password with something that matches your requirements and conventions.
CREATE DATABASE magento_integration_tests;
GRANT ALL ON magento_integration_tests.* TO 'magento2_test_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'ftYx4pm6^x9.&^hB';
Once you have the database setup you will need to create your configuration file. This lives under the folder dev/tests/integration/etc. Here you can find a template configuration file install-config-mysql.php.dist. Create a copy of this file without the .dist suffix with the appropriate configuration options. For example:
<?php
return [
'db-host' => 'localhost',
'db-user' => 'magento2_test_user',
'db-password' => 'ftYx4pm6^x9.&^hB',
'db-name' => 'magento_integration_tests',
'db-prefix' => '',
'backend-frontname' => 'backend',
'admin-user' => \Magento\TestFramework\Bootstrap::ADMIN_NAME,
'admin-password' => \Magento\TestFramework\Bootstrap::ADMIN_PASSWORD,
'admin-email' => \Magento\TestFramework\Bootstrap::ADMIN_EMAIL,
'admin-firstname' => \Magento\TestFramework\Bootstrap::ADMIN_FIRSTNAME,
'admin-lastname' => \Magento\TestFramework\Bootstrap::ADMIN_LASTNAME,
'amqp-host' => 'localhost',
'amqp-port' => '5672',
'amqp-user' => 'guest',
'amqp-password' => 'guest',
];
To run the integration tests via the command line you will first need to be inside the integration test folder.
cd dev/tests/integration
You can then run all the integration test by calling the phpunit bin file that is in the vendor folder.
../../../vendor/bin/phpunit
Again like the unit tests your can run a folder of tests or even single test file with the following
../../../vendor/bin/phpunit ../../../app/code/Acme/Example/Test/Integration
../../../vendor/bin/phpunit ../../../app/code/Acme/Example/Test/Integration/ExampleTest.php
More information: https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.3/test/integration/integration_test_execution.html
Great thanks to Tom Erskine, Community Testing Guru, for his incredible help and info for this section. For his complete guide, see MFTF Process in the MSI repo.
We also strongly recommend the incredible DevDocs: Magento Functional Test Framework (MFTF). These tests use Selenium and require a few extra steps to prepare.
To get started, complete all steps here to prepare your Magento install and set up MFTF: DevDocs Getting Started.
Run the Selenium Server:
-
Download the latest Selenium Server Standalone JAR: https://www.seleniumhq.org/download/
-
Download a Selenium web driver for your web browser into the same directory that contains the Selenium server.
-
Add the directory with the web driver to PATH.
-
Run the Selenium server in terminal (or other command line interface):
java -jar <path_to_selenium_directory>/selenium-server-standalone-<version>.jar
This is a rough list of steps to get ready.
-
CD to the acceptance test directory of your Magento install:
cd [PATH_TO_MAGENTO]/dev/tests/acceptance -
Install the dependencies:
composer install -
Build the project:
./vendor/bin/robo build:project -
Locate and open the .env file.
-
Fill in the minimal necessary details:
#Magento Base url. It should include `index.php/` if rewrites rules are not enabled. MAGENTO_BASE_URL=http://mageto.url/ #Magento backend route name MAGENTO_BACKEND_NAME=admin #admin username MAGENTO_ADMIN_USERNAME=admin #admin password MAGENTO_ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin123
-
Generate the tests:
./vendor/bin/robo generate:tests
To run a group of tests:
```
cd [PATH_TO_MAGENTO]/dev/tests/acceptance
./vendor/bin/robo group
```
-
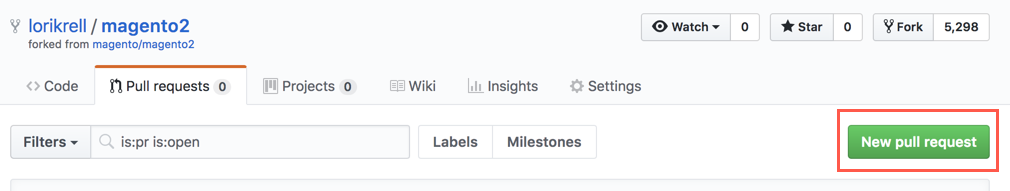
Open your forked repository in GitHub.
-
Click Pull requests on the right, and then click New pull request.
-
Ensure that you are creating a PR to the one of following branches: magento:2.3-develop or magento:2.2-develop. We accept PRs to these branches only.
-
Review the changes, then click Create pull request.
-
Fill out the PR form. Include the number for any GitHub Issue(s) for the PR. We recommend completely filling out the PR form to help code reviewers and Maintainers!
-
Click Create pull request again to submit the PR. That’s it!
After submitting your PR, you can find it in the Magento 2 Pull Requests or the PRs for your special project. Your PR undergoes automated testing, and if it passes, the Community Engineering Team considers it for inclusion in the Magento 2 core. If some tests fail, please review the responses and update with commits.
Interested in becoming a Magento Contributor? Click here to join our Slack workspace! Then come say hi in #general, follow the #announcements, and browse to find more cool channels!
- Getting Started
- Forking and Branching
- Working with commits
- Working Issues and PRs
- Community Maintainers
- Working with commits
- Magento Contributor Assistant
- Magento Automated Testing
- Test coverage contributions
- Slack Channels
- Magento 2 Core
- Multi Source Inventory
- Coding Standard
- DevDocs
- PHP 8 Compatibility
- Platform Health