When you work on small project, you will feel laravel default structure
is enough. When your project grows up, you will think to divide
your app into modules where each module will contain all of it resources
such as Controllers, Models, Views, Migrations, Config etc. This laravel-module-manager
package will help you to manage laravel modular application easily.
-
laravel 5.4 or 5.5
composer require mrabbani/laravel-module-manager -
Laravel 5.3, Add the following line to your
composer.jsonfile and runcomposer installin your terminal."mrabbani/laravel-module-manager": "^1.4"
If you are using Laravel<5.5 you have to add module manager service provider to config/app.php file
Mrabbani\ModuleManager\Providers\ModuleProvider::class,
To create new module run the bellow command:
php artisan module:create name-of-your-module
php artisan module:install {module_alias_name}
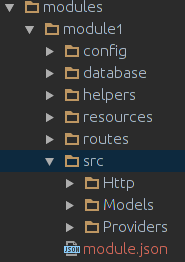
If your module name is module1 the module structure will be
By default, all of your module will be placed inside modules directory
into your application's base directory. If you want to change publish
module_manager config file by
php artisan vendor:publish
Now you can change the default modules directory by changing
module_directory value of config/module_manager.php file.
To see all module related commands run php artisan into terminal.
Available commands are:
php artisan module:create {alias}php artisan module:make:controller {alias} {ControllerName}php artisan module:make:controller {alias} {ControllerName} --resourcephp artisan module:make:command {alias} {CommandName}php artisan module:make:facade {alias} {FacadeName}php artisan module:make:middleware {alias} {MiddlewareName}php artisan module:make:migration {alias} {migration_name} --create --table=table_namephp artisan module:make:migration {alias} {migration_name} --table=table_namephp artisan module:make:model {alias} {ModelName}php artisan module:make:provider {alias} {ProviderName}php artisan module:make:request {alias} {RequestName}php artisan module:make:service {alias} {ServiceClassName}php artisan module:make:support {alias} {SupportClassName}php artisan module:make:seeder {alias} {SeederClassName}php artisan module:db:seed {alias}php artisan module:db:seed {alias} --class={SeederClassName}php artisan module:migrate {alias}php artisan module:migrate:rollback {alias}php artisan module:routesphp artisan module:install {alias}php artisan module:uninstall {alias}php artisan module:enable {alias}php artisan module:disable {alias}
'alias' is your module's alias name. you can find module's alias name in
module.jsonfile of module directory
You must install your module to activate
php artisan module:install {alias}
You have to load views, config and translation by following laravel package
view(module_alias::view_file)
you may load the module1 module's index.blade.php view like so:
view('module1::index');
you may load the module1 module's welcome line from the messages file like so:
trans('module1::messages.welcome');
you may load the module1 module's welcome line from the messages file like so:
config('messages.welcome');
You have to merge the configurations, use the mergeConfigFrom method within your ModuleServiceProvider provider's register method:
public function register()
{
$this->mergeConfigFrom(
__DIR__.'/../../config/messages.php', 'messages'
);
}
You should create a MiddlewareServiceProvider provider to register your middleware dynamically.
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
class MiddlewareServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
/**
* Register any application services.
*
* @return void
*/
public function register()
{
/**
* @var Router $router
*/
$router = $this->app['router'];
$router->aliasMiddleware('middleware-shortname', MiddlewareClassName::class);
}
}
You should register all of your module's custom provider in ModuleServiceProvider provider's register method instead application's config/app.php file.