The open-source Calendly alternative.
Learn more »
Slack
·
Website
·
Issues
·
Roadmap
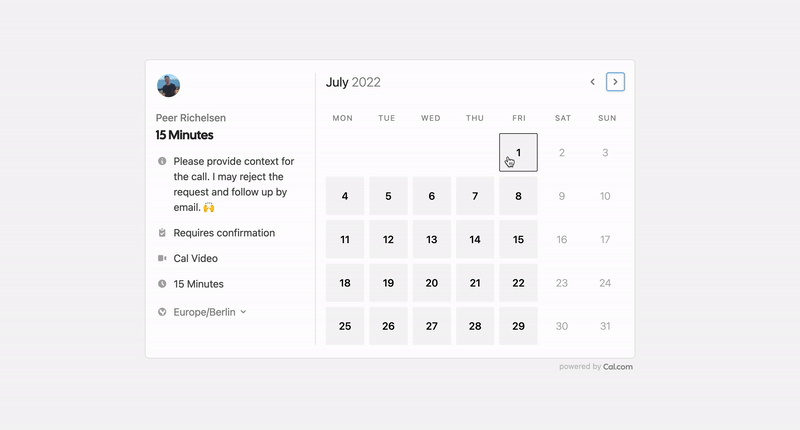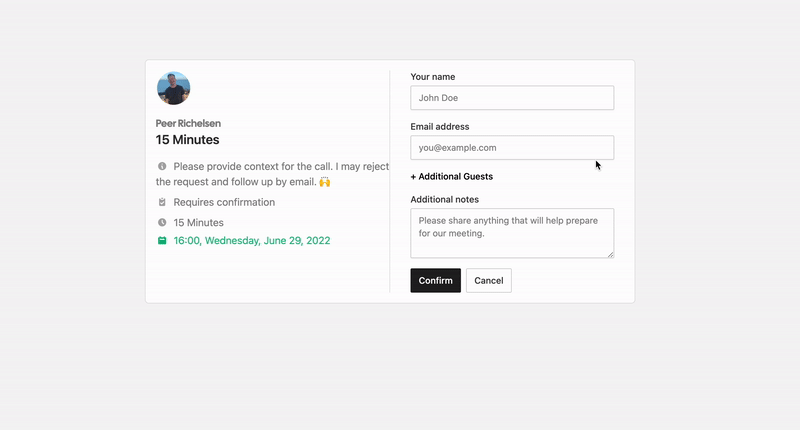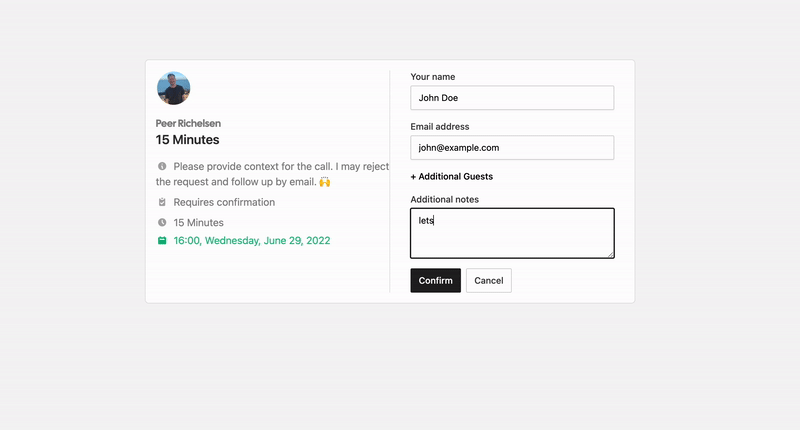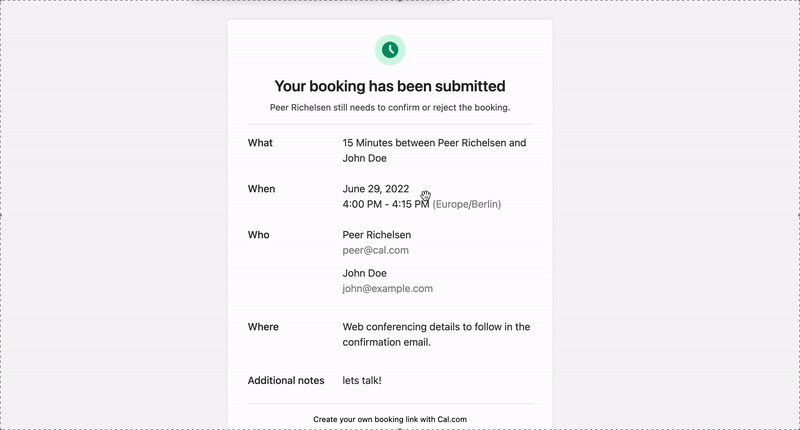
The open source Calendly alternative. You are in charge of your own data, workflow and appearance.
Calendly and other scheduling tools are awesome. It made our lives massively easier. We're using it for business meetings, seminars, yoga classes and even calls with our families. However, most tools are very limited in terms of control and customisations.
That's where Cal.com comes in. Self-hosted or hosted by us. White-label by design. API-driven and ready to be deployed on your own domain. Full control of your events and data.
Cal officially launched as v.1.0 on 15th of September, however a lot of new features are coming. Watch releases of this repository to be notified for future updates:
To get a local copy up and running, please follow these simple steps.
Here is what you need to be able to run Cal.
- Node.js (Version: >=15.x <17)
- PostgreSQL
- Yarn (recommended)
If you want to enable any of the available integrations, you may want to obtain additional credentials for each one. More details on this can be found below under the integrations section.
-
Clone the repo into a public GitHub repository (or fork https://github.com/calcom/cal.com/fork). If you plan to distribute the code, keep the source code public to comply with AGPLv3. To clone in a private repository, acquire a commercial license)
git clone https://github.com/calcom/cal.com.git
-
Go to the project folder
cd cal.com -
Install packages with yarn
yarn
-
Set up your .env file
- Duplicate
.env.exampleto.env - Use
openssl rand -base64 32to generate a key and add it underNEXTAUTH_SECRETin the .env file. - Use
openssl rand -base64 24to generate a key and add it underCALENDSO_ENCRYPTION_KEYin the .env file.
- Duplicate
- Requires Docker and Docker Compose to be installed
- Will start a local Postgres instance with a few test users - the credentials will be logged in the console
yarn dxAdd
NEXT_PUBLIC_DEBUG=1anywhere in your.envto get logging information for all the queries and mutations driven by trpc.
echo 'NEXT_PUBLIC_DEBUG=1' >> .env-
Configure environment variables in the
.envfile. Replace<user>,<pass>,<db-host>,<db-port>with their applicable valuesDATABASE_URL='postgresql://<user>:<pass>@<db-host>:<db-port>'If you don't know how to configure the DATABASE_URL, then follow the steps here to create a quick DB using Heroku
-
Create a free account with Heroku.
-
In your new app, go to
Overviewand next toInstalled add-ons, clickConfigure Add-ons. We need this to set up our database.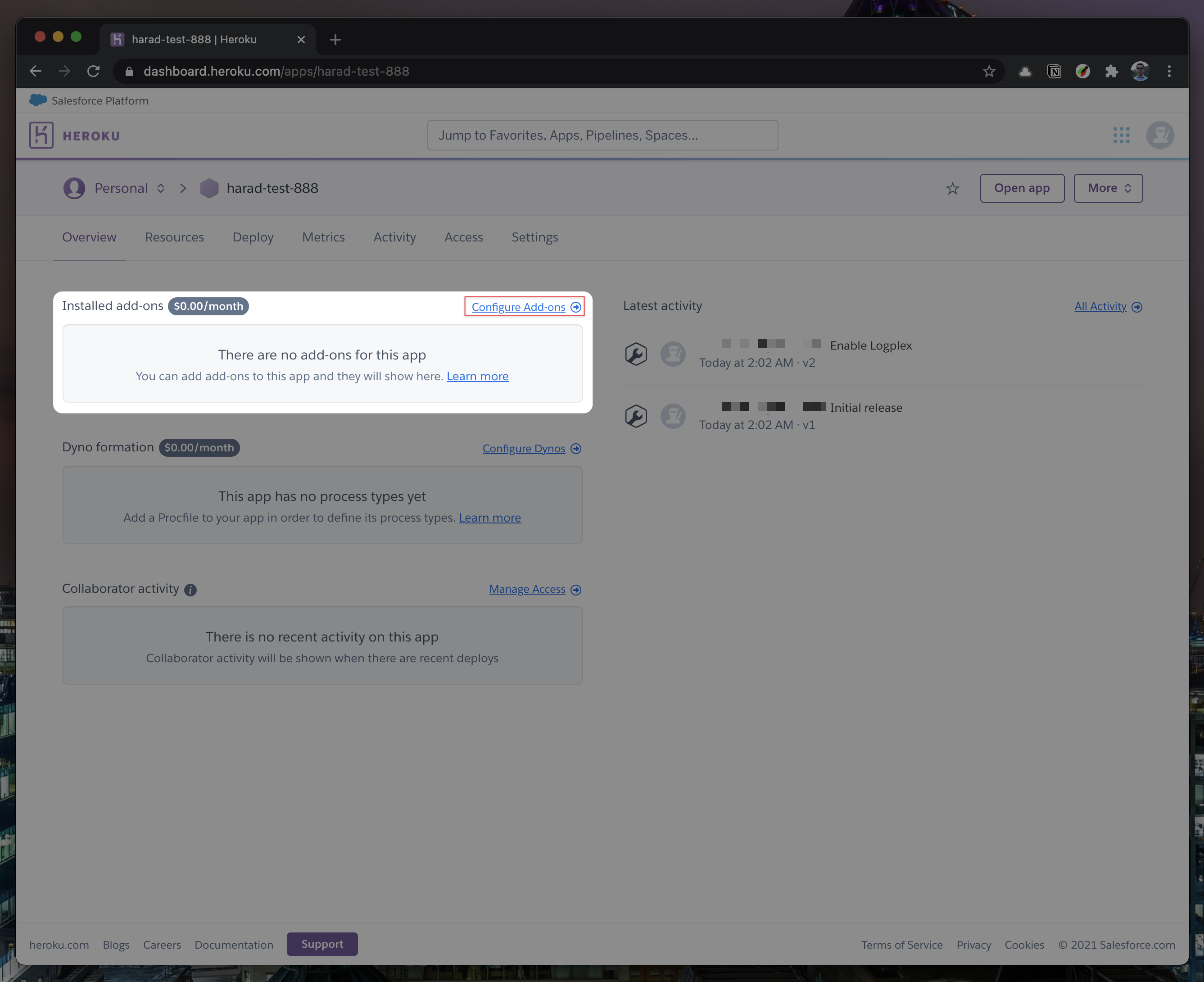
-
Once you clicked on
Configure Add-ons, click onFind more add-onsand search forpostgres. One of the options will beHeroku Postgres- click on that option.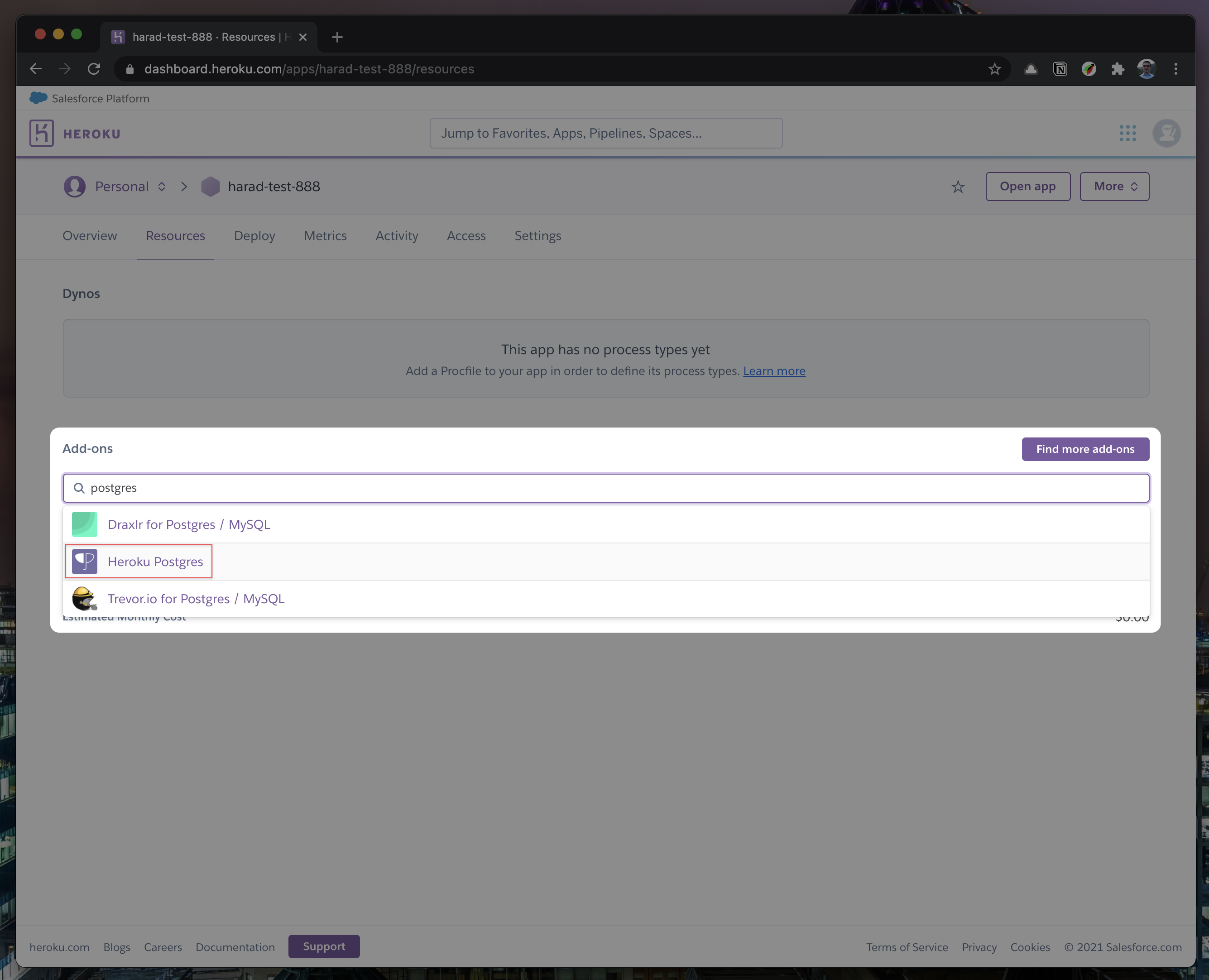
-
Once the pop-up appears, click
Submit Order Form- plan name should beHobby Dev - Free.
-
Once you completed the above steps, click on your newly created
Heroku Postgresand go to itsSettings.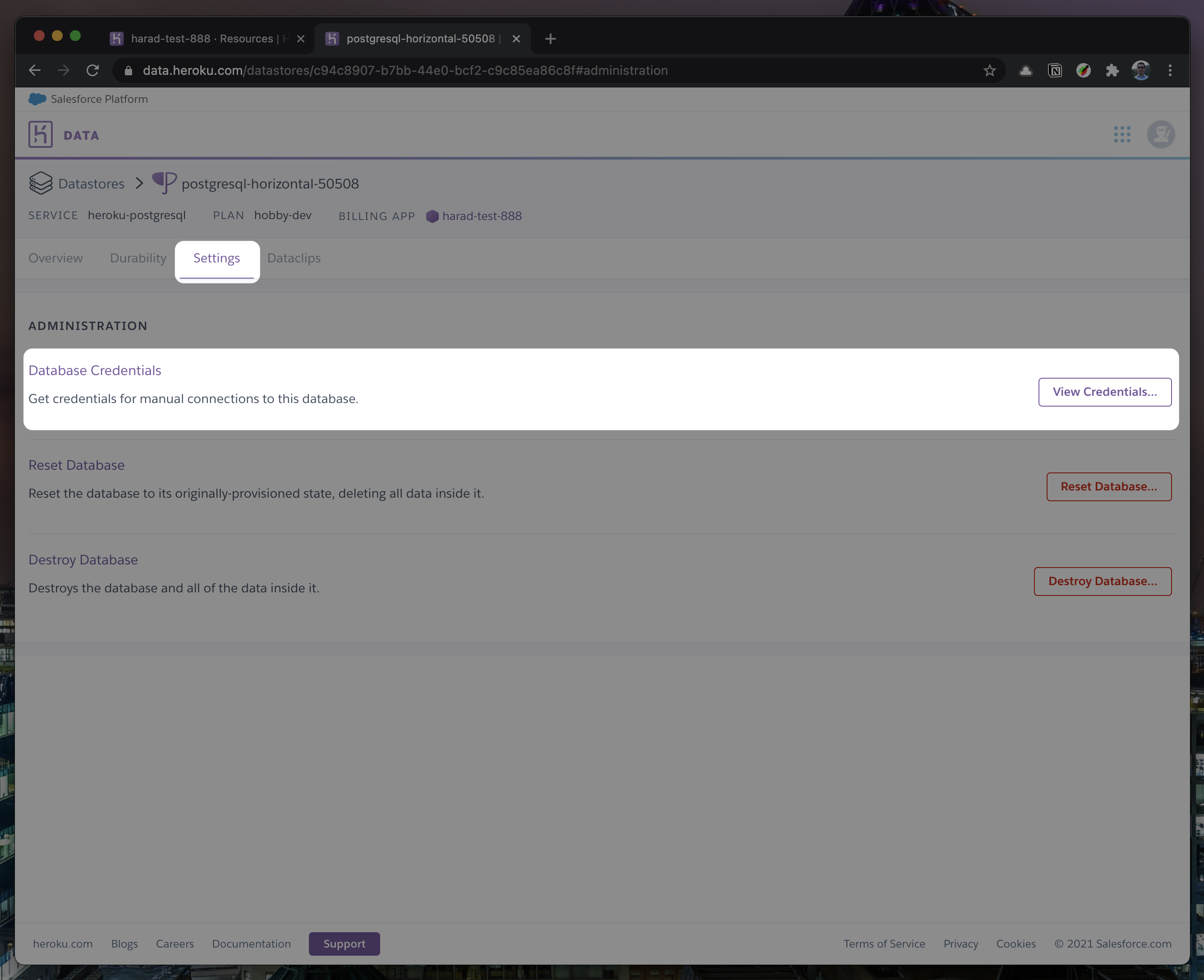
-
In
Settings, copy your URI to your Cal.com .env file and replace thepostgresql://<user>:<pass>@<db-host>:<db-port>with it.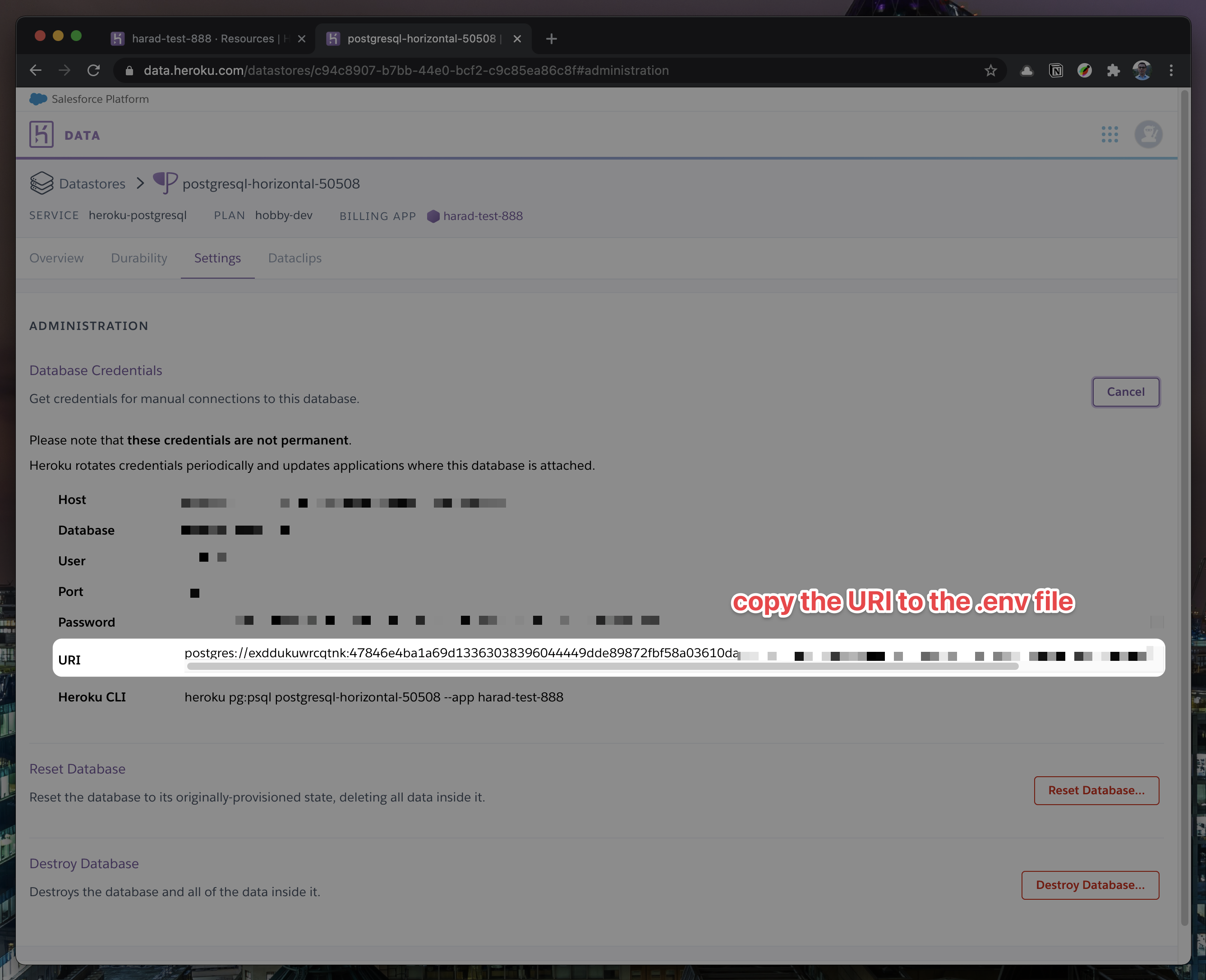

-
To view your DB, once you add new data in Prisma, you can use Heroku Data Explorer.
-
-
Set a 32 character random string in your .env file for the
CALENDSO_ENCRYPTION_KEY(You can use a command likeopenssl rand -base64 24to generate one). -
Set up the database using the Prisma schema (found in
packages/prisma/schema.prisma)yarn workspace @calcom/prisma db-deploy
-
Run (in development mode)
yarn dev
-
Open Prisma Studio to look at or modify the database content:
yarn db-studio
-
Click on the
Usermodel to add a new user record. -
Fill out the fields
email,username,password, and setmetadatato empty{}(remembering to encrypt your password with BCrypt) and clickSave 1 Recordto create your first user.New users are set on a
TRIALplan by default. You might want to adjust this behavior to your needs in thepackages/prisma/schema.prismafile. -
Open a browser to http://localhost:3000 and login with your just created, first user.
Be sure to set the environment variable NEXTAUTH_URL to the correct value. If you are running locally, as the documentation within .env.example mentions, the value should be http://localhost:3000.
# In a terminal just run:
yarn test-e2e
# To open last HTML report run:
yarn playwright show-report test-results/reports/playwright-html-report-
Pull the current version:
git pull
-
Check if dependencies got added/updated/removed
yarn
-
Apply database migrations by running one of the following commands:
In a development environment, run:
yarn workspace @calcom/prisma db-migrate
(this can clear your development database in some cases)
In a production environment, run:
yarn workspace @calcom/prisma db-deploy
-
Check for
.envvariables changesyarn predev
-
Start the server. In a development environment, just do:
yarn dev
For a production build, run for example:
yarn build yarn start
-
Enjoy the new version.
The Docker configuration for Cal is an effort powered by people within the community.
If you want to contribute to the Docker repository, reply here.
The Docker configuration can be found in our docker repository.
Issues with Docker? Find your answer or open a new discussion here to ask the community.
Cal.com, Inc. does not provide official support for Docker, but we will accept fixes and documentation. Use at your own risk.
You can deploy Cal on Railway using the button above. The team at Railway also have a detailed blog post on deploying Cal on their platform.
Currently Vercel Pro Plan is required to be able to Deploy this application with Vercel, due to limitations on the number of serverless functions on the free plan.
See the roadmap project for a list of proposed features (and known issues). You can change the view to see planned tagged releases.
Please see our contributing guide.
We have a list of help wanted that contain small features and bugs which have a relatively limited scope. This is a great place to get started, gain experience, and get familiar with our contribution process.
Don't code but still want to contribute? Join our slack and join the #i18n channel and let us know what language you want to translate.
- Set CSP_POLICY="non-strict" env variable, which enables Strict CSP except for unsafe-inline in style-src . If you have some custom changes in your instance, you might have to make some code change to make your instance CSP compatible. Right now it enables strict CSP only on login page and on other SSR pages it is enabled in Report only mode to detect possible issues. On, SSG pages it is still not supported.
- Open Google API Console. If you don't have a project in your Google Cloud subscription, you'll need to create one before proceeding further. Under Dashboard pane, select Enable APIS and Services.
- In the search box, type calendar and select the Google Calendar API search result.
- Enable the selected API.
- Next, go to the OAuth consent screen from the side pane. Select the app type (Internal or External) and enter the basic app details on the first page.
- In the second page on Scopes, select Add or Remove Scopes. Search for Calendar.event and select the scope with scope value
.../auth/calendar.events,.../auth/calendar.readonlyand select Update. - In the third page (Test Users), add the Google account(s) you'll using. Make sure the details are correct on the last page of the wizard and your consent screen will be configured.
- Now select Credentials from the side pane and then select Create Credentials. Select the OAuth Client ID option.
- Select Web Application as the Application Type.
- Under Authorized redirect URI's, select Add URI and then add the URI
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/googlecalendar/callbackand<Cal.com URL>/api/auth/callback/googlereplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - The key will be created and you will be redirected back to the Credentials page. Select the newly generated client ID under OAuth 2.0 Client IDs.
- Select Download JSON. Copy the contents of this file and paste the entire JSON string in the .env file as the value for GOOGLE_API_CREDENTIALS key.
After adding Google credentials, you can now Google Calendar App to the app store. You can repopulate the App store by running
cd packages/prisma
yarn seed-app-store
You will need to complete a few more steps to activate Google Calendar App. Make sure to complete section "Obtaining the Google API Credentials". After the do the following
- Add extra redirect URL
<Cal.com URL>/api/auth/callback/google - Under 'OAuth concent screen', click "PUBLISH APP"
- Open Azure App Registration and select New registration
- Name your application
- Set Who can use this application or access this API? to Accounts in any organizational directory (Any Azure AD directory - Multitenant)
- Set the Web redirect URI to
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/office365calendar/callbackreplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - Use Application (client) ID as the MS_GRAPH_CLIENT_ID attribute value in .env
- Click Certificates & secrets create a new client secret and use the value as the MS_GRAPH_CLIENT_SECRET attribute
- Open Zoom Marketplace and sign in with your Zoom account.
- On the upper right, click "Develop" => "Build App".
- On "OAuth", select "Create".
- Name your App.
- Choose "User-managed app" as the app type.
- De-select the option to publish the app on the Zoom App Marketplace.
- Click "Create".
- Now copy the Client ID and Client Secret to your .env file into the
ZOOM_CLIENT_IDandZOOM_CLIENT_SECRETfields. - Set the Redirect URL for OAuth
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/zoomvideo/callbackreplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - Also add the redirect URL given above as a allow list URL and enable "Subdomain check". Make sure, it says "saved" below the form.
- You don't need to provide basic information about your app. Instead click at "Scopes" and then at "+ Add Scopes". On the left, click the category "Meeting" and check the scope
meeting:write. - Click "Done".
- You're good to go. Now you can easily add your Zoom integration in the Cal.com settings.
- Open Daily and sign into your account.
- From within your dashboard, go to the developers tab.
- Copy your API key.
- Now paste the API key to your .env file into the
DAILY_API_KEYfield in your .env file. - If you have the Daily Scale Plan set the
DAILY_SCALE_PLANvariable totruein order to use features like video recording.
- Open HubSpot Developer and sign into your account, or create a new one.
- From within the home of the Developer account page, go to "Manage apps".
- Click "Create app" button top right.
- Fill in any information you want in the "App info" tab
- Go to tab "Auth"
- Now copy the Client ID and Client Secret to your .env file into the
HUBSPOT_CLIENT_IDandHUBSPOT_CLIENT_SECRETfields. - Set the Redirect URL for OAuth
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/hubspot/callbackreplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - In the "Scopes" section at the bottom of the page, make sure you select "Read" and "Write" for scope called
crm.objects.contacts - Click the "Save" button at the bottom footer.
- You're good to go. Now you can see any booking in Cal.com created as a meeting in HubSpot for your contacts.
- Create a SendGrid account (https://signup.sendgrid.com/)
- Go to Settings -> API keys and create an API key
- Copy API key to your .env file into the SENDGRID_API_KEY field
- Go to Settings -> Sender Authentication and verify a single sender
- Copy the verified E-Mail to your .env file into the SENDGRID_EMAIL field
- Add your custom sender name to the .env file into the NEXT_PUBLIC_SENDGRID_SENDER_NAME field (fallback is Cal.com)
- Create a Twilio account (https://www.twilio.com/try-twilio)
- Click ‘Get a Twilio phone number’
- Copy Account SID to your .env file into the TWILIO_SID field
- Copy Auth Token to your .env file into the TWILIO_TOKEN field
- Copy your Twilio phone number to your .env file into the TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBER field
- Add your own sender id to the .env file into the NEXT_PUBLIC_SENDER_ID field (fallback is Cal)
- Create a messaging service (Develop -> Messaging -> Services)
- Choose any name for the messaging service
- Click 'Add Senders'
- Choose phone number as sender type
- Add the listed phone number
- Leave all other fields as they are
- Complete setup and click ‘View my new Messaging Service’
- Copy Messaging Service SID to your .env file into the TWILIO_MESSAGING_SID field
- Create a verify service
- Copy Verify Service SID to your .env file into the TWILIO_VERIFY_SID field
Distributed under the AGPLv3 License. See LICENSE for more information.
Special thanks to these amazing projects which help power Cal.com:
Cal.com is an open startup and Jitsu (an open-source Segment alternative) helps us to track most of the usage metrics.