To setup the real go1 robot to train with our codebase, you need to have a Unitree Go1 EDU robot. Install Ubuntu 18.02 LTS on your arm/x86_64 computer (20.02 LTS might work but we have not tested it).
Please note that due to changes in libc / underlying kernel ABI and the fact that Unitree's sdk is statically linked, you need to make sure the versions of your OS match the one we used.
Now plug in an ethernet (RJ45) cable from your computer to the robot. You can also opt to connect to the onboard wifi of the robot, but fro our experience the WiFi connection brings a lot of latency (and sometimes even packet loss) which makes the robot unstable.
Then attach an Intel Realsense T265 to anywhere on the robot (we recommend the neck because that's the only place where the legs won't hit) and connect it via a long usb cable to your computer. Make sure that the camera can see some visual features to perform visual odomentry.
Depending on the orientation of which the T265 camera is mounted, you will need to navigate into rail_walker_gym/envs/register_real.py and change the lines where we initialized the IntelRealsenseT265Estimator class.
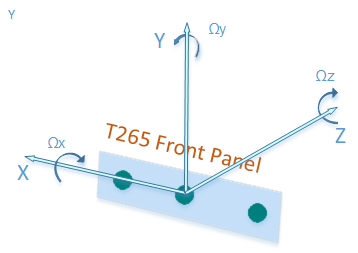
Above is an image explaining the coordinate system of original Intel T265 camera. In the code we will need to transform the local coordinate movements of the T265 camera into the local coordinate movements of the robot body. The robot body's local coordinate frame is defined as X-forward, Y-left, Z-up, and to do that you can simply change the parameters initializing the IntelRealsenseT265Estimator class by specifying the local coordinate vector (in the robot coordinate frame) of the T265's X, Y, Z axis.
Then simply execute the training script to start training / evaluating.