Current repository is used for feature generation and experiment evaluation system. Generated results are being used in a research inspired by RANLP'19 conference.
If you plan to continue research on top of this or to reproduce, please check Quick Start in docs.
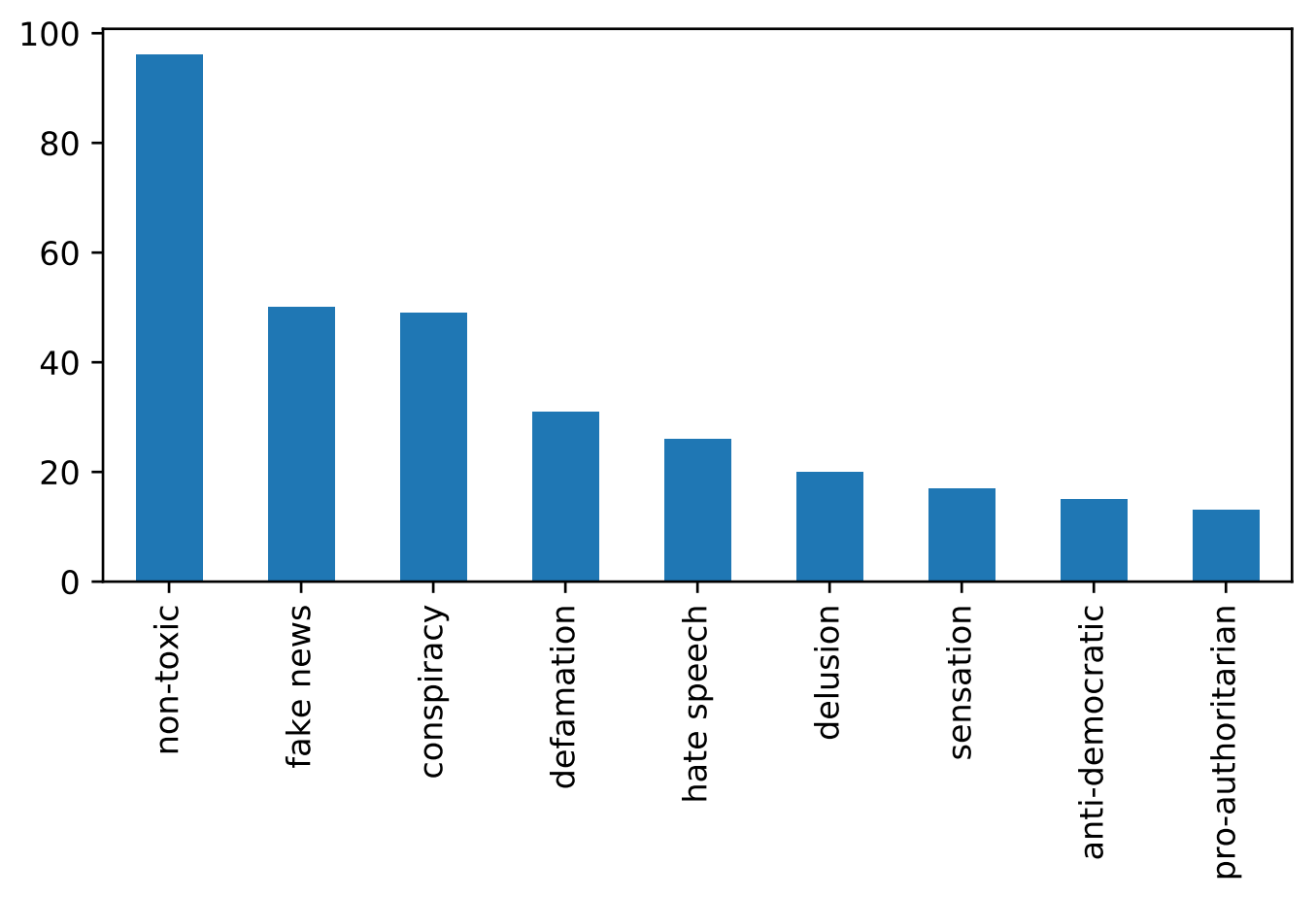
Contains 221 articles, manually labelled by Krasimir Gadjokov between 2011-2017. As well as 96 non-toxic articles fetched from credible bulgarian news outlets in 2019. To incorporate even more features we use Google API for articles translation. Each article is available in both english and bulgarian.
Toxicity categories are as follows (examples are in Bulgarian):
| Category | Example |
|---|---|
| fake news (фалшиви новини) | click here |
| defamation (клевета) | click here |
| sensation (сензация) | click here |
| hate speech (реч на омраза) | click here |
| delusion (заблуда) | click here |
| conspiracy (конспирация) | click here |
| anti-democratic (анти-демократичен) | click here |
| pro-authoritarian (про-авториратерен) | click here |
| non-toxic (нетоксичен) | click here |
Labels' source of truth: https://mediascan.gadjokov.com/
Dataset can be downloaded from here.
Detailed information about dataset, can be found in docs.
We have generated following feature sets for both English and Bulgarian:
| Language | Feature set | Title | Text |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulgarian | BERT | 768 | 768 |
| Bulgarian | LSA | 15 | 200 |
| Bulgarian | Stylometry | 19 | 6 |
| Bulgarian | XLM | 1024 | 1024 |
| English | BERT | 768 | 768 |
| English | ELMO | 1024 | 1024 |
| English | NELA | 129 | 129 |
| English | USE | 512 | 512 |
| - | Media | 6 |
We have conducted experiments by combinding different feature sets, as well as introducing a meta classification. Meta classification is based on posterior probablities of other experiments result. For each experiment setup we use fine-tuned LogisticRegression. Provided results are avaraged after 5-fold experiment split.
| Language | Feature set | Accuracy | F1-macro |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | Baseline | 30.30 | 05.17 |
| Bulgarian | BERT(title), BERT(text) | 47.69 | 32.58 |
| Bulgarian | XLM(title), XLM (text) | 38.50 | 24.58 |
| Bulgarian | Styl(title), Styl(text) | 31.89 | 08.51 |
| Bulgarian | LSA(title), LSA(text) | 55.59 | 42.11 |
| Bulgarian | Bulgarian combined | 39.43 | 24.38 |
| English | USE(title), USE(text) | 53.70 | 40.68 |
| English | NELA(title), NELA(text) | 36.36 | 23.04 |
| English | BERT(title), BERT(text) | 52.05 | 39.78 |
| English | ELMO(title), ELMO(text) | 54.60 | 40.95 |
| English | English combined | 42.04 | 15.64 |
| - | Media meta | 42.04 | 15.64 |
| - | All combined | 38.16 | 26.04 |
| - | Meta classifier | 59.06 | 39.70 |
Please cite [1] if you found the resources in this repository useful.
[1] Y Dinkov, I Koychev, P Nakov Detecting Toxicity in News Articles: Application to Bulgarian
@article{dinkov2019detecting,
title={Detecting Toxicity in News Articles: Application to Bulgarian},
author={Dinkov, Yoan and Koychev, Ivan and Nakov, Preslav},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.09785},
year={2019}
}
This research is part of the Tanbih project, which aims to limit the effect of "fake news", propaganda and media bias by making users aware of what they are reading. The project is developed in collaboration between the Qatar Computing Research Institute (QCRI), HBKU and the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL).
This research is also partially supported by Project UNITe BG05M2OP001-1.001-0004 funded by the OP "Science and Education for Smart Growth" and the EU via the ESI Funds.