Required :
- netdb.h
- netinet/in.h
- sys/socket.h
The above mentioned header files are required by the compiler to compile the code for the tcp\ip implementation!
Live implementation of project click here
Source code for site click here
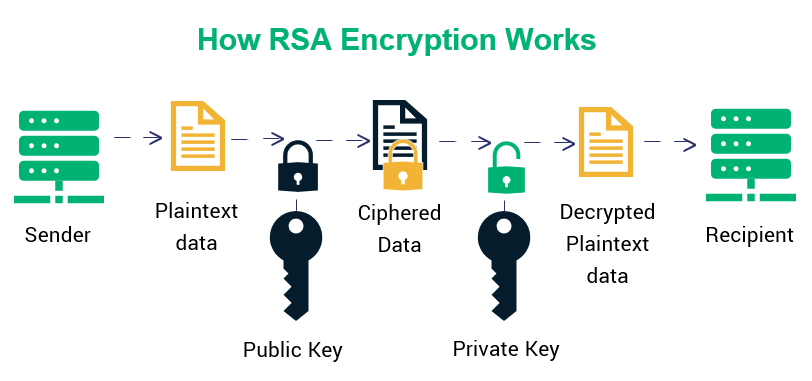
Encryption is the process of scrambling or enciphering data so it can be read only by someone with the means to return it to its original state. It is a crucial feature of a safe and trustworthy Internet. It helps provide data security for sensitive information.
Two main types of data encryption exist - asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, and symmetric encryption.
In this article we are going to implement asymmetric encryption using RSA algorithm.
This type of encryption uses two separate keys for encryption and decryption — a public key and a private key.
The public key can be given to anyone, trusted or not, while the private key must be kept secret.Eg:Diffie-Hellman key exchange , RSA
Diffie-Hellman key exchangeis used by whatsapp to exchange keys forend to end encryption.
RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) is a public-key cryptosystem that is widely used for secure data transmission. The acronym RSA comes from the surnames of Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman, who publicly described the algorithm in 1977.
The security of RSA relies on the practical difficulty of factoring the product of two large prime numbers
It is based on the principle that it is easy to multiply large prime numbers, but factoring large numbers is very difficult even for most powerful computers. For example, it is easy to check that 31 and 37 multiply to 1147, but trying to find the factors of 1147 is a much longer process.
Don't believe? Ok Can you please factorize 1522605027922533360535618378132637429718068114961380688657908494580122963258952897654000350692006139 ???
The RSA algorithm is named after those who invented it in 1978: Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman.
RSA algoritm is implemented in the following steps.
-
The generation of public and private key in RSA involves following steps:
-
At first select two large prime numbers (more than 100 digits)
p1andp2. -
Calculate modulo(n) :
n = p1 * p2 -
Calculate the totient function:
ϕ(n) = (p1−1) (p2−1).
Thetotient functiongives the number of numbers that are coprime tomodulo(n).
Two numbers are
coprimeif their HCF is 1. Example : 5 and 6 arecoprime.-
Select an integer
esuch that is coprime tototient function (ϕ(n))and1 < e < ϕ(n).
The pair(e,n)now serves as public key. -
The private key
(d)should be calculated such thatd.e = 1 mod ϕ(n).
Mathematically ,dcan be calculated using the formula :
where we increase the value of i till d comes out as integer. The pair `(d,n)` now serves as private key.d = (i * ϕ(n) + 1) / 2>The value of `d` can also be found using [`extended euclidean algorithm`](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extended_Euclidean_algorithm) -
Example: For the sake of calculation, we have taken two digit prime numbers.
int x = 61, int y = 53;
int n = x * y;
// n = 3233.
// compute the totient, phifunction
int phifunction = (x-1)*(y-1);
// phifunction = 3120.
int e = findCoprime(phifunction);
// find an 'e' which is > 1 and is a co-prime of phifunction.
// e = 17 satisfies the current values.since 17 and 3120 have no common factor except 1.
int i=1,d;
while(i){
d = (phifunction*i+1)/e;
if(e*d==(phifunction*i+1)){
i=0;
break;
}
// printf("%d \n",i);
i++;
}
// d = 2753 for the example values.
typedef struct public_keys{
long int e;
long int n;
}public_keys;
public_keys.e = 17;
public_keys.n = 3232;
typedef struct private_keys{
long int d;
long int n;
}private_keys;
private_keys.d = 17;
private_keys.n = 3232;
// Given the plaintext P=123, the ciphertext C is :
C = (123^17) % 3233 = 855;
// To decrypt the cypher text C:
P = (855^2753) % 3233 = 123;-
Now the pubic key(e,n) is used for encryption.Given any text , we first convert the text into [`ASCII`](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ASCII) and each ASCII code is encrypted using public key(e,n) as below:
Given a plaintext P, represented as an ASCII , the ciphertext C is calculated as:
then the encrypted number C is converted into character.
C = pow(P,e) mod n//let 123 is the number we get after converting plain Text into ASCII C = (123^17) % 3233 = 855; // 855 is encrypted which can be decrypted only using the private key before
-
Now the private key(d,n) is used for decryption.Given the encrypted number , we first decrypt the number into equivalent [`ASCII`](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ASCII) and then convert into equivalent character(which is the required character).
Given a plaintext P, represented as an ASCII , the ciphertext C is calculated as:
then the encrypted number C is converted into character.
P= pow(C,d) mod n// To decrypt the cypher text C=855: P = (855^2753) % 3233 = 123; // finally 855 is decrypted into 123
🔴 RSA in a nutshell
-
RSA is used in hybrid encryption and digital signature.
-
Bank uses RSA to protect data such as costumer information and transactions record.
-
In e-commerce, RSA is useful to encrypt user identity in transaction.
🔴 RSA is used in SSL
-
RSA is so secure and strong that A compiuter took almost 4 hours to factorize the number I previously asked you to facorize see here .
to surprise , to bruteforce 2048 0r 4096 bit RSA key , even the most powerful computers as of now will take time more than the age of the universe.And dont count on the cost even to start the bruteforce. Yep, I amnot kidding !
-
RSA overcomes the weakness of symmetric algorithm i.e. authenticity and confidentiality.
-
Using small prime numbers to generate public and private key isnot convincing as it will be almost effortless to bruteforce.
What makes RSA great is that it cannot be bruteforced despite knowing how to bruteforce it
-
RSA scores high in slowness compared to other encryption systems. It is not convenient then to use it to encrypt a whole file.
-
It is estimated that there is very high possibility of bruteforcing of RSA by Quantum Computer in the near future.