Linked list structures leverage the EUTXO model to enhancing scalability and throughput significantly. By linking multiple UTXOs together through a series of minting policies and validators, it can improve the user experience interacting with smart contract concurrently.
This project is funded by the Cardano Treasury in Catalyst Fund 10 and is aimed at enhancing the capabilities of Cardano smart contracts in handling complex data structures.
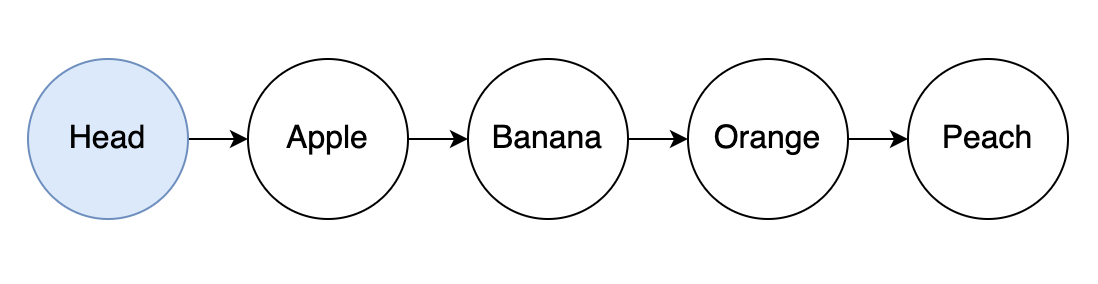
The Aiken Linked List is an on-chain, sorted linked list solution designed for blockchain environments, specifically utilizing NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) and datums. It provides a structured and efficient way to store and manipulate a list of key/value pairs on-chain.
Each entry in the list comprises:
- NFT: A unique identifier for each entry.
- EntryDatum: A data structure containing the key/value pair, a reference to the entry's NFT, and a pointer to the next NFT in the list.
data EntryDatum = EntryDatum {
key :: BuiltinByteString,
value :: Maybe SomeValue,
nft :: NFT,
next :: Maybe NFT
}- key: A unique identifier for the entry.
- value: The value associated with the key. It can be Nothing for the head entry.
- nft: The NFT representing the entry.
- next: The NFT of the next entry in the list, or Nothing for the last entry.
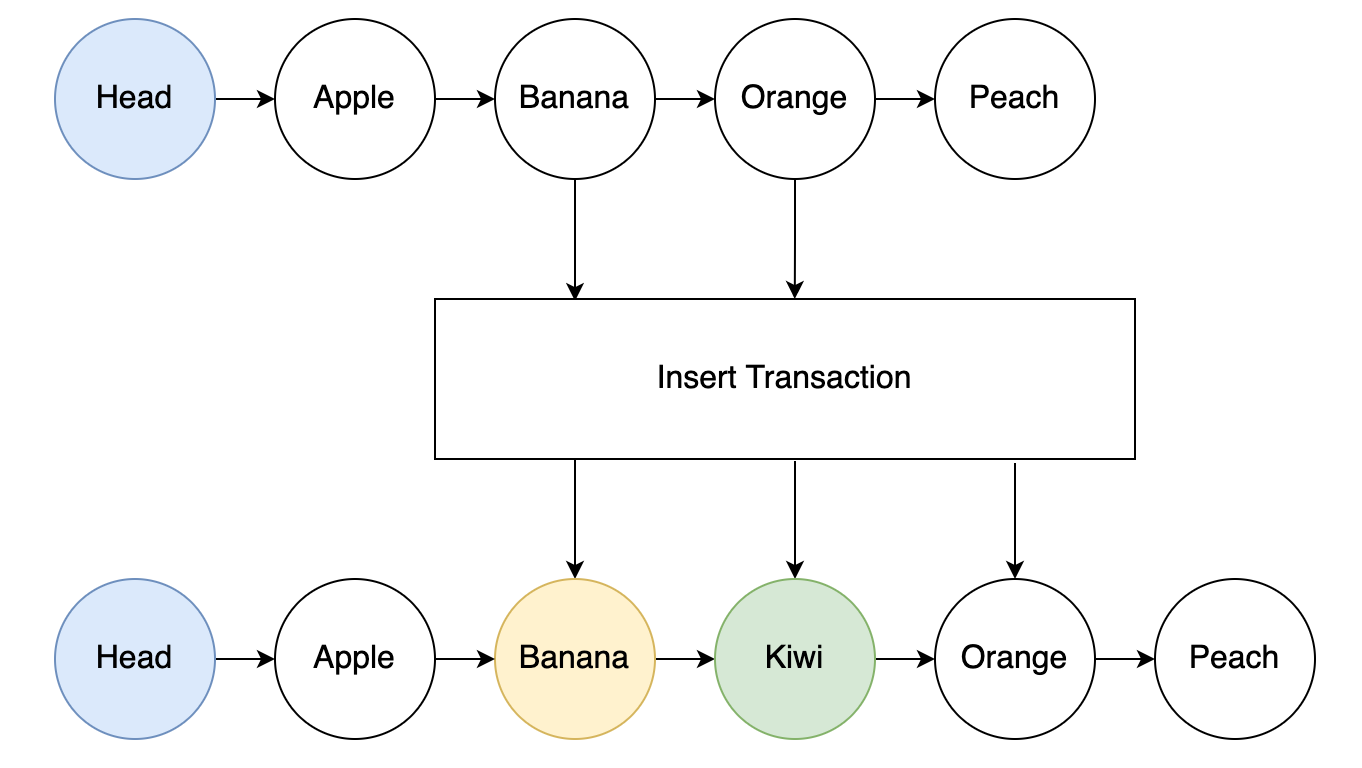
Insertion involves:
- Inputs: Two adjacent list entries.
- Outputs:
- The first input entry, modified to point to the new entry.
- The newly inserted entry, pointing to the second input entry.
- The second input entry, unchanged.
Validation Rules
- Keys must maintain the order: a < b < c, where a is the lowest, b is the new key, and c is the highest.
- The pointers must be correctly updated to maintain list integrity.
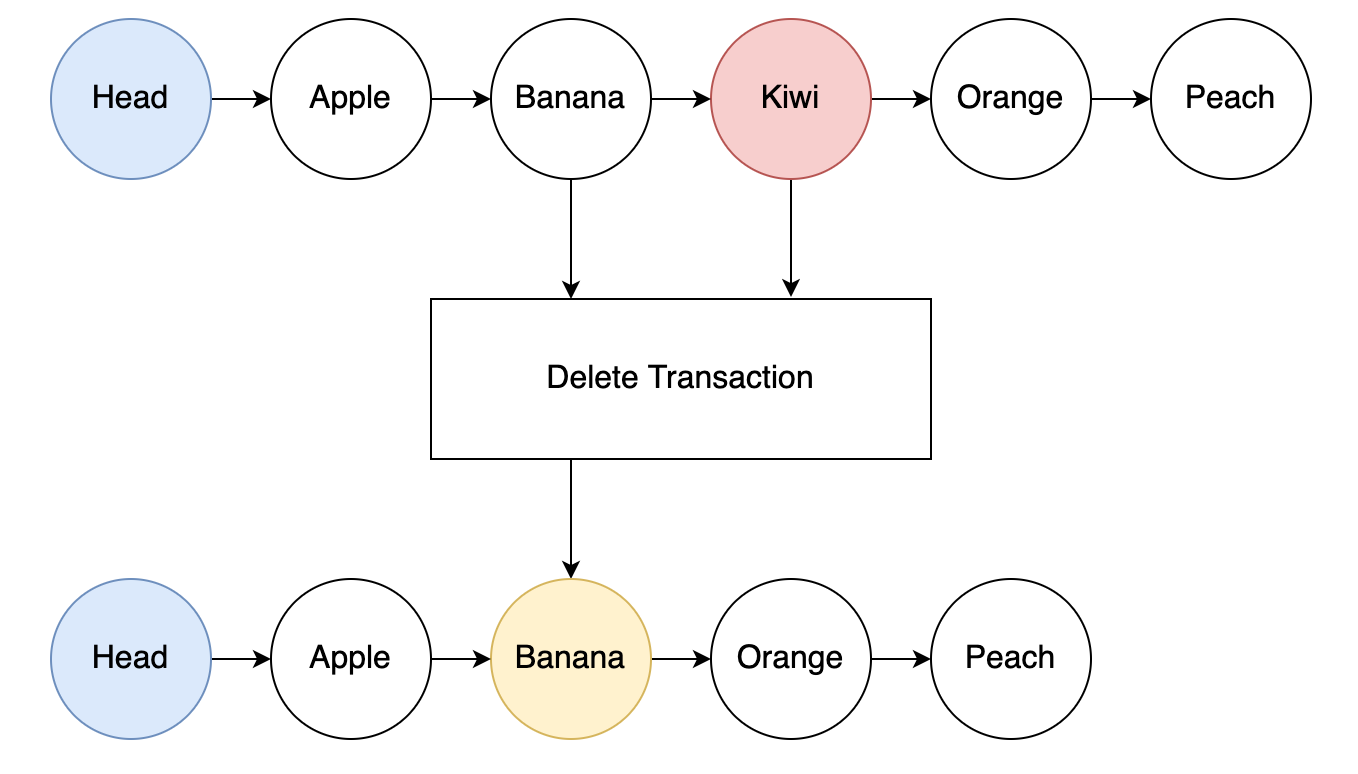
To remove an entry:
- Inputs: The entry to remove and its preceding entry.
- Output: The preceding entry is modified to point to what the removed entry was pointing to.
NFTs serve as robust and unique pointers within the list. Their uniqueness is ensured by a specific minting policy related to the list's head NFT.
- Efficiency: As on-chain lookups are inefficient, off-chain structures are recommended for this purpose.
- Datum Hashes: Not suitable for pointers due to the complexity of updates and security concerns.
- Security: The integrity of the list is maintained through careful minting policies and entry validation.
- Forwarding Minting Policy: A feature of Plutus to control NFT minting dynamically.
- List Head: Utilizes an empty head entry for validating insertions at the start of the list.
- End-of-List Insertions: Handled by ensuring the last entry points to Nothing.
The Aiken Linked List implementation provides several functions to create and manipulate Linked List. Below is a brief overview of each function:
init: Constructs the Linked List headdeinit: Destructs the Linked Listinsert: Inserts a node into the linked listremove: Removes a node from the linked list
Before you begin, ensure you have aiken installed on your system.
Once Aiken is installed, you should be able to seamlessly use the repository to develop, build and run packages.
Download the Git repository:
git clone https://github.com/Anastasia-Labs/aiken-linked-list.gitNavigate to the repository directory:
cd aiken-linked-listExecute the test suite:
aiken checkBuild:
aiken buildFor a complete example, including tests and further explanations, reger to the provided sample validator: sample.ak.
Linked list can be leveraged in smart contract applications where the order of inputs is not crucial, and multiple users can interact with the contracts simultaneously. For example, consider a decentralized voting system where users can cast their votes concurrently. A linked list data structure can be employed to store and manage the votes efficiently. Each user's vote can be represented as a node in the linked list, containing relevant information such as the user's address and their chosen candidate.
This documentation and the implementation of the Aiken Linked List draw inspiration from an original idea presented in the Plutonomicon. We acknowledge the innovative concepts and approaches outlined in their work, specifically regarding associative data structures on blockchain platforms.
For further details on the foundational ideas and their context, please refer to the Plutonomicon's overview of associative data structures: Plutonomicon's Associative Data Structures Overview.
We express our gratitude to the creators and contributors of the Plutonomicon for their pioneering work in this area, which has significantly influenced the development of our Aiken Linked List.