-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 337
Client Applications in MSAL 1.x
This page is for an older MSAL.NET version. See Public client and confidential client applications for updated documentation.
Contrary to ADAL.NET (which proposes the notion of AuthenticationContext, which is a connection to Azure AD), MSAL.NET, proposes a clean separation between public client applications, and confidential client applications:
- Confidential client applications are typically applications which run on servers (Web Apps, Web API, or even service/daemon applications). They are considered difficult to access, and therefore capable of keeping an application secret. Confidential clients are able to hold configuration time secrets. Each instance of the client has a distinct configuration (including clientId and secret). These values are difficult for end users to extract. A web app is the most common confidential client. The clientId is exposed through the web browser, but the secret is passed only in the back channel and never directly exposed.
- On the contrary public client applications are typically applications which run on devices (phones for instance) or desktop machines. They are not trusted to safely keep application secrets, and therefore access Web APIs in the name of the user only (they only support public client flows). Public clients are unable to hold configuration time secrets, and as a result have no client secret
MSAL.NET defines IPublicClientApplication interfaces for public client and IConfidentialClientApplication for confidential client applications, as well as a base interface IClientApplicationBase for the contract common to both types of applications.
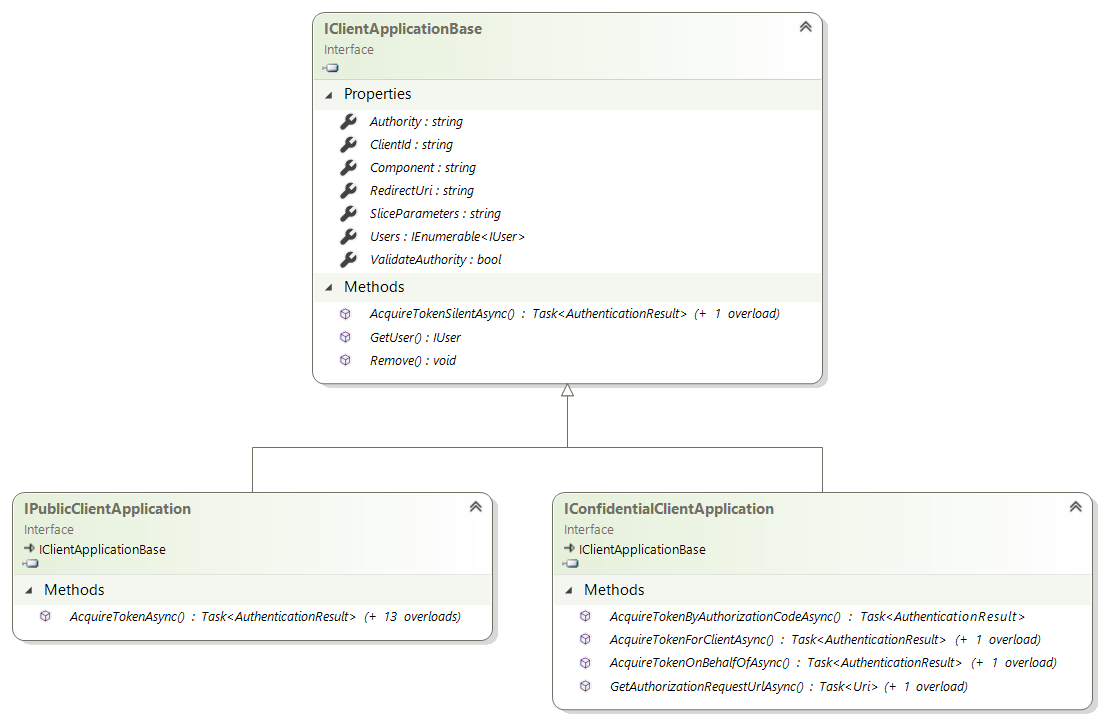
It's immediately obvious that:
-
Both kinds of applications can acquire a token silently (in case the token is already in the token cache)
-
Public client applications have many ways of acquiring a token. Most involve a UI, which can be controlled by the application developer.
There are two special public client application flows, which don't present a UI in a web control but these flows are not yet implemented in MSAL / the v2.0 endpoint. These are:
- Device Code Flow, which is for devices which are not capable of displaying a web page but are limited to displaying text
- Username / password flow (where no UI is presented)
-
Confidential client applications, on the other hand, don't have methods to acquire tokens interactively. Instead, they support the following grants:
- Client credential, which is used when the service wants to call another service with no user - here it's important to understand that the client is the application. It's not a user
- On behalf of flow, which is used when services want to call another service in the name of a user, which credentials were passed in some way, usually a token.
-
The application also manages users. It's possible to get a user from its identifier, and to remove a user (of course user management does not make sense in the client credential case)
Contrary to ADAL.NET's Authentication context, the clientID (also named applicationID or appId) is passed once at the construction of the Application, and no longer needs to be repeated when acquiring a token. This is the case both for a public and a confidential client application. Constructors of confidential client applications are also passed client credentials.

the application developer can also provide
- the authority:
- The default value for authority is the value of the
DefaultAuthoritystatic member that is "https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/". Azure AD v2.0 applications are multi-tenant by default. - It's always possible for the application developer to target a specific tenant for a line of business application.
- It's also possible to target a more specific category of users (such as only business or only personal accounts). For this, the authority will need to be
- https://login.microsoftonline.com/organizations/ for businesses (read Azure AD accounts). Interestingly using /organizations in MSAL targets the same accounts than using /common with ADAL (as the Azure AD v1.0 endpoint is only about Azure AD accounts)
- https://login.microsoftonline.com/consumers/ for personal accounts (read MSA)
- The default value for authority is the value of the
- a token cache that s/he would have de-serialized.
For public client applications developers using MSAL.NET:
- don't need to pass the
RedirectUrias its automatically computed by MSAL.NET. This RedirectUri is set to the following values depending on the platform:-
urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oobfor all the Windows platforms -
msal{ClientId}://authfor Xamarin Android and iOS
-
However, it is possible to override the Redirect Uri using the PublicClientApplication RedirectUri property for instance:
RedirectUriOnAndroid = "msauth-5a434691-ccb2-4fd1-b97b-b64bcfbc03fc://com.microsoft.identity.client.sample";
RedirectUriOnIos = "adaliosxformsapp://com.yourcompany.xformsapp";
- still have the possibility of bypassing the authority validation by setting the
ValidateAuthorityproperty of the application tofalse. Note that the validation is not done in the constructor, but the first time an interaction with the STS is required (for instance the first time the developer tries to acquire a token). - The valid authorities are the same as presented [Authority validation], except ADFS authorities which are not supported yet in MSAL.Net
Finally, MSAL
PublicClientApplicationfor WinRT have another boolean property namedUseCorporateNetwork. Its behavior is explained in detail in Properties of PlatformParameter specific to WinRT and UWP.
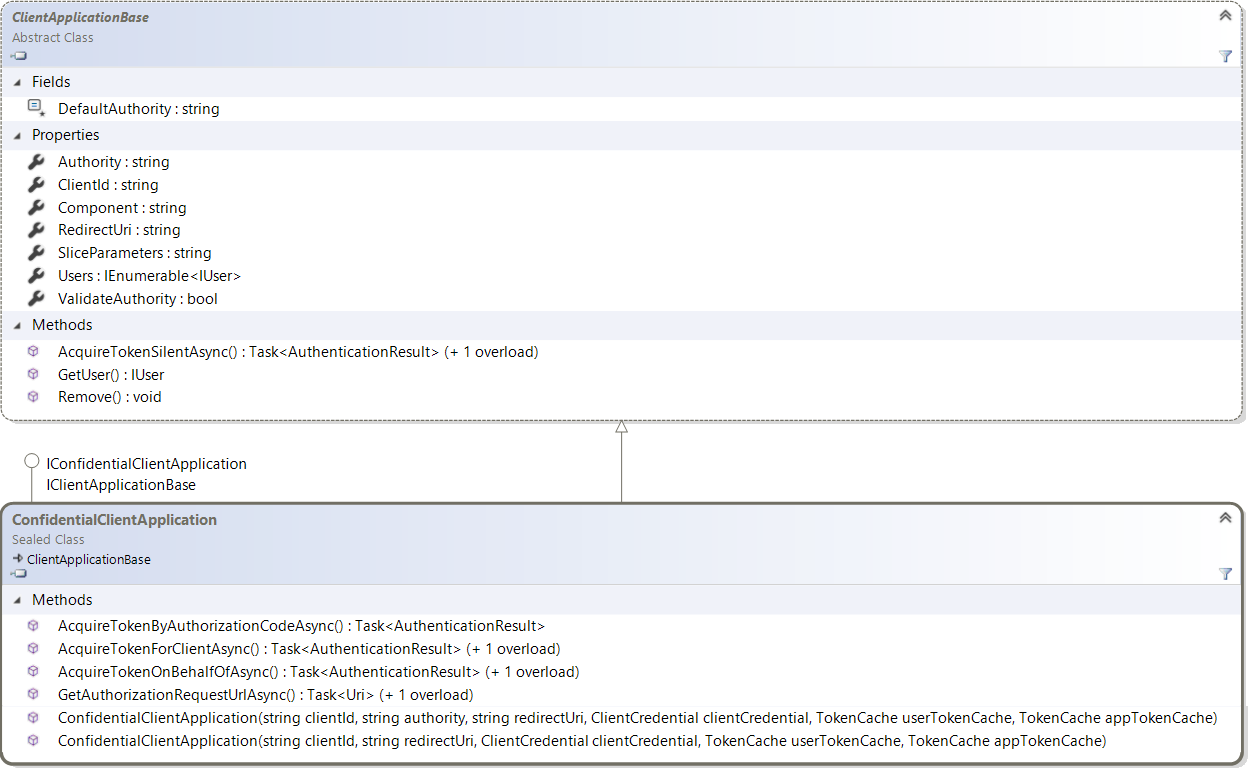
In addition to the ClientId, confidential client application constructors also take:
- A redirect URI (or Reply URI), which is the URI at which Azure AD will contact back the application with the token. This can be the URL of the Web application / Web API if the confidential is one of these. Tip: This redirect URI needs to be registered in the app registration. This is especially important when you deploy an application that you have initially tested locally; you then need to add the reply URL of the deployed application in the application registration portal.
- client credentials of type ClientCredential which represent the application identity (a secret string, or a certificate which public key was shared with Azure AD part of the application registration)

Optionally, the application developer can also provide
- the authority, if he does not want to target the Azure AD common endpoint (which is
DefaultAuthority) - two caches of type TokenCache:
- the user token cache (for the on-behalf-of grant). This is the same cache as in the case of public client applications.
- the application cache, which is only used for the client credential flow where the application acquires tokens in its own name, that is for no user (
AcquireTokenForClientAsync)
Important: don't use the same cache instance for both arguments!
- Home
- Why use MSAL.NET
- Is MSAL.NET right for me
- Scenarios
- Register your app with AAD
- Client applications
- Acquiring tokens
- MSAL samples
- Known Issues
- AcquireTokenInteractive
- WAM - the Windows broker
- .NET Core
- Xamarin Docs
- UWP
- Custom Browser
- Applying an AAD B2C policy
- Integrated Windows Authentication for domain or AAD joined machines
- Username / Password
- Device Code Flow for devices without a Web browser
- ADFS support
- Acquiring a token for the app
- Acquiring a token on behalf of a user in Web APIs
- Acquiring a token by authorization code in Web Apps
- High Availability
- Token cache serialization
- Logging
- Exceptions in MSAL
- Provide your own Httpclient and proxy
- Extensibility Points
- Clearing the cache
- Client Credentials Multi-Tenant guidance
- Performance perspectives
- Differences between ADAL.NET and MSAL.NET Apps
- PowerShell support
- Testing apps that use MSAL
- Experimental Features
- Proof of Possession (PoP) tokens
- Using in Azure functions
- Extract info from WWW-Authenticate headers
- SPA Authorization Code