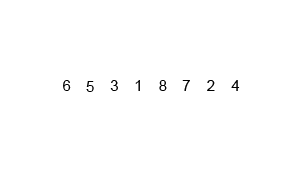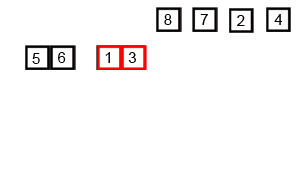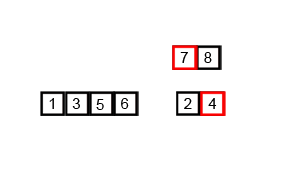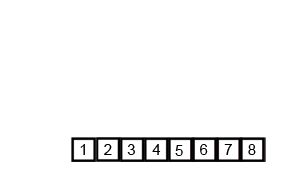Sorting is a skill that every software engineer and developer needs some knowledge of. Not only to pass coding interviews but as a general understanding of programming itself. The different sorting algorithms are a perfect showcase of how algorithm design can have such a strong effect on program complexity, speed, and efficiency.
Selection sort is also quite simple but frequently outperforms bubble sort. If you are choosing between the two, it’s best to just default right to selection sort. With Selection sort, we divide our input list / array into two parts: the sublist of items already sorted and the sublist of items remaining to be sorted that make up the rest of the list. We first find the smallest element in the unsorted sublist and place it at the end of the sorted sublist. Thus, we are continuously grabbing the smallest unsorted element and placing it in sorted order in the sorted sublist. This process continues iteratively until the list is fully sorted.
to see the code open/run Selection_Sort.py Python3 Selection_Sort.py
Insertion sort is both faster and well-arguably more simplistic than both bubble sort and selection sort. Funny enough, it’s how many people sort their cards when playing a card game! On each loop iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the array. It then finds the location where that element belongs within another sorted array and inserts it there. It repeats this process until no input elements remain.
> to see the code open/run Insertion_Sort.py
> Python3 Insertion_Sort.py
Merge sort is a perfectly elegant example of a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It simple uses the 2 main steps of such an algorithm:
(1) Continuously divide the unsorted list until you have N sublists, where each sublist has 1 element that is “unsorted” and N is the number of elements in the original array.
(2) Repeatedly merge i.e conquer the sublists together 2 at a time to produce new sorted sublists until all elements have been fully merged into a single sorted array.
> to see the code open/run Merge_Sort.py > Python3 Merge_Sort.py
Like Merge Sort, QuickSort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It picks an element as pivot and partitions the given array around the picked pivot. There are many different versions of quickSort that pick pivot in different ways.
- Always pick first element as pivot.
- Always pick last element as pivot (implemented below)
- Pick a random element as pivot.
- Pick median as pivot.
The key process in quickSort is partition(). Target of partitions is, given an array and an element x of array as pivot, put x at its correct position in sorted array and put all smaller elements (smaller than x) before x, and put all greater elements (greater than x) after x. All this should be done in linear time.
> to see the code open/run Quick_Sort.py > Python3 Quick_Sort.py