This repository contains Torch implementation of MeshNet architecture. MeshNet is volumetric convolutional neural network based on dilated kernels [1] for image segmentation. Model has been trained for brain tissue segmentation from imperfect labeling obtained using FreeSurfer automatic approach. The repository also contains weights of trained model with volumetric dropout for gray and white matter.
Brain Atlas segmentation with brainchop.org
To get brain atlas segmentation (https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.00457 extension of this work) you don't need to run any code. Just sign up at brainchop.org, upload your 3T MRI T1 image and get brain atlas in 1-2 minutes.
Watch video with example of brain atlas segmentation.
The repository has following structure:
- ./models/
Contains code for Deep Neural network architectures
- vdp_model.lua MeshNet model with volumetric dropout
- nodp_model.lua MeshNet model without volumetric dropout
- ./saved_models/
Contains saved weights and csv with train and validation loss during training
- ./model_Mon_Jul_10_16:43:55_2017/
best weights and loss logs for ../models/vdp_model.lua
- ./model_Mon_Jul_10_16:43:55_2017/
- train.lua
Torch Lua code for training models - metrics.lua
Torch Lua code for calculating F1 (equivalent to DICE score) and AVD metrics and for saving prediction. - predict.lua
Torch Lua code to predict segmentation given data and model - utils.lua
Torch Lua code for utility functions. - train.sh
Example bash script for model training using train.lua. - metrics.sh
Example bash script for calculating metrics using metrics.lua. - predict.sh
Example bash script to create prediction using predict.lua. - mklabels.sh
Bash script to prepare data and labels to numpy format from Human Connectome Project [3]. (IMPORTANT: labels have been fixed after expert review) - train_fold.txt
Training fold with 20 subjects - valid_fold.txt
Validation fold with 2 subjects - npy2nifti.py
Python script to convert volume from numpy to nifti format (Uses python nipy http://nipy.org/ and numpy http://www.numpy.org/ libraries) - nifti2npy.py
Python script to convert volume from nifti to numpy format (Uses python nipy http://nipy.org/ and numpy http://www.numpy.org/ libraries)
Model has been trained on 20 subjects T1 3T MRI images with slice thickness 1mm x 1mm x 1mm (256 x 256 x 256) from Human Connectome Project [3] and validated on 2 subjects during training. More details about the training process are published at IJCNN 2017 and described in a more up to date paper [2]. IMPORTANT: model on github uses Volumetric Dropout instead of 1D Dropout (due to significant improvements). One epoch consists of 2048 subvolumes with size 68 x 68 x 68 and validated on same amount of subvolumes. Model is 219 epoch old.
Code is written on Lua using Torch deep learning library (http://torch.ch/). Additional packages are required: torch-randomkit (https://github.com/deepmind/torch-randomkit), npy4th (https://github.com/htwaijry/npy4th), torch-dataframe (https://github.com/AlexMili/torch-dataframe), csvigo (https://github.com/clementfarabet/lua---csv), torch-distributions (http://deepmind.github.io/torch-distributions/).
Model has been trained using NVIDIA Titan X (Pascal) with 12 GB. Model is using 9817 MB of GPU memory during training with batch size 1. Train time is about 3-4 days.
- You can skip this step if your T1 image with slice thickness 1mm x 1mm x 1mm and 256 x 256 x 256. Using mri_convert from FreeSurfer (https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/) conform T1 to 1mm voxel size in coronal slice direction with side length 256.
mri_convert *brainDir*/t1.nii *brainDir*/t1_c.nii -c
- Convert nifti to numpy format
python nifti2npy.py *brainDir*/t1_c.nii --npy_file *brainDir*/T1.npy
- Create segmentation using predict.lua providing path to directory with brain npy file brainDir
th predict.lua -modelFile ./saved_models/model_Mon_Jul_10_16:43:55_2017/model_219.t7 -brainPath *brainDir*
- Convert numpy segmentation file to nifti format by providing base nifti file
python npy2nifti.py segmentation.npy t1_c.nii
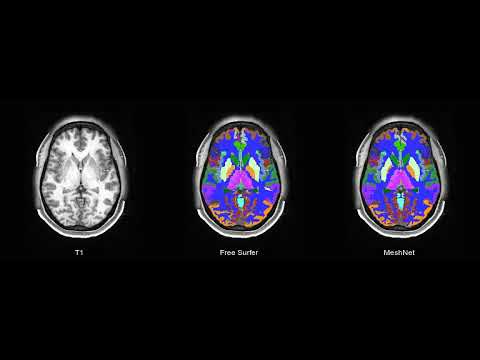
| T1 MRI | FreeSurfer | MeshNet |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[1] https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07122 Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions. Fisher Yu, Vladlen Koltun
[2] https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.00940 End-to-end learning of brain tissue segmentation from imperfect labeling. Alex Fedorov, Jeremy Johnson, Eswar Damaraju, Alexei Ozerin, Vince D. Calhoun, Sergey M. Plis
[3] http://www.humanconnectomeproject.org/ Human Connectome Project
This work was supported by NSF IIS-1318759 & NIH R01EB006841 grants. Data were provided [in part] by the Human Connectome Project, WU-Minn Consortium (Principal Investigators: David Van Essen and Kamil Ugurbil; 1U54MH091657) funded by the 16 NIH Institutes and Centers that support the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research; and by the McDonnell Center for Systems Neuroscience at Washington University.
You can ask any questions about implementation and training by sending message to afedorov@mrn.org.