Authors: Julien Aimonier-Davat (LS2N), Hala Skaf-Molli (LS2N), and Pascal Molli (LS2N)
Abstract SPARQL property path queries allow to write sophisticated navigational queries on knowledge graphs (KG). However, the evaluation of these queries on online KGs are often interrupted by fair use policies, returning only partial results. SaGe-Path addresses this issue by relying on the concept of Partial Transitive Closure (PTC). Under PTC, the exploration depth of a SPARQL property path query is limited to a predefined depth. When the depth limit is reached, frontier nodes are returned. A PTC-client is then able to reuse frontier nodes to continue the exploration of the graph. In this way, SaGe-Path follows a pay-as-you-go approach to evaluate SPARQL property path queries.
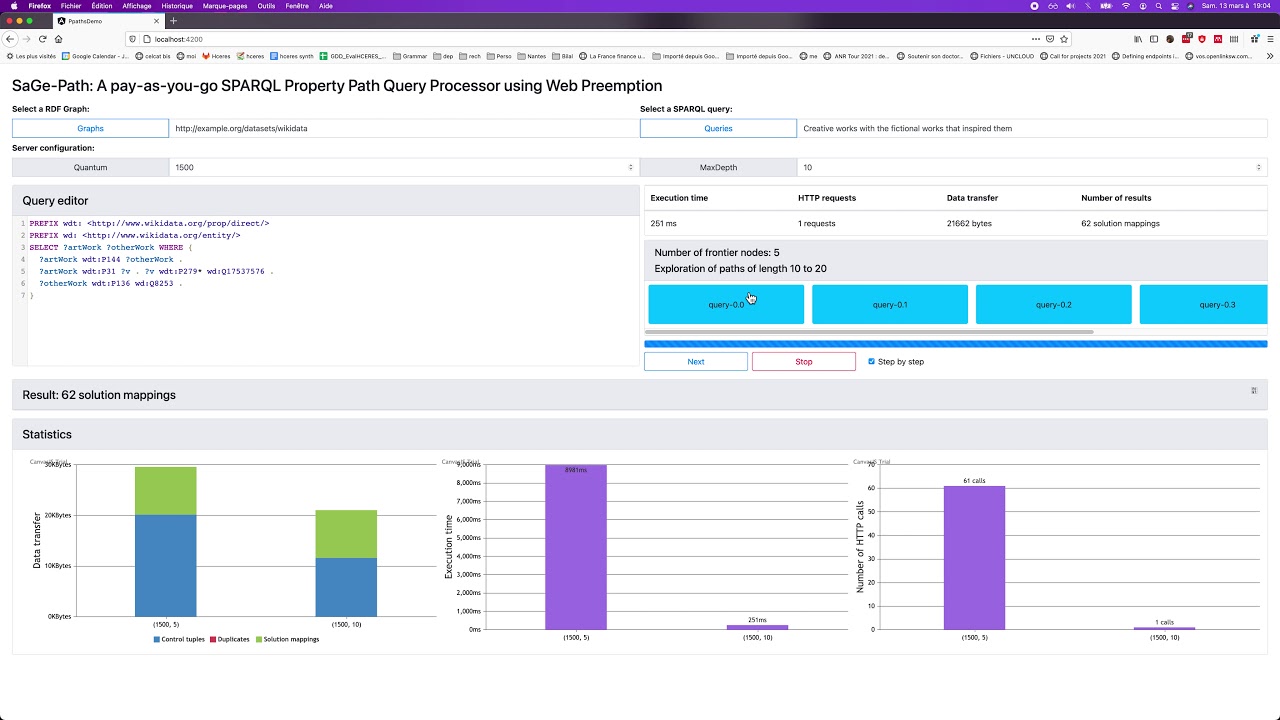
This demonstration shows how queries that do not complete on the public Wikidata SPARQL endpoint can complete using SaGe-Path. An extended user-interface provides real-time visualization of all SaGe-Path internals, allowing to understand overheads, and the effects of different parameters on performance. SaGe-Path demonstrates how complex SPARQL property path queries can be efficiently evaluated online with garanteed complete results.
- Python 3.7 (or higher)
- pip
- Virtualenv
- gcc/clang with c++11 support
- Python Development headers
You should have the
Python.hheader available on your system.
For example, for Python 3.6, install thepython3.6-devpackage on Debian/Ubuntu systems.
# Download the SaGe server and move to the ppaths-demo branch
git clone https://github.com/sage-org/sage-engine
cd sage-engine
git checkout ppaths-demo
# Create a virtual environment to isolate SaGe dependencies
virtualenv --python=/usr/bin/python3 sage-env
# Activate the virtual environment
source sage-env/bin/activate
# Install SaGe dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install -e .[hdt]To make the installation of SaGe easier, SaGe is installed in a virtual environment.
# To activate the SaGe environment (sage-env)
source sage-env/bin/activate
# To deactivate the SaGe environment
deactivateCreate a directory named datasets at the root of the project. Then, download the two .hdt datasets into the datasets directory.
wget nas.jadserver.fr/thesis/projects/ppaths/datasets/gmark.hdt
wget nas.jadserver.fr/thesis/projects/ppaths/datasets/gmark.ntCreate a config.yaml file at the root of the project with the following content.
quota: 60000
max_depth: 5
max_results: 10000
max_control_tuples: 10000
graphs:
- name: gmark
uri: http://example.org/datasets/gmark
description: Synthetic graph of 10M triples generated with the gMark framework
backend: hdt-file
file: datasets/gmark.hdt
- name: wikidata
uri: http://example.org/datasets/wikidata
description: A dump of the wikidata dataset (2017)
backend: hdt-file
file: datasets/wikidata.hdt# Do not forget to activate the SaGe environment
source sage-env/bin/activate
# Launch the Sage server with 1 worker on port 8080
sage config.yaml -w 1 -p 8080# Download the client interface
git clone https://github.com/JulienDavat/ppaths-demo.git
cd ppaths-demo
# Install the dependencies
npm install
# Run the angular server
ng serveOnce the SaGe server is started on port 8080 and the angular server is up, navigate to http://localhost:4200 on your browser !