This package is the python version of matlab package Simple-Brain-Plot contributed by Scholtens, Lianne H, de Lange, Siemon C, and van den Heuvel, Martijn P.
This tool can be used to visualize the brain areas in the following atlases:
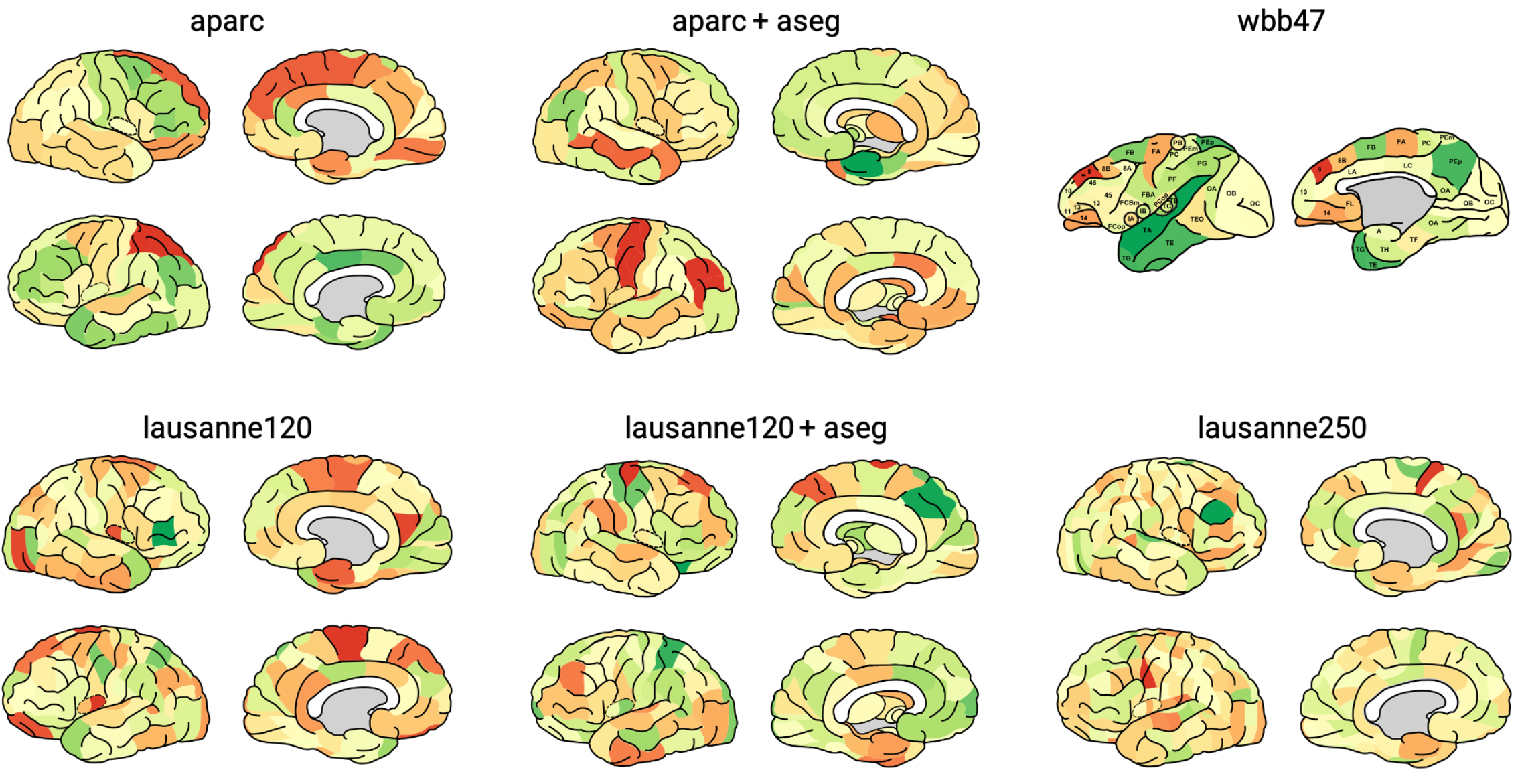
‘Desikan-Killiany’ aparc cortical atlas as present in FreeSurfer [1].
‘Desikan-Killiany’ aparc+aseg combined cortical and subcortical atlas as present in FreeSurfer [1].
120 regions Cammoun sub-parcellation of the Desikan-Killiany cortical atlas [2].
120 regions Cammoun sub-parcellation of the Desikan-Killiany cortical atlas with ASEG subcortical regions [2].
250 regions Cammoun sub-parcellation of the Desikan-Killiany atlas [2].
39 regions combined Walker-von Bonin and Bailey (WBB47) parcellation atlas of the macaque [3][4][5][6].
This package now can be installed from PyPI using pip:
pip install pysimplebrainplotimport numpy as np
import pySimpleBrainPlot as sbp
values = np.random.uniform(-1,1,128)
sbp.plotBrain('lausanne120_aseg', values)atlas (str): name of the atlas to be used.
'aparc' - Desikan-Killiany atlas (68 regions)
'aparc_aseg' - Desikan-Killiany atlas + subcortical ASEG segmentation (82 regions)
'lausanne120' - 120 regions Cammoun sub-parcellation of the Desikan-Killiany atlas (114 regions)
'lausanne120_aseg' - 120 regions Cammoun sub-parcellation + subcortical ASEG segmentation (128 regions)
'lausanne250' - 250 regions Cammoun sub-parcellation (219 regions)
'wbb47' - 39 regions combined Walker-von Bonin and Bailey parcellation atlas of the macaque (39 regions)
values (array): values to be plotted. Should be a vector with the same length as the number of regions in the atlas.
vmin (float): minimum value to be plotted. If None, the minimum value in the values vector is used.
vmax (float): maximum value to be plotted. If None, the maximum value in the values vector is used.
save_path (str): path to save the svg file.
save_file (str): prefix of the svg file.
cm (str): name of the colormap to be used. Should be a default matplotlib colormap.
scaling (float): scaling factor for the size of the svg. Default is 0.1.
viewer (bool): if True, the svg is opened in the default browser. Default is False.[1] Rahul S. Desikan, Florent Ségonne, Bruce Fischl, Brian T. Quinn, Bradford C. Dickerson, Deborah Blacker, Randy L. Buckner, Anders M. Dale, R. Paul Maguire, Bradley T. Hyman, Marilyn S. Albert, and Ronald J. Killiany. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on mri scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3):968–80, 2006. URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811906000437, doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021.
[2] Leila Cammoun, Xavier Gigandet, Djalel Meskaldji, Jean Philippe Thiran, Olaf Sporns, Kim Q. Do, Philippe Maeder, Reto Meuli, and Patric Hagmann. Mapping the human connectome at multiple scales with diffusion spectrum mri. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 203(2):386–397, 2012. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.09.031.
[3] Lianne H. Scholtens, Ruben Schmidt, Marcel A. de Reus, Martijn P. van den Heuvel. Linking Macroscale Graph Analytical Organization to Microscale Neuroarchitectonics in the Macaque Connectome. Journal of Neuroscience 3 September 2014, 34 (36) 12192-12205; URL: https://www.jneurosci.org/content/34/36/12192.short DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0752-14.2014
[4] Stephan KE, Hilgetag CC, Burns GA, O'Neill MA, Young MP, Kötter R. Computational analysis of functional connectivity between areas of primate cerebral cortex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 355:111–126, 2000. URL: https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/abs/10.1098/rstb.2000.0552 doi:10.1098/rstb.2000.0552, pmid:10703047
[5] von Bonin G, Bailey P. The neocortex of Macaca mulatta. 1947. University of Illinois, Urbana, IL.
[6] Walker EA. A cytoarchitectural study of the prefrontal area of the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol 73:59–86, 1940. doi:10.1002/cne.900730106
[7] Scholtens, Lianne H, de Lange, Siemon C, and van den Heuvel, Martijn P. 2021. “Simple Brain Plot”. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5346593