This module provides a servlet which exposes EveKit model data through a REST API. We use Swagger to annotate our REST API, which in turn makes it trivial to generate documentation and experiment with the API, as well as generate client libraries in various languages. A public instance of this module runs here. However, the servlet for this module only exposes the REST API and a Swagger configuration file for driving supporting tools. You can always view the live Swagger configuration file here.
This module assumes you have already set up an appropriate database with EveKit account and model data. See the EveKit Frontend page for an overview of the EveKit service and instructions for setting up a backing database.
The rest of this guide describes how to configure, build and deploy the EveKit Model Frontend.
The model frontend requires the setting and substitution of several parameters which control database and servlet settings. Since the model frontend is normally built with Maven, configuration is handled by setting or overriding properties in your local Maven settings.xml file. The following configuration parameters should be set:
| Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.basepath | The base location where the servlet is hosted, e.g. http://localhost:8080 |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.appname | Name of the servlet when deployed |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.properties.url | Hibernate JDBC connection URL for properties |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.properties.user | Hibernate JDBC connection user name for properties |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.properties.password | Hibernate JDBC connection password for properties |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.properties.driver | Hibernate JDBC driver class name for properties |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.properties.dialect | Hibernate dialect class name for properties |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.account.url | Hibernate JDBC connection URL for account info |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.account.user | Hibernate JDBC connection user name for account info |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.account.password | Hibernate JDBC connection password for user info |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.account.driver | Hibernate JDBC driver class name for account info |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.db.account.dialect | Hibernate dialect class name for account info |
As with all EveKit components, two database connections are required: one for retrieving general settings for system and user accounts; and, one for retrieving user account and model information. The can be (and often are) the same database.
At build and deploy time, the parameters above are substituted into the following files:
- src/main/resources/META-INF/persistence.xml
- src/main/resources/EveKitModelFrontend.properties
- src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml
If you are not using Maven to build, you'll need to substitute these settings manually.
We use Maven to build all EveKit modules. EveKit dependencies are released and published to Maven Central. EveKit front ends are released but must be installed by cloning a repository. To build the EveKit Model Frontend, clone this repository and use "mvn install". Make sure you have set all required configuration parameters before building (as described in the previous section).
This project is designed to easily deploy in a standard Servlet container. Two parameters need to be substituted in the web.xml file in order for deployment to work correctly:
| Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.basepath | The base location where the servlet is hosted, e.g. http://localhost:8080 |
| enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.appname | Name of the servlet when deployed |
If you follow the configuration and build instructions above, these parameters will be substituted for you. These settings are used to define the base path for the REST API endpoints (via Swagger).
The default pom.xml in the project includes the Tomcat Maven plugin which makes it easy to deploy directly to a Tomcat instance. This is normally done by adding two stanzas to your settings.xml:
<servers>
<server>
<id>LocalTomcatServer</id>
<username>admin</username>
<password>password</password>
</server>
</servers>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>LocalTomcat</id>
<properties>
<enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.tomcat.url>http://127.0.0.1:8080/manager/text</enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.tomcat.url>
<enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.tomcat.server>LocalTomcatServer</enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.tomcat.server>
<enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.tomcat.path>/evekit-model</enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.tomcat.path>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>The first stanza specifies the management credentials for your Tomcat instance. The second stanza defines the properties needed to install into the server you just defined. With these settings, you can deploy to your Tomcat instance as follows (this example uses Tomcat 7):
mvn -P LocalTomcat tomcat7:deploy
If you've already deployed, use "redploy" instead. See the Tomcat Maven plugin documentation for more details on how the deployment plugin works.
You can always view the Swagger UI for the public instance of the model frontend from the public instance of EveKit, either by selecting API -> Model API, or by using this direct link.
You can view the Swagger UI for another instance using the Swagger UI online demo. Navigate to the Swagger UI online demo page, then enter the URL for the Swagger configuration file for the instance you want to view. Using the configuration properties above, the URL for the Swagger configuration file is always ${enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.basepath}/${enterprises.orbital.evekit.model-frontend.appname}/api/swagger.json .
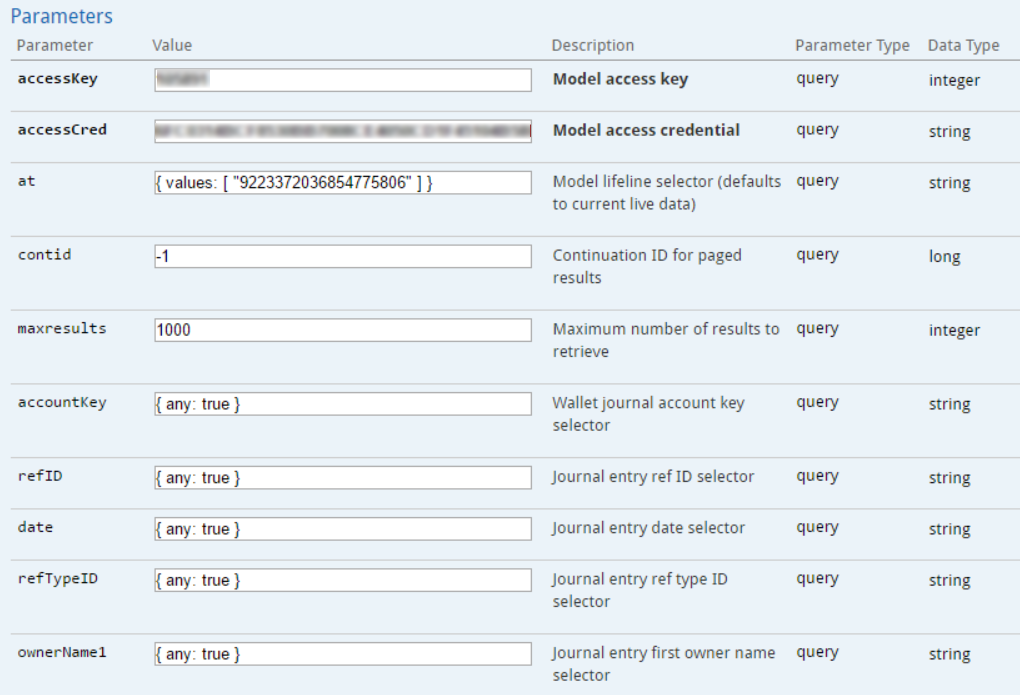
Parameters for model data REST API methods follow a standard convention. As an example, consider the Wallet Journal API (a partial image from the Swagger generated documentation):
Every API method has at least the following five parameters:
- The EveKit access key (accessKey). This is a numeric string.
- The EveKit access key credential (accessCred). This is an alphanumeric string.
- The model lifeline selector (at). This parameter determines the date range of the model data to retrieve (see syntax below).
- The continuation ID for paged results (contid). This value sets the minimum "cached data" ID which will be returned by the method (see next section on API method results).
- The maximum number of results (maxresults) to be returned by the method.
Only accessKey and accessCred are required. All remaining parameters are optional with sensible defaults. Any remaining parameters beyond the five standard parameters are selectors on data fields stored in the model data. A selector is a JSON string which can be used to filter results according to the following syntax:
{any: <boolean>}Wildcard selector. If true, then this data field is not used to filter returned model data. Setting this value to false has no effect.{like: <string>}String match selector. If the associated data field is string valued, then all returned model data must satisfy the SQL expression 'field LIKE selector'. Normal SQL 'LIKE' syntax is allowed (e.g. % as wildcard).{values: [<v1>,...,<vn>]}Set selector. The associated data field of each returned model data item must contain one of the listed values.{start: <lower>, end: <upper>}Range selector. The associated data field of each returned model data item must satisfy lower <= value <= upper.
In the sample image above, the API method will return all rows which were live at time "9223372036854775806" (Set selector for the "at" parameter). This value happens to be "Long.MAX_VALUE - 1" and so this selector will choose the latest live data. All other selectors are wild cards, indicating that all values are allowed.
If "at" were instead "{any: true}", then the complete lifeline for each data item would be returned (up to the maxresults limit). Since "at" expects a long valued argument, the "like" selector will have no effect (it will be interpreted as a wildcard). If the "at" selector specified "{values: [t1, ..., tn]}" (as in the example above), then only model data which was live at one of times t1 through tn would be returned. Finally, if the "at" selector specified "{start: t1, end: t2}", then all returned model data is guaranteed to have been live in the time range [t1, t2] (that is, inclusive).
Selectors applied to other model data fields work in a similar fashion.
The EveKit Model Frontend returns results in JSON format, for example:
[
{
"cid": 110240,
"eveKitVersion": 2,
"lifeStart": 1459167655693,
"lifeEnd": 9223372036854776000,
"accountID": 36538801,
"accountKey": 1000,
"balance": 348640657.44
}
]Every result has at least four fields:
cidCached Data ID. This is a unique EveKit internal ID. Results are always returned in ascending order by "cid". This value is also used as the continuation ID when results are paged (every method returns at most 1000 results; paging is required to retrieve additional results). Finally, "cid" is used to uniquely identify model data for the meta data REST API calls.eveKitVersionEveKit model data version. Currently "2" for all data.lifeStartTime (milliseconds UTC) when this model data was created ("live" datetime).- ```lifeEnd`` Time (milliseconds UTC) when this model data was replaced by newer data ("dead" datetime). A value of "Long.MAX_VALUE" indicates this data is the latest live data. NOTE: the example above was parsed into javascript which rounds Long.MAX_VALUE to a slightly higher value.
The segment of the lifeline a model data item occupies is therefore [lifeStart, lifeEnd). Any remaining fields will be data fields specific to the type of data returned. The model frontend also returns data in the HTTP Response headers:
DateServer time when the result was returned (UTC).EveKit-VersionVersion of EveKit server which returned result.expiresThe date when the returned data will expire. Data expiry is set according to EVE Online API server caching timers.
The model frontend REST API can be accessed directly by using the paths and arguments described in the API documentation. However, you can also use the Swagger configuration file to automatically generate appropriate client code. There are two ways to do this.
For a Javascript client, there is no need to generate client code statically. Instead, you can use the Swagger Javascript module. For example, the following HTML snippet will create a Javascript client from the public model frontend instance (note the use of rawgit.com to return a proper content type):
<!-- Set up Swagger -->
<script src='https://cdn.rawgit.com/swagger-api/swagger-js/master/browser/swagger-client.min.js' type='text/javascript'></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var url = "https://evekit-model.orbital.enterprises/api/swagger.json";
window.swagger = new SwaggerClient({
url: url,
success: function() { /* called when the client is ready */ }
});
</script>For a non-Javascript client, you can use the Swagger Editor online demo. To generate a client for the public model frontend instance, type in "https://evekit-model.orbital.enterprises/api/swagger.json" under "File->Import URL..", then use the "Generate Client" menu to download an appropriate client.
The best place to get help is on the Orbital Forum.