Natural language processing is a very exciting field right now. In recent years, the community has begun to figure out some pretty effective methods of learning from the enormous amounts of unlabeled data available on the internet. The success of transfer learning from unsupervised models has allowed us to surpass virtually all existing benchmarks on downstream supervised learning tasks. As we continue to develop new model architectures and unsupervised learning objectives, "state of the art" continues to be a rapidly moving target for many tasks where large amounts of labeled data are available.
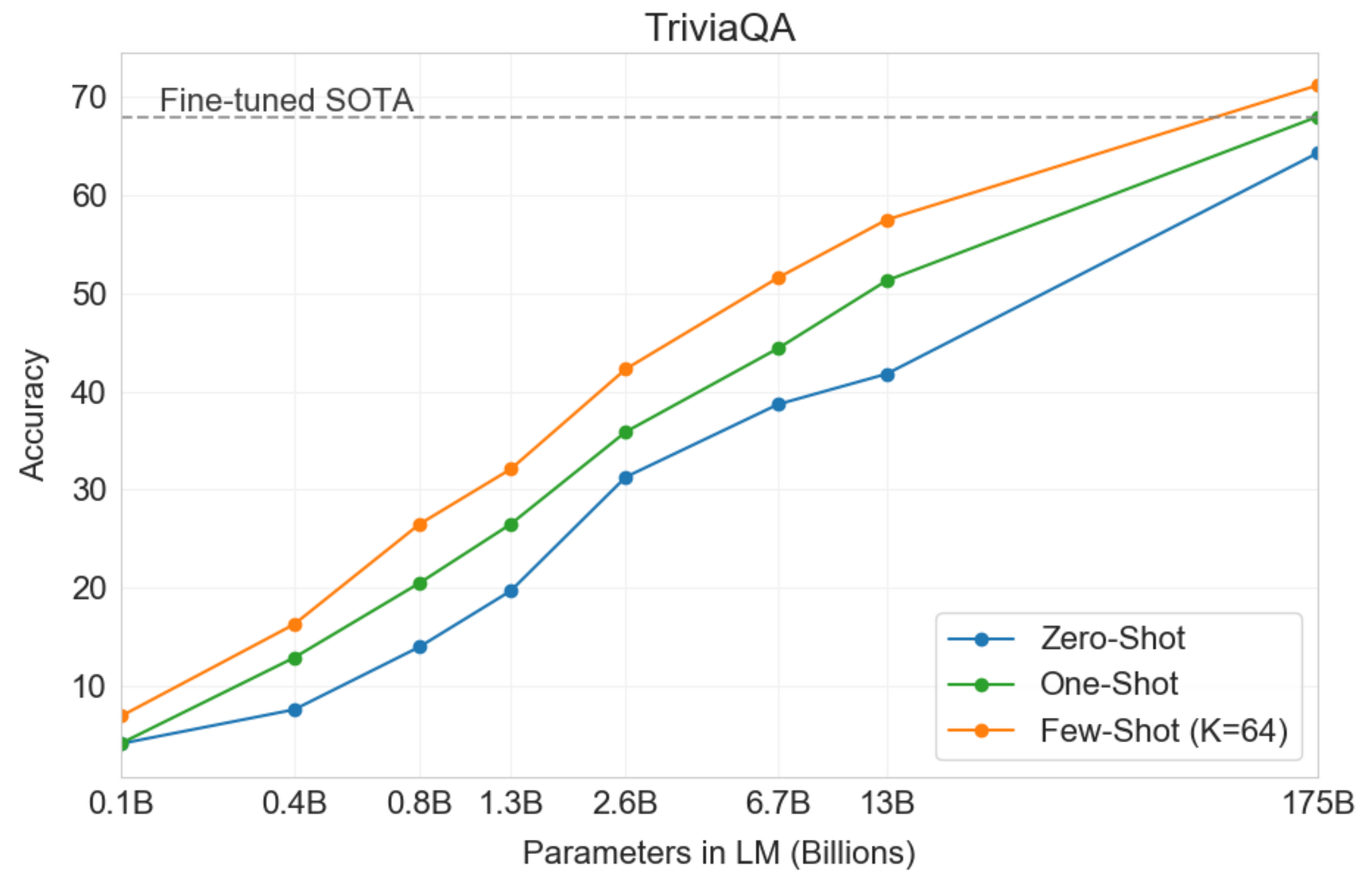
One major advantage as models continue to grow is that we see a very slow decrease in the reliance on large amounts of annotated data for downstream tasks. This week the team at Open AI released a preprint describing their largest model yet, GPT-3, with 175 billion parameters. The paper is entitled, "Language Models are Few-Shot Learners", and shows that extremely large language models can perform competitively on downstream tasks with far less task-specific data than would be required by smaller models.
However, models of this size remain impractical for real-world use. For instance, the largest version of GPT-3 must be partitioned across dozens of GPUs to even fit in memory. In many real-world settings, annotated data is either scarse or unavailable entirely. Models much smaller than GPT-3 such as BERT have still been shown to encode a tremendous amount of information in their weights (Petroni et al. 2019). It seems like if we were smart about it, we would be able to figure out some techniques for applying these models to downstream tasks in a way that takes advantage of this latent information without the need for so much task-specific annotated data.
Zero-Shot learning method aims to solve a task without receiving any example of that task at training phase. The task of recognizing an object from a given image where there weren’t any example images of that object during training phase can be considered as an example of Zero-Shot Learning task. Actually, it simply allows us to recognize objects we have not seen before.
A well-known example of this is in the GPT-2 paper where the authors evaluate a language model on downstream tasks like machine translation without fine-tuning on these tasks directly.
A common approach to zero shot learning in the computer vision setting is to use an existing featurizer to embed an image and any possible class names into their corresponding latent representations (e.g. Socher et al. 2013). They can then take some training set and use only a subset of the available labels to learn a linear projection to align the image and label embeddings. At test time, this framework allows one to embed any label (seen or unseen) and any image into the same latent space and measure their distance.
In conventional object recognition process, it is necessary to determine a certain number of object classes in order to be able to do object recognition with high success rate. It is also necessary to collect as many sample images as possible for selected object classes. Of course, these sample images should contain objects taken from diverse angles in various contexts/environments in order to be comprehensive. Although there exists lots of object classes that we can effortlessly gather sample images of, there also exists cases that we are not always so lucky.
Imagine that we want to recognize animals that are on the edge of extinction or live in extreme environments (in the depths of the ocean/jungle or hard to reach mountain peaks) that humans are not able to visit whenever they wish. It is not easy to collect sample images of these sort of animals. Even if you would achieve to collect enough images, remember images should not be similar and they should be as unique as possible - You need to make a lot of effort to achieve that.
This animal (Ili Pika) was seen a few summers ago, in China
In addition to the difficulty of recognizing different object classes with a limited number of images, labeling for some object classes is not as easy as ordinary people can do. In some cases, labeling can only be done after the subject is truly mastered or in the presence of an expert. Fine grained object recognition tasks like recognition of fish species or tree species can be considered as examples of labelling under the supervision of an expert. An ordinary person will call/label all the tree she/he is viewed as tree or all the fish she/he is viewed as fish. These are obviously true answers but imagine that you want to train a network in order to recognize tree or fish species. In that case, all aforementioned true answers are useless and you need an expert to help you with labelling task. Again, you need to make a lot of effort to achieve that.
Now that after mentioning what Zero-Shot learning is, let’s implement a Zero-Shot learning model step by step. But before we do that, let’s elaborate our approach.
Github: https://github.com/huggingface
Medium: https://medium.com/huggingface
Hugging Face is an open-source provider of NLP technologies.
Hugging Face has created multiple repositiories for Natural Language Processing and we will be using the Transformers repository from Github.
The repository is available here
deepset/sentence_bert which is the smallest version of the S-BERT model could also be used. However, our experiments use larger models which are currently available only in the sentence-transformers Github Repository.
Transformers provides thousands of pretrained models to perform tasks on texts such as classification, information extraction, question answering, summarization, translation, text generation, etc in 100+ languages. It's aim is to make cutting-edge NLP easier to use for everyone.
Transformers is backed by the two most popular deep learning libraries, PyTorch and TensorFlow, with a seamless integration between them, allowing us to train your models with one then load it for inference with the other.
-
Easy-to-use state-of-the-art models
-
Lower compute costs, smaller carbon footprint
-
Choose the right framework for every part of a model's lifetime
-
Easily customize a model or an example to your needs