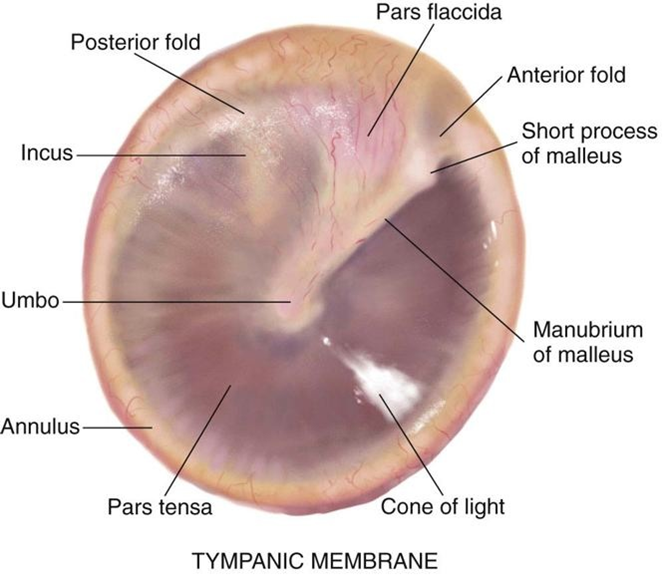
Otitis Media (OM) is an infection of the middle ear. It is one of the most common childhood illnesses and the second most important reason leading to the loss of hearing. It is most common in developing countries and was ranked fifth on the global burden of disease and affected 1.23 billion people in 2013.
OM is often misdiagnosed or not diagnosed at all, especially when it is in the early stages. It is often either under-diagnosed or over-diagnosed depending on the factors like clinicians, symptoms, otoscopes etc. Detection of OM requires a good medical practitioner (ENT), whose availability is difficult in remote village areas especially in developing countries. That is why OM is ignored amongst these kinds of groups and is a second major cause of hearing loss.
The aim of the study is to develop a diagnostic system using Ear Drum (Tympanic Membrane) images and applying machine learning to automatically extract certain features and perform image classification which can help diagnose otitis media(OM) with greater accuracy. This diagnostic system will provide a reliable data to a survey volunteer to advise the patient or his family to visit an ENT or take professional help if OM is present.
One of the biggest challenge faced during the project was the collection of image data for normal and infected tympanic membrane. We obtained the ear disease dataset from an ENT doctor at AIMS. The dataset consists oof around 250 images with 6 classes. Details of the classes:
 |
 |
 |
| Normal Ear | Glue Ear | Otomycosis |
Now we are ready to build a CNN. After dabbling a bit with tensorflow, I decided it was way too much work for something incredibly simple. I decided to use keras. Keras is a high-level API wrapper around tensorflow. It made coding lot more palatable. The approach I used was similar to this. I used a 3 convolutional layers in my architecture initially.
Transfer learning consists of taking features learned on one problem, and leveraging them on a new, similar problem. For instance, features from a model that has learned to identify racoons may be useful to kick-start a model meant to identify tanukis.
Transfer learning is usually done for tasks where your dataset has too little data to train a full-scale model from scratch.
The most common incarnation of transfer learning in the context of deep learning is the following worfklow:
- Take layers from a previously trained model.
- Freeze them, so as to avoid destroying any of the information they contain during future training rounds.
- Add some new, trainable layers on top of the frozen layers. They will learn to turn the old features into predictions on a new dataset.
- Train the new layers on your dataset.
tf.keras.applications.ResNet50(
include_top=True,
weights="imagenet",
input_tensor=None,
input_shape=None,
pooling=None,
classes=1000,
**kwargs)
Instantiates the ResNet50 architecture.
Using keras.applications for initilizing model architecture with imagenet weights. Similarly we used InceptionResnetV2 and VGG16 from keras applications and used imagenet weights for initialization.
 |
 |
| Retracted Typanic Membrane | Wax |
We have developed a webapp using Flask API and have deployed it on Heroku that enables us to operate entirely on cloud. A front-end for the website has been deployed on Netlify which could be accessed by clicking here!