- This file provides technical documentation related to UCSC-Keysight's software development project that seeks to create OpenTAP plugins to control Universal Robots' (UR) cobot model UR3e.
- These plugins are loosely being designed to potentially extend to other cobots in the future.
- The immediate purpose of these plugins will tentatively be used in 6G testing as described here.
A package is a technique used to compress a plugin into a single file with a .TapPackage extension, which simplifies the installation and setup process for operators.
-
This plugin can be compressed into a package with the following steps:
git clone https://github.com/UCSC-Keysight/OpenTAP-Cobot-Plugin.git cd OpenTAP-Cobot-Plugin/openTap dotnet build bin\tap package create ./package.xml
-
Operators can install a package into an existing OpenTAP installation with the following commands:
# Navigate to the root directory of an existing OpenTAP installation. tap package install <PATH-TO-PACKAGE-FILE>
The following instructions are intended for programmers to continue development for the plugin.
-
The plugin can be developed locally using the following commands:
# Starts Universal Robots' Simulator docker network create --subnet=192.168.56.0/24 ursim_net docker run -it -e ROBOT_MODEL=UR3e --net ursim_net --ip 192.168.56.101 -p 30002:30002 -p 30004:30004 -p 6080:6080 --name ur3e_container universalrobots/ursim_e-series # Setups plugin and launches editor git clone https://github.com/UCSC-Keysight/OpenTAP-Cobot-Plugin.git cd OpenTAP-Cobot-Plugin/openTap dotnet build bin\tap editor
The plugin can be developed using a container with the following resources:
runall.sh script manual page
runall.sh [bigl:d:f:o:] (Automation script for setting up OpenTAP/UR Sim/ROS2 (TBD))
-b force builds containers instead of pulling from Docker Hub
-i Opens an interactive shell to the opentap container
-g Opens editor GUI within the opentap container hosted on a VNC webserver (Also includes environment dir with testplans and scripts)
-l (license-server-ip) Creates an env variable for the LM_LICENSE_FILE
-f (file1) (file2) (fileN) Transfers 1 or more testplan files to the container to be automatically run (Unless -i or -g is set)
-d (dir) Moves all testplan files within directory to the container be automatically run (Unless -i or -g is set)
-o set output directory for test data and testplan logs (to be implemented)
By default runall.sh pulls images from Docker Hub on the ucsckeysight account.
Including the -d or -f flags with the interactive shell or gui does not automatically run any testplans,
but instead imports them to the environment directory to prevent override in stdout.
Initial build time will average from 2-4 minutes,
after the initial build all further use is cached and instant.
All environmental variables and imported code is stored via volume mounts and do not interfere with the image itself, but store persistent state.
-
The PolyScope interface can be accessed by navigating to http://localhost:6080/vnc_auto.html on Google Chrome.
-
The existing plugin can be tested with the following steps:
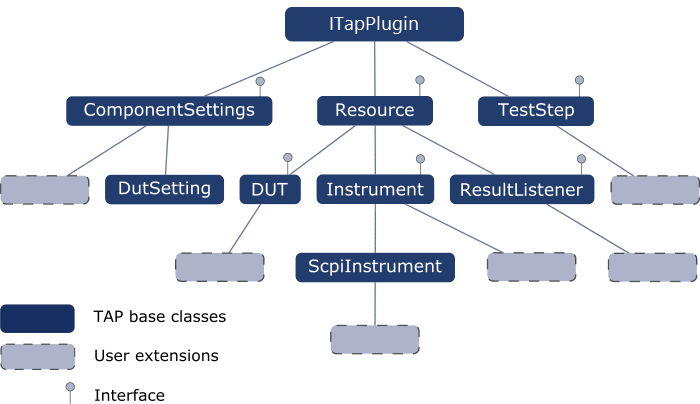
OpenTAP implements an object hierarchy that plays a critical role in their software architecture.
The primary purpose of the hierarchy is to enforce modularization that'll encapsulate logic categorically which is used to control, manage and separate responsibilities within their software. There are four main categories that you should be aware of:
- The
DeviceUnderTest(DUT) class encapsulates logic strictly related to the object we're interested in collecting data about. - The
Instrumentclass encapsulates logic that strictly relates to a physical tool. In general, this logic would implement some functionality that seeks to condition, expose or otherwise measure a parameter related to the DUT. - The
TestStepclass is the fundamental unit of work; essentially, it is used to tie everything together. OpenTAPs best practices recommend that it performs a single step - The
ResultListenerclass is used to arbitrate the collection and management of data produced by test steps.
The prototype only uses an instrument named UR3e and a test step MoveCobot.
- A tool responsible for performing a conditioning action to the DUT; namely, modifying its location via the cobot arm.
- Object strictly encapsulates logic related to this responsibility.
- Implements
send_request_movement()which is used to modify the state of the cobot given an arbitrary move command. - Implements logic used to display its information on the GUI.
- Implements
- Instantiates a
UR3eobject - Implements logic used to collect URScript input from the end-user stored in
command. - Invokes the
UR3efunctionsend_request_movement(command)
- Creates a TCP socket connection.
- Sends requests to UR3e simulator's internal server.
- Receives response back from UR3e simulator's internal server.