Implement a simple Neural network trained with backprogation in Python3.
- Feed Forward
- Feed Backward * (BackPropagation)
- Update Weights Iterating the above three steps
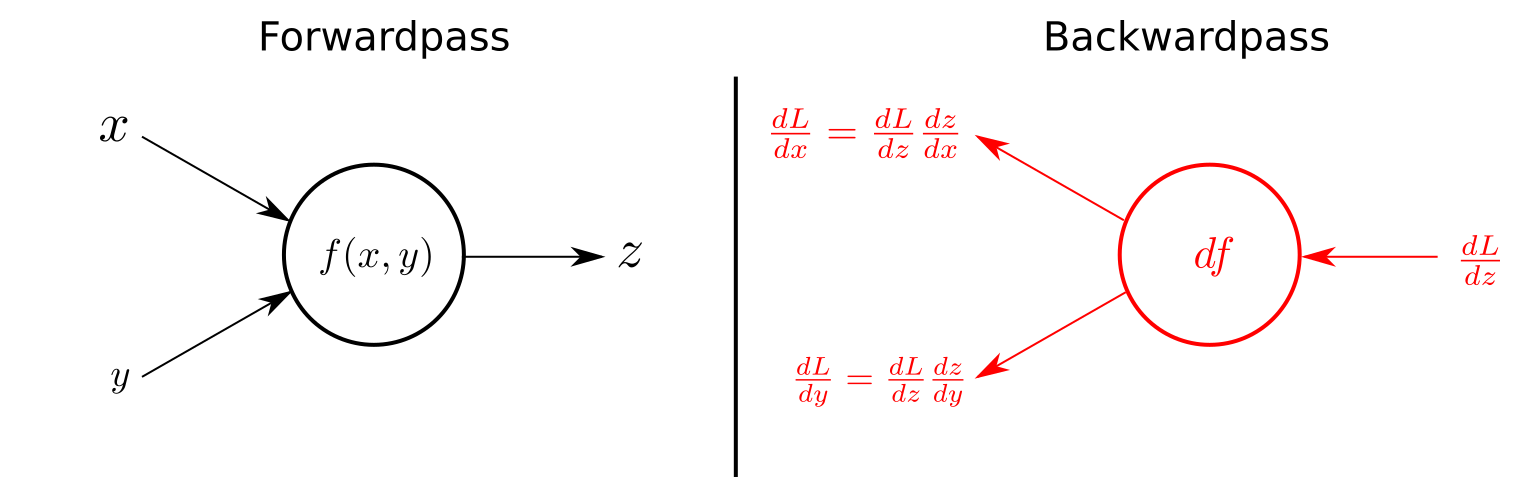
Backpropagation is the implementation of gradient descent in multi-layer neural networks. Since the same training rule recursively exists in each layer of the neural network, we can calculate the contribution of each weight to the total error inversely from the output layer to the input layer, which is so-called backpropagation.
Gradient descent is a first-order iterative optimization algorithm, which is used to find the local minima or global minima of a function. The algorithm itself is not hard to understand, which is:
- Starting from a point on the graph of a function;
- Find a direction ▽F(a) from that point, in which the function decreases fastest;
- Go (down) along this direction a small step γ, got to a new point of a+1; By iterating the above three steps, we can find the local minima or global minima of this function.
The advantage of this method is that the gradient is accurate and the function converges fast. But when the training dataset is enormous, the evaluation of the gradient from all data points becomes expensive and the training time can be very long.
Another method is called stochastic gradient descent, which samples (with replacement) a subset (one or more) of training data to calculate the gradient.
Stochastic Gradient Descent
每次迭代:
Input為一筆資料的features,模型透過feed forward運算出predict_Y (outputs)
將所有Outputs與其相對之targets比較,利用Gradient Descent找出每個Neuron中的weights的改變方向
修正Weights,下一筆資料用新的權重來進行prediction,如此類推直至收斂。
1.0
Python==3
(demo_1_xor.py) Here we used XOR dataset for our first demo.
# dataset = [(inputs), (outputs)]
train_dataset = [
[(1, 0), [1]],
[(0, 0), [0]],
[(0, 1), [1]],
[(1, 1), [0]]
]
test_dataset = [
[(1, 0), [1]],
[(0, 0), [0]]
]
Build the NN model with 1 hidden layer (2-3-1)
(n_input(2) -> n_hiddens(3,) --> n_output(1))
nn = NeuralNetwork(learning_rate=0.1, debug=False)
nn.add_layer(n_inputs=2, n_neurons=3)
nn.add_layer(n_inputs=3, n_neurons=1)
nn.train(dataset=train_dataset, n_iterations=100, print_error_report=True)
nn.test(test_dataset)
It is just a rough neural netowrk with bp.
- Hidden Layers can be added at initial.
- More Activation Functions
Concepts:
- 類神經網路--BackPropagation 詳細推導過程 By Mark Chang
- Gradient Descent and Backpropagation By Ken Chen
- gradient descent optimization algorithms By Tommy Huang
- Delta Rule By Wikipedia
- Figure_1 Feedforward vs. Feedbackward
Coding: