-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Fluence Interrogation Panel
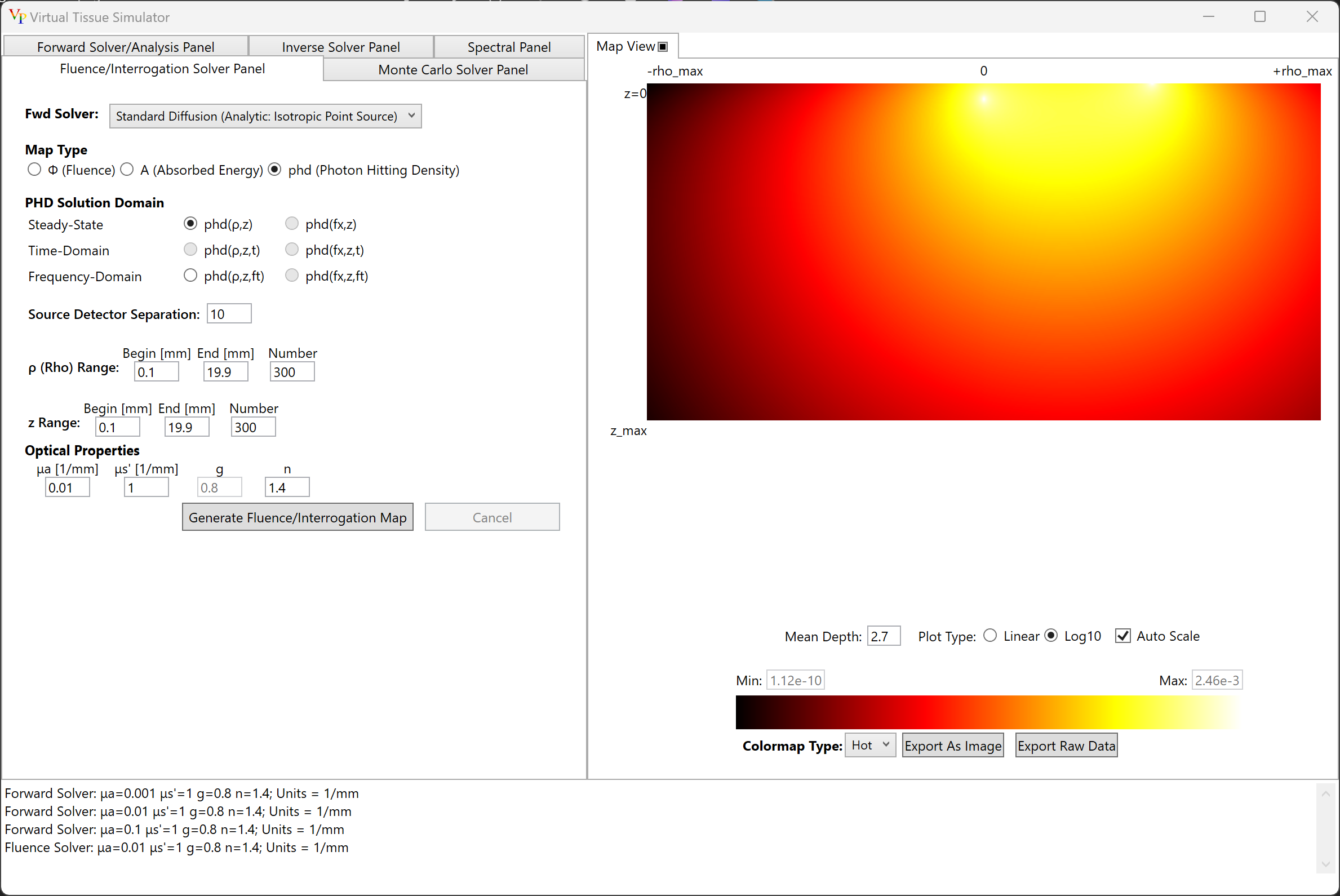
-
Fluence (Phi): Provides internal spatial distribution of fluence using forward models as specified above.
-
Absorbed Energy (mua*Phi): Provides internal distribution of the absorbed energy density which is simply the fluence distribution multiplied by the absorption coefficient.
-
Photon Hitting Density (PHD): Provides a graphical display of the product of two Green's functions:the first being the relative probabilty that a source photon will visit a given location within the medium and the second being the probability that a photon emanating from that location is subsequently captured by the detector. Method inspired by Schotland et al., 1993. Our implementation follows that of Feng et al, 1995. While the source representation can be modified, the detector is always considered to be a hemisperical detector located at the tissue surface.
% this script replots the data that is exported from the Fluence/Interrogation Solver Panel
% input: saved text file, e.g. fluence.txt
fid = fopen('fluence.txt');
xValues={};
line1 = strsplit(fgetl(fid));
xValues=str2double(line1(4:end-1)); % get rid of header and last null datapoint
line2=strsplit(fgetl(fid));
yValues=str2double(line2(4:end-1)); % get rid of header and last null datapoint
line3=strsplit(fgetl(fid));
mapValues=str2double(line3(4:end-1)); % get rid of header and last null datapoint
fclose(fid);
figure;
map2D=reshape(mapValues,size(xValues,2),size(yValues,2)); % rehydrate linear data
imagesc(xValues,yValues,log10(map2D'));
axis ij;
axis equal;
axis([min(xValues) max(xValues), min(yValues) max(yValues)]);
colormap('hot');
colorbar;
xlabel('x [mm]');
ylabel('z [mm]');References:
Schotland, J.C., Haselgrove, J.C., and Leigh, J.S., ”Photon Hitting Density” Applied Optics, 32(4):448-453, 1993.
Feng, Zeng, Chance. ”Photon migration in the presence of a single defect: a perturbation analysis” Applied Optics, 34(19):3826-3837, 1995.
Virtual Photonics Technology Initiative
Project Site | Discussion | Education