The W55RP20 is a System-in-Package (SiP) developed by WIZnet, integrating Raspberry Pi's RP2040 microcontroller, WIZnet's W5500 Ethernet controller, and 2MB of Flash memory into a single chip. These sections will guide you through the steps of configuring a development environment for micropython using the W55RP20 product from WIZnet.
| Image | Name | Etc |
|---|---|---|
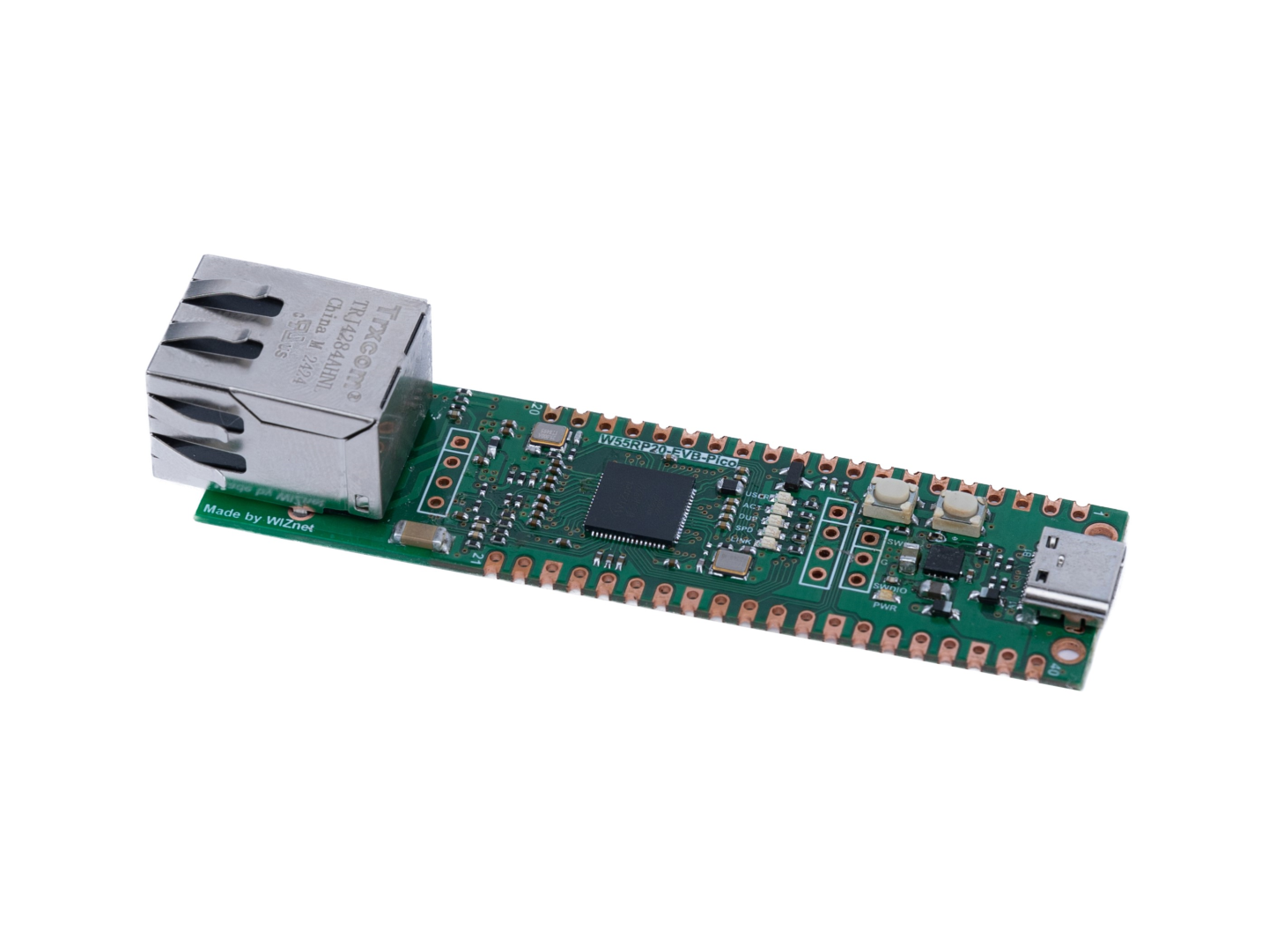 |
W55RP20-EVB-PICO | W55RP20 Document |
The W55RP20 has internal connections between the RP2040 and W5500 via GPIO pins. The connection table is as follows:
| I/O | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| O | GPIO20 | Connected to CSn on W5500 |
| O | GPIO21 | Connected to SCLK on W5500 |
| I | GPIO22 | Connected to MISO on W5500 |
| O | GPIO23 | Connected to MOSI on W5500 |
| I | GPIO24 | Connected to INTn on W5500 |
| O | GPIO25 | Connected to RSTn on W5500 |
- Clone
cd [user path]
git clone https://github.com/WIZnet-ioNIC/WIZnet-ioNIC-micropython.git
git submodule update --init- Build
cd WIZnet-ioNIC-micropython/ports/rp2
make BOARD=W55RP20_EVB_PICO- uf2 file writing
Hold down the BOOTSEL button on your W55RP20-EVB-PICO board, press and release the RUN button, and you should see a removable disk pop-up.
cp build-W55RP20_EVB_PICO/firmware.uf2 /media/[user name]/RPI-RP2- examples
The MicroPython examples for the W55RP20-EVB-PICO can be found at the following path. Please refer to this for guidance.
WIZnet-ioNIC-micropython/WIZnet-ioNIC_examplesThe pre-built bin files (WIZnet-ioNIC-micropython_Bin.zip) can be found at the following path:
https://github.com/WIZnet-ioNIC/WIZnet-ioNIC-micropython/releases
For the guide document that includes the video, please refer to the link below. https://maker.wiznet.io/mason/projects/how%2Dto%2Dbuild%2Dwiznet%2Dionic%2Dmicropython/
File: Loopback.py
In the main function, uncomment the server_loop() call to activate server mode on the W55RP20 board.
def main():
w5x00_init() # Initialize network
###TCP SERVER###
server_loop() # Enable server function (uncomment this line)
###TCP CLIENT###
#client_loop() # Client function (comment this line)Use the following network settings:
IP: 192.168.11.20
Port: 5000
Testing Client
Use another device on the same network to connect as a TCP client to the server.
import socket
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(('192.168.11.20', 5000))
s.sendall(b'Hello, Server!')
data = s.recv(1024)
print('Received', data.decode('utf-8'))
s.close()File: Loopback_dhcp.py
The functionality is the same as the loopback setup. The only difference is that this version uses DHCP to automatically get the IP address.
File: HTTP_Client.py
This code uses the WIZnet W5x00 series Ethernet chip (specifically W55RP20) to connect to a network and send HTTP GET and POST requests. Using the urequests module, the code sends HTTP requests and prints the responses, verifying that the network communication is working correctly.
Sends a GET request to http://httpbin.org/get, printing the status code and response content. Then sends a POST request to http://httpbin.org/post with some JSON data, and prints the result as JSON. Expected Output:
The response status code (200 OK) and response content from the GET request are printed. The JSON response from the POST request is also printed.
By default, the code uses a static IP address 192.168.11.20. The network settings are defined as follows:
nic.ifconfig(('192.168.11.20', '255.255.255.0', '192.168.11.1', '8.8.8.8'))To use a dynamic IP (DHCP), modify the settings as follows:
#None DHCP
# nic.ifconfig(('192.168.11.20','255.255.255.0','192.168.11.1','8.8.8.8'))
#DHCP
nic.ifconfig('dhcp')File: sntp.py
This code demonstrates how to initialize a WIZnet W5x00 series Ethernet chip to connect to a network and synchronize time with an SNTP server. The example supports both static and dynamic IP configurations, allowing the device to send an SNTP request to an NTP server and print the received time in UTC.
Setting up UDP socket...
Creating SNTP request packet...
Resolving NTP server address...
Sending NTP request to pool.ntp.org (192.168.x.x)
Waiting for SNTP response...
SNTP response received!
NTP Time (UTC): (2024, 11, 25, 10, 30, 45, 0, 329)
Attempt 1 failed, retrying in 1 second(s)...(Exception details)
NTP request timed out.If there are any connection issues, you may see messages like:
Attempt 1 failed, retrying in 1 second(s)...(Exception details)
NTP request timed out.For IP settings, refer to previous examples for how to configure static or dynamic IP addresses.
File: redis_client.py
Dependency: picoredis.py
When run on the W55RP20 through Thonny, this script connects to a Redis server and performs a few operations:
- Ping Command: Sends an empty
pingrequest and another with the string "os" to the Redis server. The server responds withPONGandosrespectively. - Set Command: Creates a key named
picowith the valuetest from picoon the Redis server. - Get Command: Retrieves the value of the
picokey from the Redis server and prints it, verifying that the key was properly stored.
For more details on available Redis commands, please visit the official documentation: Redis Commands.
File: iperf3.py
When executed as a server process, this script performs the following actions:
- Obtains an IP address via DHCP
- Opens and listens on port 5201
Due to the nature of MicroPython execution, the test results may show lower performance compared to the board's actual capabilities. This is an inherent limitation of the interpreted language environment.
For more accurate iPerf test results that reflect the true performance of the W55RP20-EVB-Pico board, we recommend using the C language implementation.
Please refer to the following repository for a C-based iPerf implementation:
This C implementation will provide more representative performance metrics for the W55RP20-EVB-Pico board.
File: iperf3_test.py
This script is designed to test the iperf3.py running on the W55RP20 board from a Windows environment.
The primary purpose of this script is to facilitate iPerf3 testing between a Windows machine and a W55RP20 board running the iperf3.py script.
To use this script, follow these steps:
- Ensure the
iperf3.pyscript is running on your W55RP20 board. - Note the IP address displayed by the W55RP20 board.
- Open a command prompt or PowerShell window on your Windows machine.
- Navigate to the directory containing this script.
- Run the script using the following command format:
File: dns_client.py
This code demonstrates how to use the WIZnet W5x00 series Ethernet chip to perform DNS (Domain Name System) resolution. The example shows how to convert domain names into IP addresses using the built-in socket interface, supporting both static and dynamic IP configurations.
WIZnet chip DNS example
MAC Address: 00:11:22:33:44:55
IP Address: ('192.168.7.111', '255.255.255.0', '192.168.7.1', '168.126.63.1')
IP address of www.wiznet.io is 111.111.111.111File: mqtt_client_test.py
File: w5x00.py, umqttsimple.py
This MicroPython script implements an MQTT client for W55RP20, utilizing the umqttsimple library. It connects to an MQTT broker, publishes messages periodically, and handles reconnections.
Connected to 192.168.1.2 MQTT Broker1734315706: New connection from 222.98.173.219 on port 1883.
1734315706: New client connected from 222.98.173.219 as wiz2 (c1, k60).
1734315706: No will message specified.
1734315706: Sending CONNACK to wiz2 (0, 0)
1734315706: Received PUBLISH from wiz2 (d0, q0, r0, m0, 'kkk', ... (10 bytes))
1734315709: Received PUBLISH from wiz2 (d0, q0, r0, m0, 'kkk', ... (10 bytes))
1734315712: Received PUBLISH from wiz2 (d0, q0, r0, m0, 'kkk', ... (10 bytes))
...The mqtt_server variable must be changed to the actual IP address of your MQTT broker. For example, if you're using AWS EC2, use the public IP address of your EC2 instance.
The port variable should be set to the actual port number of your MQTT broker. While MQTT typically uses port 1883, this may vary depending on your broker's configuration.
Set the topic_pub variable to the topic name you want to publish to. This defines the subject or category of your messages.
Configure the topic_msg variable with the actual message content you wish to publish. This is the payload that will be sent to the specified topic.
Adjust firewall settings to allow external access to the MQTT broker if required.
For enhanced security, it's recommended to set allow_anonymous to false and implement user authentication.
When connecting from external networks, ensure you're using the public IP address.
If using cloud services like EC2, open the necessary port (typically 1883) for MQTT communication in the security group settings.
Depending on your network environment, port forwarding may be necessary.
Regularly update your broker software and client libraries to ensure you have the latest security patches and features.