Flappy Bird Game trained on a Double Dueling Deep Q Network with Prioritized Experience Replay implemented using Pytorch.
Here I will explain how to run the game which runs automatically using saved model, also I will breif you about basics of Q Learning, Deep Q learning, Dueling architecture and Prioritized Experience Replay.
You will need Python 3.X.X with some packages which you can install direclty using requirements.txt.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Use the following command to run the game where '--model' indicates the location of saved DQN model.
python3 play_game.py --model checkpoints/flappy_best_model.dat
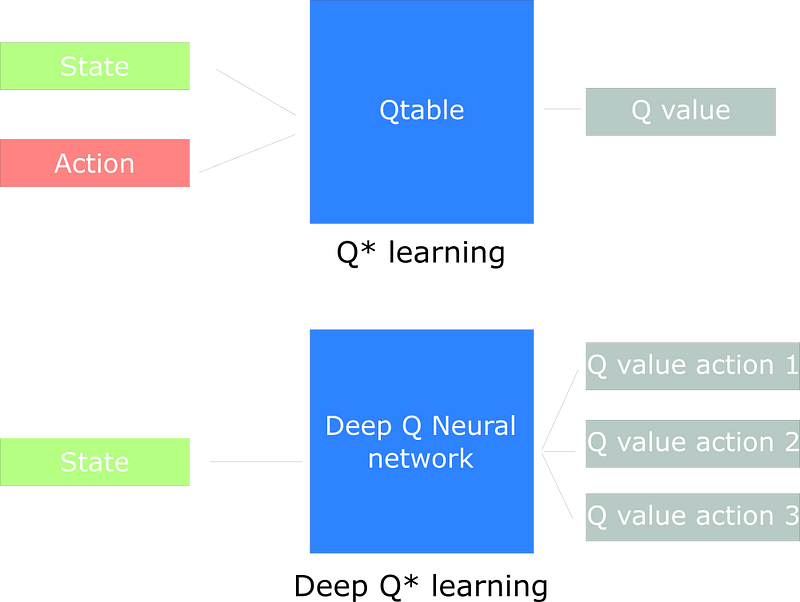
Q Learning is off policy learning method in reinforcement learning which is a developement over on-policy Temporal Difference control algorithm. Q-learning tries to estimate a state-action value function for target policy that deterministically selects the action of highest value.
The problem with Tradition Q learning is that it is not suitable for continuous environment (like Flappy Bird) where an agent can be in infinite number of states. So it is not feasible to store all states in a grid which we use in tradition Q learning. So we use Deep Q learning in these environments.
Deep Q learning is based on Deep Neural Network which takes current state in the form of image or say continuous value and approximates Q-values for each action based on that state.
Take a look at this article which explains Deep Q Learning
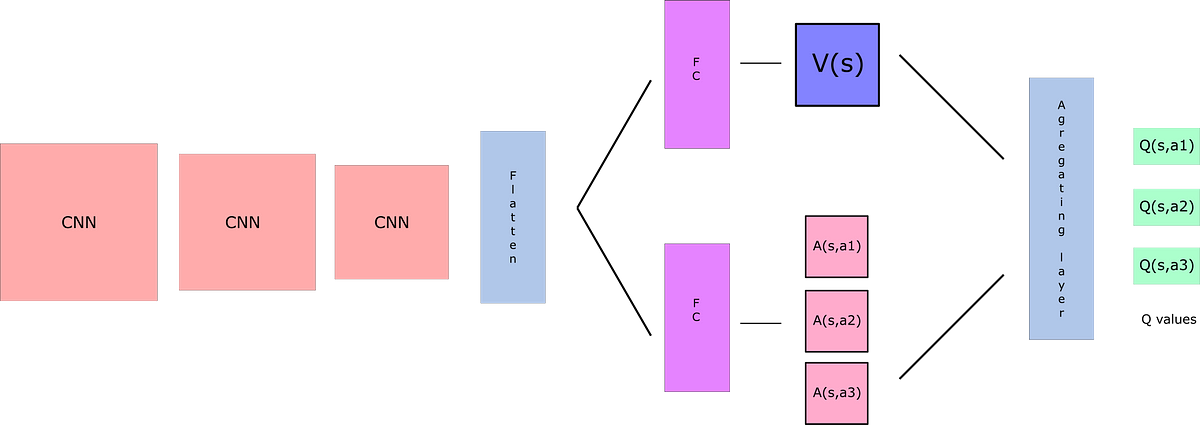
Here I have used Dueling architecture to calculate Q values. Q-values correspond to how good it is to be at that state and taking an action at that state Q(s,a). So we can decompose Q(s,a) as the sum of: V(s) - the value of being at that state A(s) - the advantage of taking that action at that state (how much better is to take this action versus all other possible actions at that state).
Q(s,a) = V(s) + A(s,a)
The idea behind PER was that some experiences may be more important than others for our training, but might occur less frequently. Because we sample the batch uniformly (selecting the experiences randomly) these rich experiences that occur rarely have practically no chance to be selected. We want to take in priority experience where there is a big difference between our prediction and the TD target, since it means that we have a lot to learn about it.
pt = |dt| + e
where,
pt = priority of the experience
dt = magnitude of TD error
e = constant assures that priority do not become 0
Take a look at this article which explains Double Dueling and PER
- Aditya Jain : Portfolio
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE.md file for details
- The Game has been taken from this repository
- Thanks Siraj Raval for Move37 course on theschool.ai which helped understand these concepts.