This is a brainlife wrapper for the resting state HRF estimation and deconvolution method. https://github.com/BIDS-Apps/rsHRF
This App requires an fMRI (bold) and anatomical brain mask.
{
"bold": "testdata/bold.nii.gz",
"mask": "testdata/mask.nii.gz",
"estimation": "canon2dd"
}
The estimation parameter (analysis method) can be set to one of the following
'canon2dd (canonical shape with 2 derivatives), '
'sFIR (smoothed Finite Impulse Response) , '
'FIR (Finite Impulse Response)')
Please refer to https://github.com/compneuro-da/rsHRF for MATLAB version
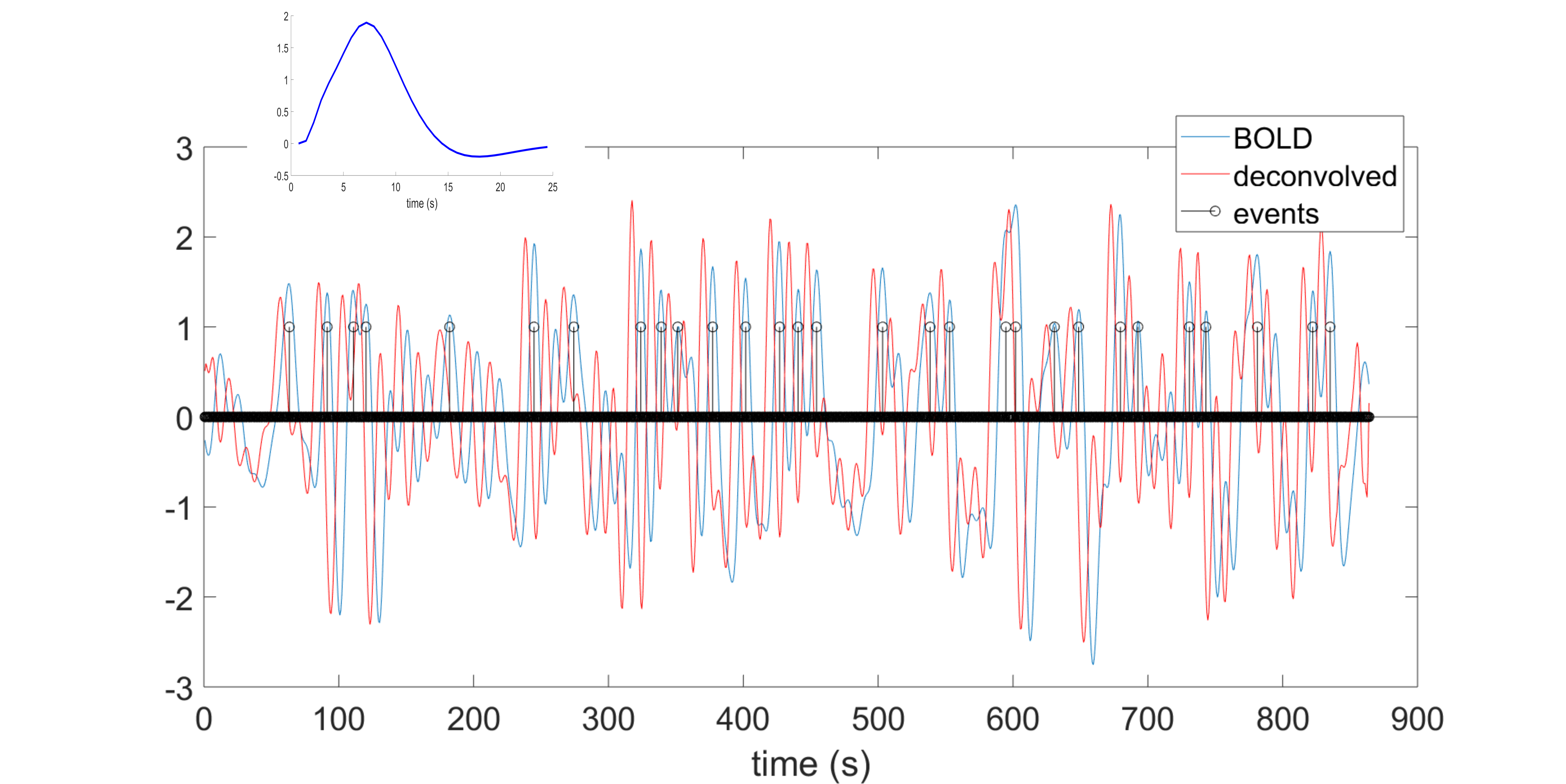
This toolbox is aimed to retrieve the onsets of pseudo-events triggering an hemodynamic response from resting state fMRI BOLD voxel-wise signal. It is based on point process theory, and fits a model to retrieve the optimal lag between the events and the HRF onset, as well as the HRF shape, using either the canonical shape with two derivatives, or a (smoothed) Finite Impulse Response.
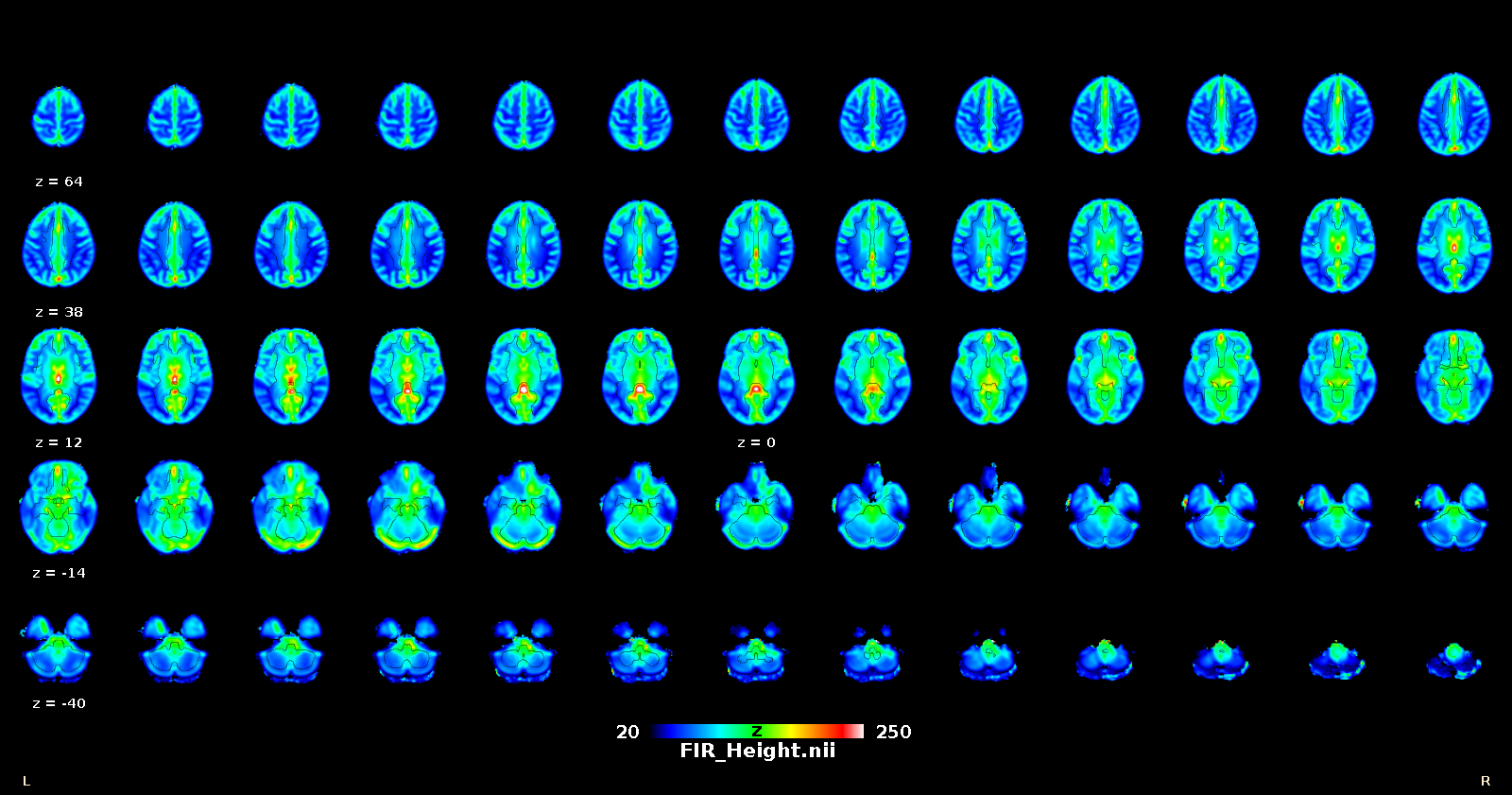
Once that the HRF has been retrieved for each voxel, it can be deconvolved from the time series (for example to improve lag-based connectivity estimates), or one can map the shape parameters everywhere in the brain (including white matter), and use the shape as a pathophysiological indicator.
The input is voxelwise BOLD signal, already preprocessed according to your favorite recipe. Important thing are:
- bandpass filter in the 0.01-0.08 Hz interval (or something like that)
- z-score the voxel BOLD time series
To be on the safe side, these steps are performed again in the code.
The input can be images (3D or 4D), or directly matrices of [observation x voxels].
It is possible to use a temporal mask to exclude some time points (for example after scrubbing).
The demos allow you to run the analyses on several formats of input data.
A BIDS-App has been made for easy and reproducible analysis. Its documentation can be accessed at:
http://bids-apps.neuroimaging.io/rsHRF/
-
Guorong Wu
-
Nigel Colenbier
-
Sofie Van Den Bossche
-
Daniele Marinazzo
-
Madhur Tandon (Python - BIDS)
-
Asier Erramuzpe (Python - BIDS)
References
-
Guo-Rong Wu, Wei Liao, Sebastiano Stramaglia, Ju-Rong Ding, Huafu Chen, Daniele Marinazzo*. "A blind deconvolution approach to recover effective connectivity brain networks from resting state fMRI data." Medical Image Analysis, 2013, 17:365-374. PDF
-
Guo-Rong Wu, Daniele Marinazzo. "Sensitivity of the resting state hemodynamic response function estimation to autonomic nervous system fluctuations." Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 2016, 374: 20150190. PDF
-
Guo-Rong Wu, Daniele Marinazzo. "Retrieving the Hemodynamic Response Function in resting state fMRI: methodology and applications." PeerJ PrePrints, 2015. PDF
More input parameters cloud be exposed (https://github.com/BIDS-Apps/rsHRF/blob/4546c38feeb196cce5cfc60563398d32906891e6/rsHRF/CLI.py)