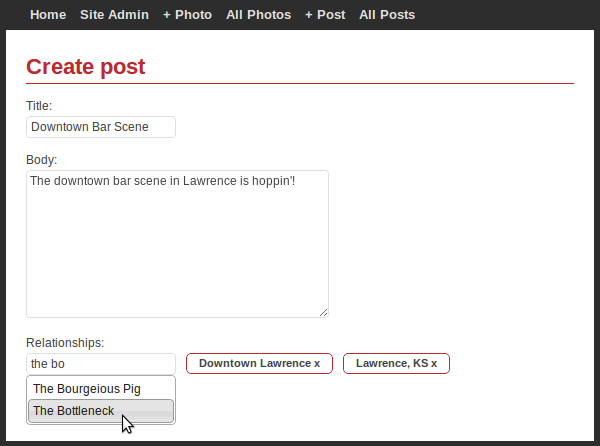
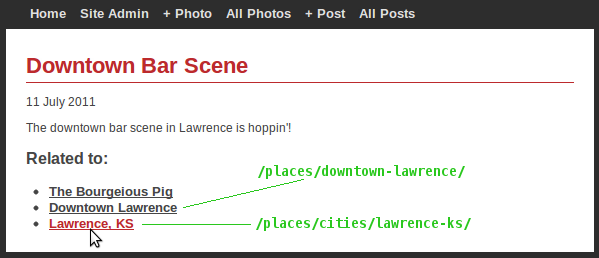
relate anything to anything. the image below is a screenshot of the example app and shows a blog post that has been "related" to 2 "Place" models and a "City" model:
check the documentation for more examples and an in-depth description of the app (or keep reading for the 30 second version).
the purpose of this project is to allow you to create database-level relationships between various objects using a consistent api.
bundled with the source code is an example app which shows how generic-m2m can be used to create "tags" between models. it uses nathanborror's basic apps with django-completion (shameless plug) to allow users to "autocomplete" various relationships between models, so if I'm a user and want to create a new blog post I can tag it with relationships to objects representing a city, a place, a funny photo of a cat, etc.
say you have a couple models:
class Food(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=255)
related = RelatedObjectsDescriptor()
def __unicode__(self):
return self.name
class Beverage(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=255)
related = RelatedObjectsDescriptor()
def __unicode__(self):
return self.name
Here's a sample interactive interpreter session to show the basic API:
>>> pizza = Food.objects.create(name='pizza')
>>> pepperoni = Food.objects.create(name='pepperoni')
>>> beer = Beverage.objects.create(name='beer')
>>> soda = Beverage.objects.create(name='soda')
>>> pizza.related.connect(pepperoni)
<RelatedObject: pizza related to pepperoni ("")>
>>> pizza.related.connect(beer)
<RelatedObject: pizza related to beer ("")>
>>> pepperoni.related.related_to()
[<RelatedObject: pizza related to pepperoni ("")>]
>>> pizza.related.all()
[<RelatedObject: pizza related to beer ("")>, <RelatedObject: pizza related to pepperoni ("")>]
>>> pizza.related.all().generic_objects()
[<Beverage: beer>, <Food: pepperoni>]
>>> Food.related.all()
[<RelatedObject: pizza related to beer ("")>, <RelatedObject: pizza related to pepperoni ("")>]