Distributor is a WordPress plugin that makes it easy to distribute and reuse content across your websites — whether in a single multisite or across the web.
You can learn more about Distributor's features at DistributorPlugin.com and documentation at the Distributor documentation site.
Note: The latest stable version of the plugin is the stable branch. Download the stable branch if you are intending to use the plugin in a Production environment.
- Features
- Requirements
- Installation
- How to Distribute Content
- Known Caveats/Issues
- Developers
- Changelog
- Contributing
Distributor supports safe, SEO-friendly content reuse and sharing via "pushing" and "pulling".
While logged in and editing or viewing any single post (or custom post type) that can be distributed, a Distributor admin bar item will appear, that will facilitate sharing ("pushing") that content to any connection.
In the admin dashboard, a top level Distributor menu item links to the "pull" screen. Here, editors can share ("pull") content from any connection into the current site.
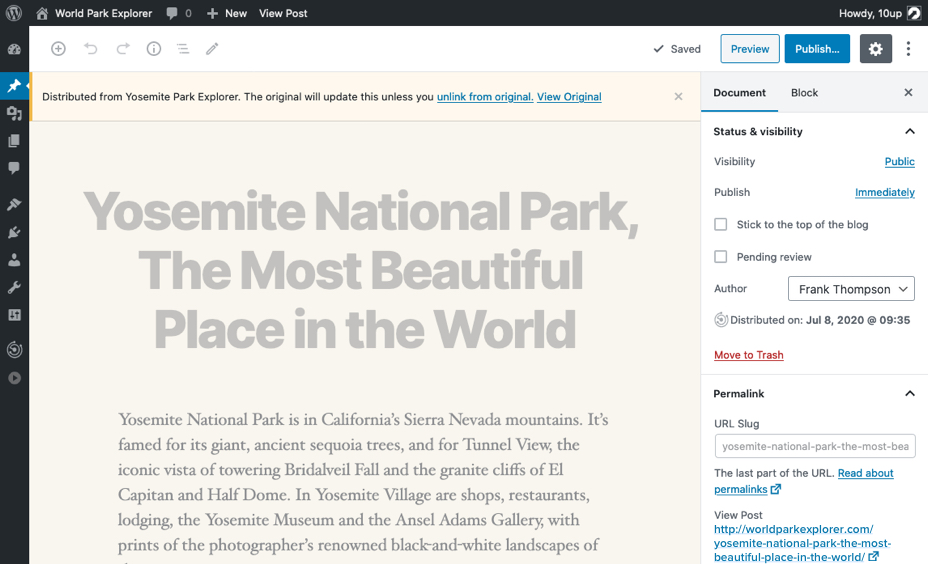
Content this is distributed (via Push or Pull) is connected to the original. Reposted content receives updates from the original, canonical source automatically.
There are two connection types: internal and external.
- Internal connections are other sites inside of the same multisite network. Any user logged into the network can distribute any content in the network to any other sites in the network where that user has permission to publish posts (assuming the site supports the same post type).
- External connections are external websites, connected by the JSON REST API using the Authorization Setup Wizard for External Connections leveraging Application Passwords. External connections can be added in the WordPress admin dashboard under
Distributor>External Connections. Administrators can decide which user roles are allowed to distribute content to and from that connection (Editors and Administrators by default). All users with those roles will inherit the permissions of the user account used to establish the remote connection.
Distributor is built with the same extensible approach as WordPress itself, with fully documented hooks and filters to customize its default behavior and create custom distribution workflows. You can even create connections to other platforms.
- PHP 7.4+
- WordPress 5.7+
- External connections require HTTP Basic Authentication or WordPress.com OAuth2 (must be on WordPress VIP) be set up on the remote website. For Basic Auth, we recommend using Application Passwords built in to WordPress.
- For external connections, Distributor needs to be installed on BOTH sides of the connection.
- Version 2.0.0 of Distributor requires version 2.0.0 on BOTH sides of all connections. For other version 2.0.0 specific changes, please see our migration guide.
For Production use, we recommend registering and downloading the plugin from DistributorPlugin.com – it's 100% free. You will be emailed a direct link to download the latest, production-ready build. Alternatively, you can download the latest release from GitHub.
You can upload and install the archived (zip) plugin via the WordPress dashboard (Plugins > Add New -> Upload Plugin) or manually inside of the wp-content/plugins directory, and activate on the Plugins dashboard.
To help inform our roadmap, keep adopters apprised of major updates and changes that could impact their websites, and solicit opportunities for beta testing and feedback, we’re asking for a little bit of information in exchange for a free key that unlocks update notifications and 1-click upgrades inside the WordPress dashboard. Your information is kept confidential. You can register here and input your key in Distributor settings in the dashboard (network dashboard for multisite users). Note that you need to input the email address you used to register Distributor (included in the email with your registration key) as that is linked to the registration key.
- Ensure that the current version of Distributor is active on BOTH sites being connected. We'll refer to these as mainsite.com and remotesite.com.
- On mainsite.com, navigate to
Distributor>External Connectionsand clickAdd New. - Enter a label for the connection (e.g.,
remotesite). - Enter the URL (e.g.
https://remotesite.com) for your remote site below the External Site URL and press theAuthorize Connectionbutton. - You will be prompted to enter the user name and password of an administrative role of the
remotesite.comif you are not already logged intoremotesite.comand then redirected to the Authorize Application screen. - At the Authorize Application screen, enter the name of the main site and press the 'Yes, I approve of this connection' button
- Review the roles selected in
Roles Allowed to Pushare the ones you want to support, update if necessary, then press theUpdate Connectionbutton.
There are two methods for distributing content between multiple WordPress sites, Push and Pull. Pushing allows you to share content from your site to one or more connected sites while Pulling allows you to bring content into your site from one of your connected sites. In either method, once content has been distributed it will stay in sync with any changes made to the origin post (when Pushing the origin is the site being Pushed from, when Pulling the origin is the site being Pulled from).
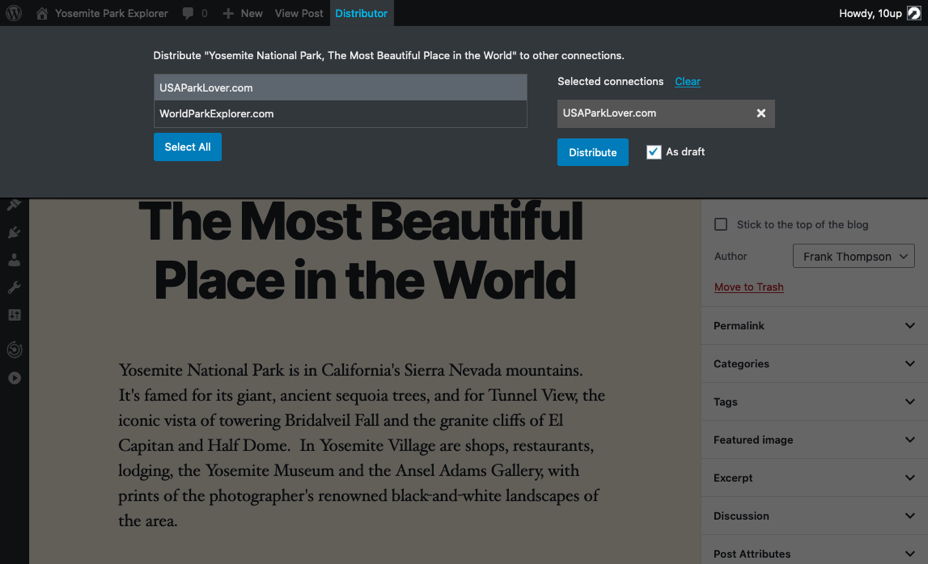
The Distributor menu in the WP Admin Bar will appear after a piece of content has been published. Hovering over that menu item will expose the Push menu that displays the list of connected sites on the left, the list of sites that have been selected for push distribution on the right, and a button to Distribute the content to those selected sites.
The same Push menu and set of Distributor options are also available after publishing a piece of content within the WordPress Block Editor.
After you click the Distribute button, Distributor will push the content to the selected connected sites, showing a View link when those pieces of content have been distributed, and noting Post successfully distributed. once the content has completed distributing to selected sites.
When viewing that piece of content in the Block Editor, there will be a Distributor notice in the Status & visibility section noting how many sites the content has been distributed to.
The same Push menu is available in the WP Admin Bar if you are using the Classic Editor. The Distributor notice is also available in the Publish metabox noting how many sites the content has been distributed to.
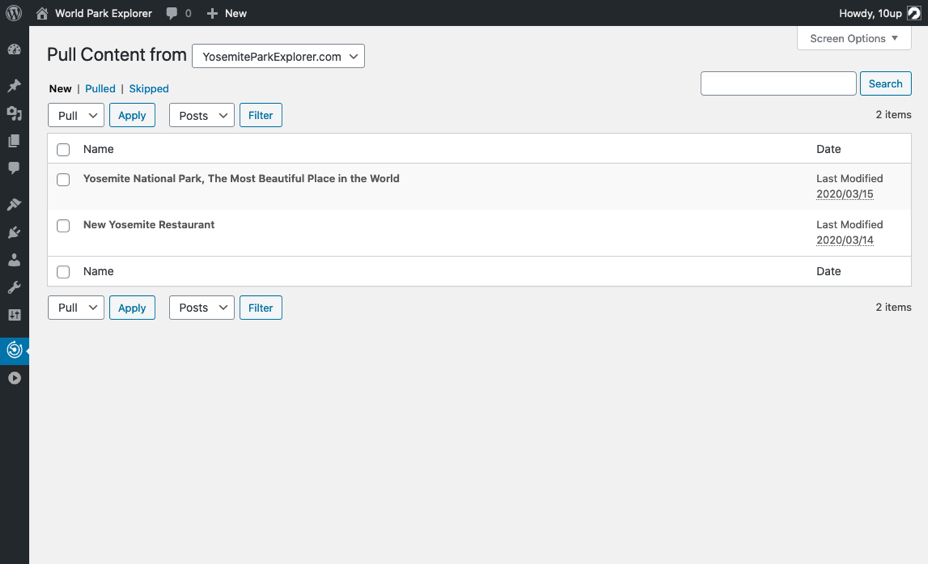
Navigating to the Distributor > Pull Content screen in the WP Admin will present you with a dropdown to select any of the sites you are connected to and will display all available pieces of content that can be Pulled into the current site. You can select Posts, Pages, and other Custom Post Types to filter on this screen; you can use the Bulk Edit menu to Pull or Skip more than one piece of content at a time; and you can use individual row actions on each piece of content pull, view, or skip each piece of content.
After you have Bulk Pulled several pieces of content or used the row actions to Pull a single piece of content, the Pull Content screen will show a confirmation message that the Pull action was successful and redirect you to the Pulled list view to see all the items that have been pulled into the current site. The same process will happen if you opt to Skip specific piece(s) of content.
You can navigate to the Posts > All Posts table list view to see all content that has been pushed or pulled to the current site via the Distributor column denoted with the Distributor icon (). Rows that include the Distributor icon will link off that icon to the origin site and post where that content was either pushed or pulled from.
Active: 10up is actively working on this, and we expect to continue work for the foreseeable future including keeping tested up to the most recent version of WordPress. Bug reports, feature requests, questions, and pull requests are welcome.
Remote Request Timeouts - With external connections, HTTP requests are sent back and forth - creating posts, transfering images, syncing post updates, etc. In certain situations, mostly commonly when distributing posts with a large number of images (or very large file sizes), using poorly configured or saturated servers / hosts, or using plugins that add significant weight to post creation, Distributor requests can fail. Although we do some error handling, there are certain cases in which post distribution can fail silently. If distribution requests are taking a long time to load and/or failing, consider adjusting the timeout; you can filter the timeout for pushing external posts using the dt_push_post_timeout filter. More advanced handling of large content requests, and improved error handling is on the road map for a future update.
Post Meta Associations - A distributed post includes all of the post meta from the original version. Sometimes arbitrary post meta references an ID for another piece of content on the original site. Distributor does not "bring along" the referenced content or update references for arbitrary post meta (it will take care of updating references in the case of core WordPress features, such as the featured image ID). This issue is very common when using field management plugins like Advanced Custom Fields (ACF). This can be addressed on a case by case basis by extending the plugin; for external connections, you can manually handle post meta associations using the dt_push_post hook. For internal connections, use the dt_push_post hook. Note that while named the same, these hooks accept different parameters.
Deleting Distributed Posts - When a post that has been distributed is deleted, the distributed copies will become unlinked ("forked") from the original and thus become editable. Similarly, when a distributed post is unpublished, distributed copies will not be unpublished. More sophisticated "removal" workflow is on the road map for a future update.
Gutenberg Block Mismatch - When distributing a Gutenberg post to another site that supports Gutenberg, if a block in the post does not exist on the receiving site, the block will be converted to a "Classic" HTML block.
Parent Posts - Distributor does not "bring along" parent (or child posts). If your post (or custom post type) has a parent or a child, it will distribute it as if it's an orphan.
Custom Post Type Support - Internal Connections (multisite) support multiple post types. In order for distribution to work with External Connections that have custom post type content, that post type needs to be registered with the argument show_in_rest => true on the external site.
Unable to Push to New Custom Post Types - If new Custom Post Types are created after establishing an External Connection, you will only be able to Pull those from an External Connection. To ensure you are able to Push new Custom Post Types to an External Connection, you will need to update the External Connection by editing it and then clicking the Update connection button.
Backwards Compatibility - While we strive to be mindful of backwards compatibility much the same way WordPress itself is, we do not currently guarantee continued interoperability between different versions of Distributor. We assume the current userbase for this plugin has a high degree of control over any site that has been set up as an external connection and urge you to keep Distributor up to date.
Distributing Post content - By default, post content is rendered before being copied. This means that shortcodes are expanded before being distributed and remote posts will not have the shortcode, but rather the expanded HTML content.
Distributing Authors - By default, distributed posts reference the original site as the "author" with a link to it. This can be altered by extending Distributor with custom code to make it sync authors.
Distributing Post Date - By default, the "post date" on distributed posts is the date its published on the remote site, not the date published on the origin site. This can be overridden by extending Distributor with custom code to make it preserve the post date.
Distributing Canonical URL - By default, canonical URL of distributed post will point to original content, which corresponds to SEO best practices. This can be overridden by extending Distributor with custom code and removing Distributor's default front end canonical URL filtering (look for 'get_canonical_url' and 'wpseo_canonical').
Drafts as Preferred Status - By default, drafts are the preferred status and can't be changed at the source site.
Conflicts with Security plugins - Oftentimes the communication Distributor attempts to make across sites using the REST API will be flagged by various security plugins and surreptitiously blocked. If you run into an issue like this, please reach out to the support for your security plugin and ask about getting Distributor unblocked (here is an example for doing so with Wordfence).
See Distributor Developer Documentation.
A complete listing of all notable changes to Distributor are documented in CHANGELOG.md.
Please read CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md for details on our code of conduct and CONTRIBUTING.md for details on the process for submitting pull requests to us.