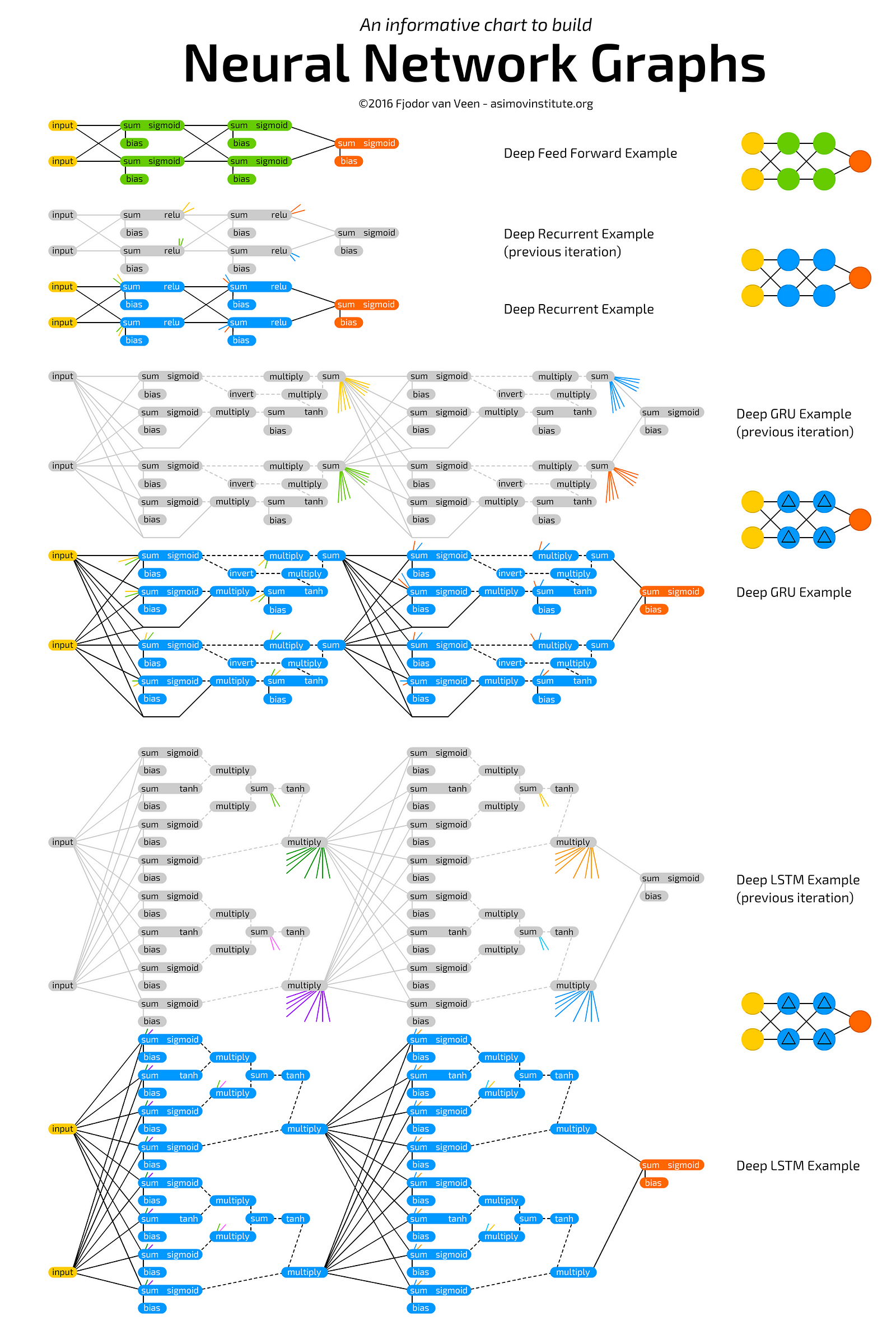
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning or hierarchical learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on learning data representations, as opposed to task-specific algorithms. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.
Deep learning models are loosely related to information processing and communication patterns in a biological nervous system, such as neural coding that attempts to define a relationship between various stimuli and associated neuronal responses in the brain.
Deep learning architectures such as deep neural networks, deep belief networks and recurrent neural networks have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, audio recognition, social network filtering, machine translation, bioinformatics and drug design, where they have produced results comparable to and in some cases superior to human experts.
- Introduction
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
- Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs)
- Autoencoders