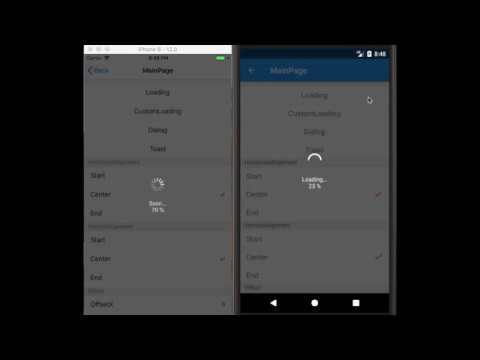
This is a collection of Custom Dialogs that can be defined with XAML for .NET MAUI (Android / iOS).
All dialogs can be created with XAML or c# code in a NETStandard project. Also, they can be arranged the position where you want by specifying LayoutAlignment and Offset properties. Optionally, the animations when the dialog is appearing or disappearing can be set.
iOS: iOS14.2
Android: API22
https://www.nuget.org/packages/AiForms.Maui.Dialogs/
Install-Package AiForms.Maui.Dialogs -preThis is the dialog that can be defined with XAML or c# code. This dialog allows you to freely design the dialog content and arrange anywhere without custom renderer and effects.
It is necessary for Dialog to create the dedicated DialogView derived from ConentView as the following:
public partial class MyDialogView : DialogView
{
public MyDialogView()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
public override void SetUp()
{
// called each opening dialog
}
public override void TearDwon()
{
// called each closing dialog
}
public override void RunPresentationAnimation()
{
// define opening animation
}
public override void RunDismissalAnimation()
{
// define closing animation
}
public override void Destroy()
{
// define clean up process.
}
void Handle_OK_Clicked(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
// send complete notification to the dialog.
DialogNotifier.Complete();
// Use this if you want to specify an arbitrary object for the result.
DialogNotifier.Complete(result);
}
void Handle_Cancel_Clicked(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
// send cancel notification to the dialog.
DialogNotifier.Cancel();
}
}<extra:DialogView
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:extra="clr-namespace:AiForms.Dialogs;assembly=AiForms.Maui.Dialogs"
x:Class="Sample.Views.MyDialogView"
CornerRadius="10" OffsetX="0" OffsetY="0" UseCurrentPageLocation="false"
VerticalLayoutAlignment="Center" HorizontalLayoutAlignment="Center" >
<StackLayout WidthRequest="200">
<Label Text="{Binding Title}" />
<Button Text="Cancel" Clicked="Handle_Cancel_Clicked"/>
<Button Text="OK" Clicked="Handle_OK_Clicked" />
</StackLayout>
</extra:DialogView>You should make use of ContentView Xaml Template with Visual Studio.
Once a DialogView defined, IDialog methods can be used from wherever. To show a dialog, you get an IDialog instance from AiForms.Dialogs.Dialog.Instance and call its ShowAsync method.
using AiForms.Dialogs;
public async Task SomeMethod()
{
var ret = await Dialog.Instance.ShowAsync<MyDialogView>(new{Title="Hello"});
// If canceled, ret is false; Otherwise is true.
// Optionally, view model can be passed to the dialog view instance.
// When the dialog is closed, all related resource automatically are disposed.
// Also, IReusableDialog that keeps the state can be created.
var reusableDialog = Dialog.Instance.Create<MyDialogView>();
ret = await reusableDialog.ShowAsync();
// Even if the dialog is closed, disposing process is not executed.
// ShowAsync can be used any number of times until disposing it.
reusableDialog.Dispose();
}
public async Task SomeResultMethod()
{
var ret = await Dialog.Instance.ShowResultAsync<MyDialogView,MyResult>(new{Title="Hello"});
// Use ShowResultAsync to return any type for the result.
// The object set in Complete<T>(result) is returned.
// Returns null in case of Cancel.
}If you have a clear separation between View and ViewModel and do not want to reference the View from the ViewModel, you can launch dialogs on a ViewModel basis.
To use this feature, you will need to do some initial configuration with Configurations.SetIocConfig.
prism.RegisterTypes(registry =>
{
// Register View and ViewModel with RegisterDialog.
registry.RegisterDialog<VmDialog, VmDialogViewModel>();
});
prism.OnInitialized(container =>
{
var registry = container.Resolve<IDialogViewRegistry>();
// In SetIocConfig, specify a function that returns the View type
// from the ViewModel type and a Resolver function that returns a View instance.
// If these functions are registered correctly, any framework should work,
// even if it is not Prism.
AiForms.Dialogs.Configurations.SetIocConfig(
type => registry.Registrations.Where(x => x.ViewModel == type).LastOrDefault()?.View,
container.Resolve
);
});// Passing a VmDialogViewModel instance generates and displays a VmDialog
// VmDialogViewModel is automatically set in BindingContext.
await Dialog.Instance.ShowAsync(new VmDialogViewModel { Title = "hoge" });
// It is also possible to pass type arguments. In this case, no arguments can be passed.
// Since an instance is created internally using a pre-registered Resolver
// constructor injection can be handled.
await Dialog.Instance.ShowAsync<SomeViewModel>();
// Some methods explicitly indicate VM startup.
await Dialog.Instance.ShowFromModelAsync<SomeViewModel>();
// This one can pass parameters by specifying the parameter type as the second type argument.
await Dialog.Instance.ShowFromModelAsync<SomeViewModel, int>();Prepare a ViewModel with IDialogViewModel<T> applied and receive it with the DialogInitializeAsync method.
public class VmDialogViewModel: IDialogViewModel<int>
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public int Number { get; set; }
public VmDialogViewModel()
{
}
public async Task DialogInitializeAsync(int parameter)
{
await Task.Delay(100);
Number = parameter;
}
}This is the dialog that disappears after some second, which is similar to Android Native Toast Control. This can be defined with XAML or c# code and allows you to freely design the content and arrange anywhere. This feature will be discontinued.
It is necessary for Toast to create the dedicated ToastView derived from ConentView as the following:
public partial class MyToastView : ToastView
{
public MyToastView()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// define appearing animation
public override void RunPresentationAnimation() {}
// define disappearing animation
public override void RunDismissalAnimation() {}
// define clean up process.
public override void Destroy() {}
}<extra:ToastView
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:extra="clr-namespace:AiForms.Dialogs;assembly=AiForms.Maui.Dialogs"
x:Class="Sample.Views.MyToastView"
HorizontalLayoutAlignment="Center"
VerticalLayoutAlignment="Center"
OffsetX="50" OffsetY="50" Duration="{Binding Duration}" >
<StackLayout WidthRequest="150" Spacing="0">
<Label Text="{Binding Title}" />
</StackLayout>
</extra:ToastView>Once a ToastView is defined, IToast methods can be used from wherever. To show a Toast, you get an IToast instance from AiForms.Dialogs.Toast.Instance and call its Show method.
using AiForms.Dialogs;
public async Task SomeMethod()
{
Toast.Instance.Show<MyToastView>(new{Title="Hello",Duration=1500});
// Optionally, view model can be passed to the toast view instance.
}This is the dialog that can't be close by a user, which is appropriate for the notification of loading progress. This has two modes, one is default built-in dialog, the other is custom dialog using LoadingView the same as Dialog or Toast. LoadingView allows you to freely design the content and arrange anywhere. Both of these have the function that notifies progress to the view.
To show a Default Loading Dialog, you get an ILoading instance from AiForms.Dialogs.Loading.Instance and call its StartAsync method.
The following code describes how to use default Loading Dialog:
using AiForms.Dialogs;
using AiForms.Dialogs.Abstractions;
public async Task SomeMethod()
{
// Loading settings
Configurations.LoadingConfig = new LoadingConfig {
IndicatorColor = Color.White,
OverlayColor = Color.Black,
Opacity = 0.4,
DefaultMessage = "Loading...",
};
await Loading.Instance.StartAsync(async progress =>{
// some heavy process.
for (var i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
await Task.Delay(50);
// can send progress to the dialog with the IProgress.
progress.Report((i + 1) * 0.01d);
}
});
}It is necessary for Custom Loading to create the dedicated LoadingView derived from ConentView as the following:
public partial class MyLoadingView : LoadingView
{
Animation animation;
public MyLoadingView()
{
InitializeComponent();
animation = new Animation(v=>{
image.Rotation = 360 * v;
if(v <= 0.3){
image.Scale = 1.0 - 0.5 * v / 0.3;
}
else if(v <= 0.6){
image.Scale = 0.5 + 0.8 * (v - 0.3) / 0.3;
}
else {
image.Scale = 1.3 - 0.2 * (v - 0.6) / 0.4;
}
},0,1,Easing.Linear,()=>{
});
}
// Start Loading animation
public override void RunPresentationAnimation()
{
this.Animate("sample", animation, 16, 1440, null, (v, c) => {
image.Rotation = 0;
image.Scale = 1;
}, () => true);
}
// Stop animation
public override void RunDismissalAnimation()
{
this.AbortAnimation("sample");
}
// Clean up
public override void Destroy() {}
}<extra:LoadingView
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:extra="clr-namespace:AiForms.Dialogs;assembly=AiForms.Maui.Dialogs"
x:Class="Sample.Views.MyLoadingView"
x:Name="Me"
OverlayColor="#2000FF00" >
<StackLayout WidthRequest="60" HeightRequest="60" Spacing="0">
<Image x:Name="image" WidthRequest="36" HeightRequest="36" Source="icon.png" />
<Label Text="{Binding Message}" FontSize="Micro" />
<Label Text="{Binding Progress,Source={x:Reference Me},StringFormat='{0:P0}'}" FontSize="Micro" />
</StackLayout>
</extra:LoadingView>LoadingView has a Progress property of type double, the progress can be expressed by binding the Progress property of itself.
Once a LoadingView is defined, you can create an IReusableLoading instance using ILoading.Create method. Using the StartAsync method of the IReusableLoading instance can show a custom loading dialog.
using AiForms.Dialogs;
public async Task SomeMethod()
{
// Create a IReusableLoading instance.
var reusableLoading = Loading.Instance.Create<MyLoadingView>();
// Optionally, view model can be passed to the dialog view instance.
await reusableLoading.StartAsync(async progress => {
// heavy process
await Task.Delay(1000);
// can send progress to the LoadingView with the IProgress.
progress.Report(1.0);
});
// StartAsync can be used any number of times until disposing it.
reusableLoading.Dispose();
}- A dialog is shown by specifying a Type or a view instance. Optionally, A view model can be passed to in order to bind.
- If canceled, return is false; Otherwise true.
- When the dialog is closed, all related resource automatically are disposed.
- A IReusableDialog instance is created by specifying a Type or a view instance. Optionally, A view model can be passed to in order to bind.
- A dialog is shown.
- If canceled, return is false; Otherwise true.
- Even if the dialog is closed, disposing process is not executed.
- A toast is shown by specifying a Type. Optionally, A view model can be passed to in order to bind.
Task StartAsync(Func<IProgress<double>, Task> action, string message = null, bool isCurrentScope = false)
- A loading dialog is shown and awaited a Task.
- The action is a Func to do target process and return Task. This function has an IProgress instance as a parameter, it allows you to report the progress.
- The message is any string to show below the loading indicator.
- The isCurrentScope is a flag to change the dialog parent view. If true, the dialog parent changes from KeyWindow to current ViewController's view. This only works on iOS.
- A loading dialog is shown without awaiting.
- A loading dialog is hidden.
- The message is changed.
- A IReusableLoading instance is created by specifying a Type or a view instance. Optionally, A view model can be passed to in order to bind.
- A custom loading dialog is shown and awaited a Task.
- A custom loading dialog is shown without awaiting.
- A custom loading dialog is hidden.
This is global default loading dialog settings. Once this instance is set to AiForms.Dialogs.Abstractions.Configurations static property, these will be enabled.
Note that these settings are not used when a custom loading is used.
- OffsetX
- The adjustment relative value from the horizontal layout position.
- OffsetY
- The adjustment relative value from the vertical layout position.
- IndicatorColor
- The icon color for Loading indicator.
- FontSize
- The size for Loading description string.
- FontColor
- The color for Loading description string.
- OverlayColor
- The color of the dialog overlay view.
- Opacity
- The entire opacity. (0-1)
- DefaultMessage
- The default string for loading description.
- ProgressMessageFormat
- The string format for loading description.
- e.g.
{0}\n{1:P0}0:message 1:progress
- IsReusable
- The bool value whether loading view is reused. (default: false)
- Each time a dialog is closed, the instance is disposed of. But if this value turns true, the instance will be reused, even if a dialog is closed, it won't be disposed of.
This is base class of DialogView, ToastView, and LoadingView.
This view is used to specify HorizontalLayoutAlignment, VerticalLayoutAlignment, OffsetX, OffsetX and determine itself position. This view can be set a VisualElement.
Also, the animations the time a dialog appears and disappears, and the cleaning up process the time the dialog is destroyed can be written in virtual methods.
- ProportionalWidth
- The double value in proportion to the Device width. (0-1)
- In case not specified, the WidthRequest value or AutoSizing is used.
- ProportionalHeight
- The double value in proportion to the Device height. (0-1)
- In case not specified, the HeightRequest value or AutoSizing is used.
- VerticalLayoutAlignment
- The vertical position enumeration value (Start / Center / End / Fill) (default: Center)
- HorizontalLayoutAlignment
- The horizontal position enumeration value (Start / Center / End / Fill) (default: Center)
- OffsetX
- The adjustment relative value from the horizontal layout position.
- OffsetY
- The adjustment relative value from the vertical layout position.
- CornerRadius
- The value of a dialog corner radius.
- AutoRotateForIOS
- Whether the screen Auto rotate is enabled for iOS. (default: true)
- DialogMargin
- The margin between window and dialog.
- RunPresentationAnimation
- Write the animation process the time a dialog appears.
- RunDismissalAnimation
- Write the animation process the time a dialog disappears.
- Destroy
- Write the process of cleaning up itself view, which is called when the dialog is destroyed.
Note that animation duration is assumed for 250ms. If it is set larger than the time, the animation may be aborted.
This view is used in order that IDialog or IReusableDialog shows a dialog. This can be used All ExtraView properties and virtual methods and the following properties and virtual methods.
- IsCanceledOnTouchOutside
- The bool value of whether canceling when out of the dialog is touched. (default: ture)
- OverlayColor
- The background color out of the dialog.
- UseCurrentPageLocation
- The bool value of whether the base location of HorizontalLayoutAlignment and VerticalLayoutAlignment is the current page area or the window area.
- If it is true, each edge will be not window's edge but current page edge.
- The controller to notify cancelation or completion from the view to the IDialog instance.
- In the view, if tapping a button make the dialog complete or cancel, write as the follwing code:
void Handle_OK_Clicked(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
DialogNotifier.Complete();
}
void Handle_Cancel_Clicked(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
DialogNotifier.Cancel();
}Altenatively, you can use it in a ViewModel.
<ex:DialogView DialogNotifier="{Binding Notifier}">public IDialogNotifier Notifier { get; set; }
async void Show()
{
await Dialog.Instance.ShowAsync<MyDialogView>(this);
}
void Complete()
{
Notifier.Complete();
}
void Cancel()
{
Notifier.Cancel();
}- SetUp
- Write the process of preparing for itself, which is called just before each opening the dialog for IReusableDialog.
- TearDown
- Write the process of preparing for the next time and cleaning up, which is called just after each closing the dialog for IReusableDialog.
This view is used in order that IToast shows a toast. This can be used All ExtraView properties and virtual methods and the following properties.
Note that a toast can't go over each window edge using OffsetX and OffsetY properties on Android.
- Duration
- The millisecond value until disappearing a toast. (1-3500) (default:1500)
This view is used in order that IReusableLoading shows a loading dialog. This can be used All ExtraView properties and virtual methods and the following properties.
- Progress
- The value of type double for expressing progress.
- This value can be used to express the progress in your custom view.
- OverlayColor
- The background color out of the dialog.
The MIT Licensed.