A package to build multi-staged concurrent workflows with a centralized logging output.
The package could be used to define and execute CI/CD tasks(either sequential or concurrent). A tool with similar goals would be Jenkins Pipeline. However, compared to Jenkins Pipeline, this package has fewer constructs since the logic is specified in code, as opposed to a Jenkinsfile.
It's tiny by design and is valuable when used as a glue rather than a container.
$ go get gopkg.in/myntra/pipeline.v1
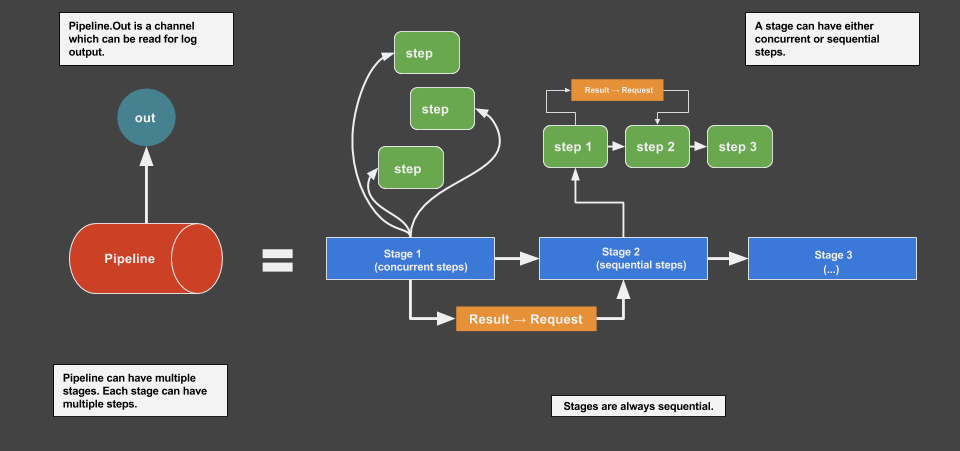
The package has three building blocks to create workflows : Pipeline, Stage and Step . A pipeline is a collection of stages and a stage is a collection of steps. A stage can have either concurrent or sequential steps, while stages are always sequential.
The step block is where the actual work is done. Stage and pipeline act as flow governors.
Step is the unit of work which can be concurrently or sequentially staged with other steps. To do that, we need to implement the
Step interface.
type Step interface {
Out
Exec(*Request) *Result
Cancel() error
}To satisfy the interface we need to embed pipeline.StepContext and implement Exec(*Request)*Result, Cancel()error methods in the
target type. For e.g:
type work struct {
pipeline.StepContext
}
func (w work) Exec(request *pipeline.Request) *pipeline.Result {
return &pipeline.Result{}
}
func (w work) Cancel() error {
return nil
}The pipeline.StepContext type provides a Status method which can be used to log to the out channel. The current step receives a
Request value passed on by the previous step. Internally data(Request.Data and Request.KeyVal) is copied from the previous step's
Result.
The api NewStage(name string, concurrent bool, disableStrictMode bool) is used to stage work either sequentially or concurrently. In terms of the pipeline package, a unit of work is an interface: Step.
The following example shows a sequential stage. For a more complex example, please see: examples/advanced.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/myntra/pipeline"
)
type work struct {
pipeline.StepContext
id int
}
func (w work) Exec(request *pipeline.Request) *pipeline.Result {
w.Status(fmt.Sprintf("%+v", request))
duration := time.Duration(1000 * w.id)
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * duration)
msg := fmt.Sprintf("work %d", w.id)
return &pipeline.Result{
Error: nil,
Data: struct{msg string}{msg:msg},
KeyVal: map[string]interface{}{"msg": msg},
}
}
func (w work) Cancel() error {
w.Status("cancel step")
return nil
}
func readPipeline(pipe *pipeline.Pipeline) {
out, err := pipe.Out()
if err != nil {
return
}
progress, err := pipe.GetProgressPercent()
if err != nil {
return
}
for {
select {
case line := <-out:
fmt.Println(line)
case p := <-progress:
fmt.Println("percent done: ", p)
}
}
}
func main() {
// create a new pipeline
workpipe := pipeline.NewProgress("myProgressworkpipe", 1000, time.Second*3)
// func NewStage(name string, concurrent bool, disableStrictMode bool) *Stage
// To execute steps concurrently, set concurrent=true.
stage := pipeline.NewStage("mypworkstage", false, false)
// a unit of work
step1 := &work{id: 1}
// another unit of work
step2 := &work{id: 2}
// add the steps to the stage. Since concurrent is set false above. The steps will be
// executed one after the other.
stage.AddStep(step1)
stage.AddStep(step2)
// add the stage to the pipe.
workpipe.AddStage(stage)
go readPipeline(workpipe)
result := workpipe.Run()
if result.Error != nil {
fmt.Println(result.Error)
}
fmt.Println("timeTaken:", workpipe.GetDuration())
}Check examples directory for more.
pipeline.Out(): Get all statuses/logs.pipeline.Progress: Get progress in percentage.
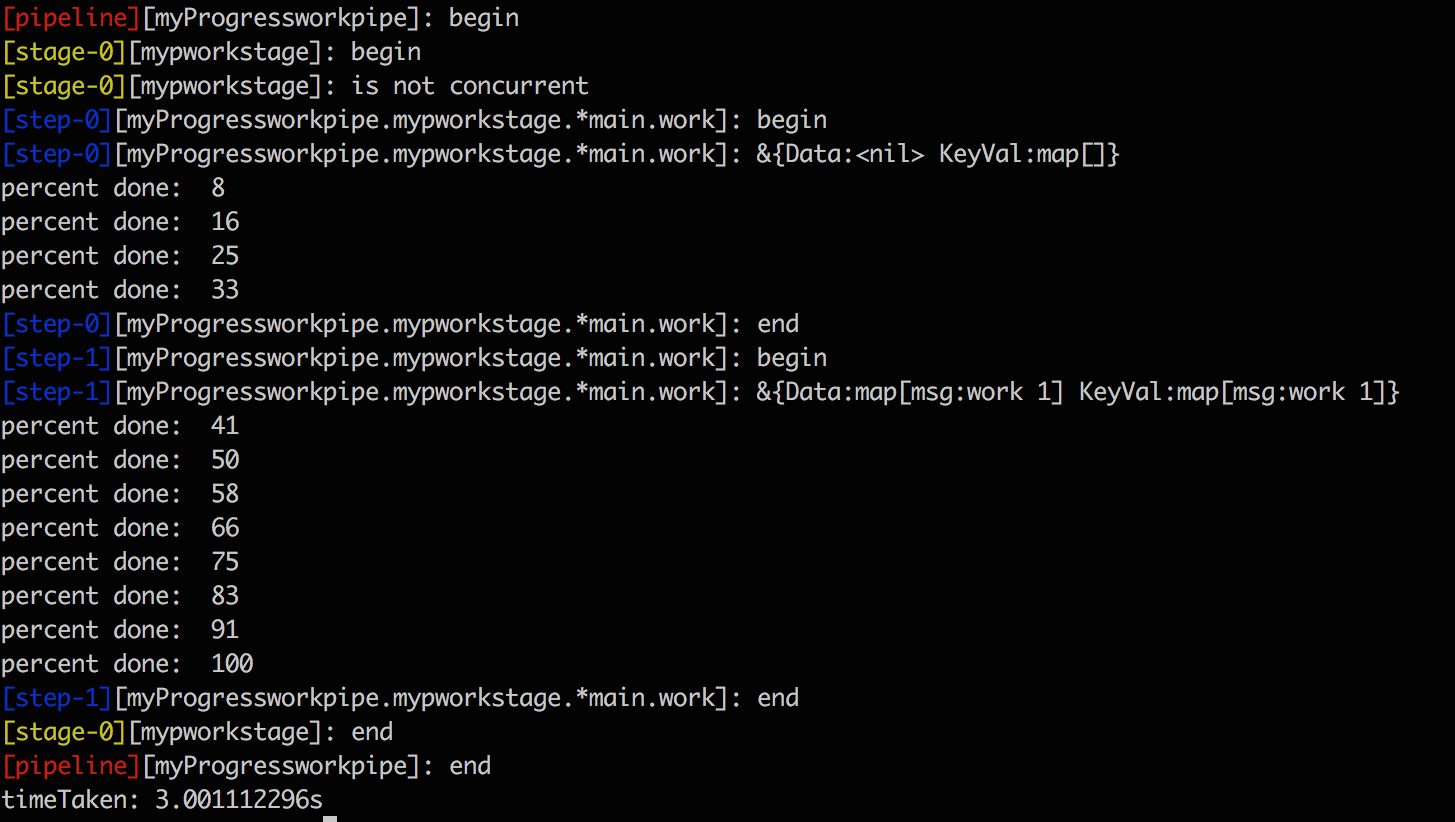
Output of the above example: