-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 959
Debug language server
Use command :CocList services to open services list, you will have id state and filetypes for each service.
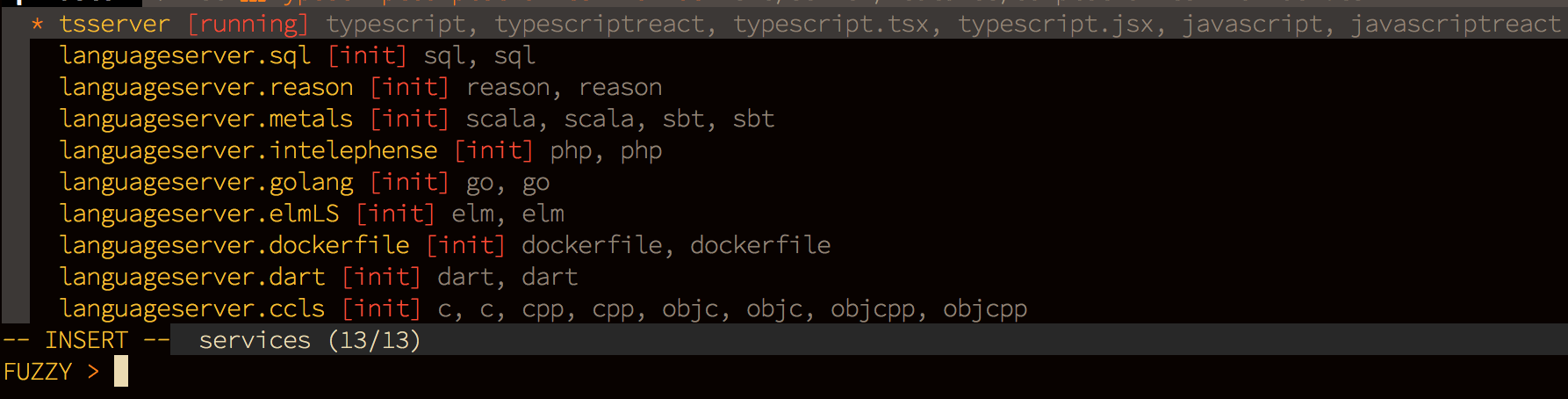
If a service id starts with languageserver, it comes from languageserver configuration in coc-settings.json, if not, it's from an extension of coc.nvim.
The service does not start when a buffer's filetype does not match, use :CocCommand document.echoFiletype to get the detected filetype of the current buffer used by coc.nvim.
The same as VS Code, each language server has its own output channel, the output channel can be opened by:
:CocCommand workspace.showOutput
To make an output channel track all LSP communication, set trace.server to verbose in your coc-settings.json.
For example, to make tsserver from coc-tsserver extension track LSP communication, use:
"tsserver.trace.server": "verbose",To make a user defined language server track LSP communication, add a trace.server section in your language server configuration:
"languageserver":{
"ccls": {
"command": "ccls",
"filetypes": ["c", "cpp", "objc", "objcpp"],
"trace.server": "verbose",
"initializationOptions": {
"cacheDirectory": "/tmp/ccls"
}
}
}However, the output of LSP communication is very terse. You can use LSP Log Parser to parse/view/filter the logs:

You can use Google Chrome to debug a language server which is using node IPC (the language server has to be implemented by JavaScript like CSS language server from coc-css) for communication.
First, add execArgv to the language server settings:
"css.execArgv": ["--nolazy", "--inspect-brk=6045"]
After the css service starts, open Chrome with the url chrome://inspect.
Make sure the Discover network targets option is checked and you have the address added to Target discovery settings, and then you will have the debugging target.
Note it's recommended you install coc-json for automatic JSON completion.