python3 -m venv scrapingdemosource ./scrapingdemo/bin/activatepip install requestspip install beautifulsoup4import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import reUse the Requests library to send a request to a web page from which you want to scrape the data. In this case, https://books.toscrape.com/. To commence, enter the following:
page = requests.get('https://books.toscrape.com/')First, create a Beautiful Soup object and pass the page content received from your request during the initialization, including the parser type. As you’re working with an HTML code, select HTML.parser as the parser type.
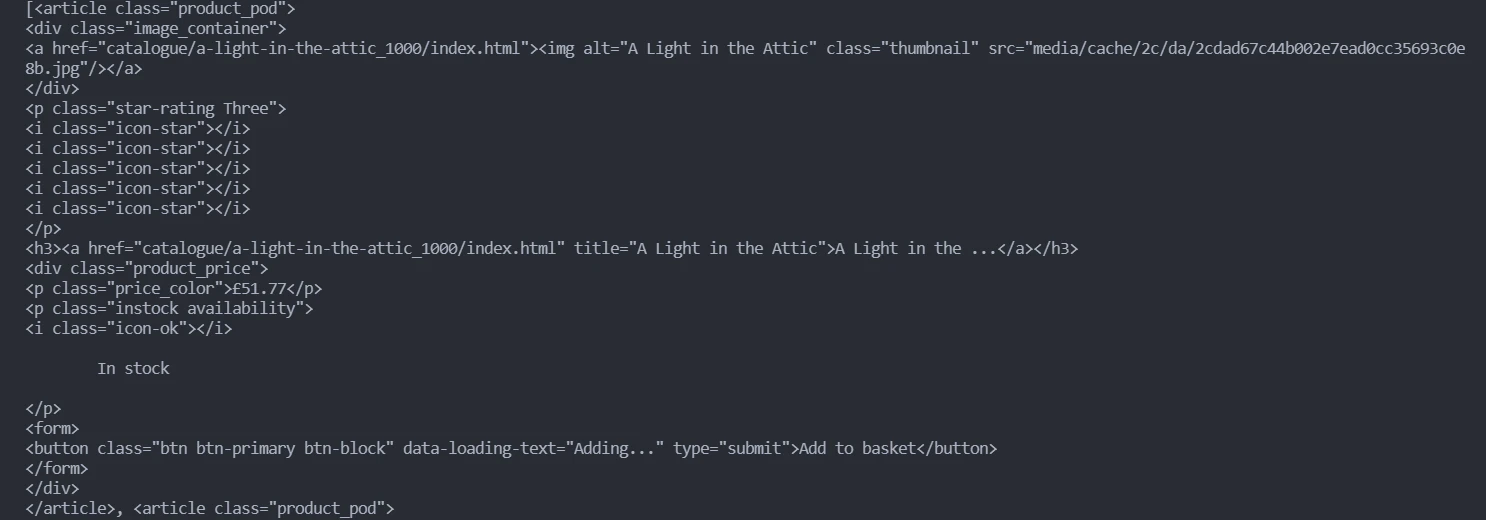
By inspecting the elements (right-click and select inspect element) in a browser, you can see that each book title and price are presented inside an article element with the class called product_pod. Use Beautiful Soup to get all the data inside these elements, and then convert it to a string:
soup = BeautifulSoup(page.content, 'html.parser')
content = soup.find_all(class_='product_pod')
content = str(content)Since the acquired content has a lot of unnecessary data, create two regular expressions to get only the desired data.
First, inspect the title of the book to find the pattern. You can see above that every title is present after the text title= in the format title=“Titlename”.
Then, create an expression that returns the data inside quotations after the title= by specifying "(.*?)".
The first expression is as follows:
re_titles = r'title="(.*?)">'First, inspect the price of the book. Every price is present after the text £ in the format £=price before the paragraph tag </p>.
Then, create an expression that returns the data inside quotations after the £= and before the </p> by specifying £(.*?)</p>.
The second expression is as follows:
re_prices = '£(.*?)</p>'To conclude, use the expressions with re.findall to find the substrings matching the patterns. Lastly, save them in the variables title_list and price_list.
titles_list = re.findall(re_titles, content)
price_list = re.findall(re_prices, content)To save the output, loop over the pairs for the titles and prices and write them to the output.txt file.
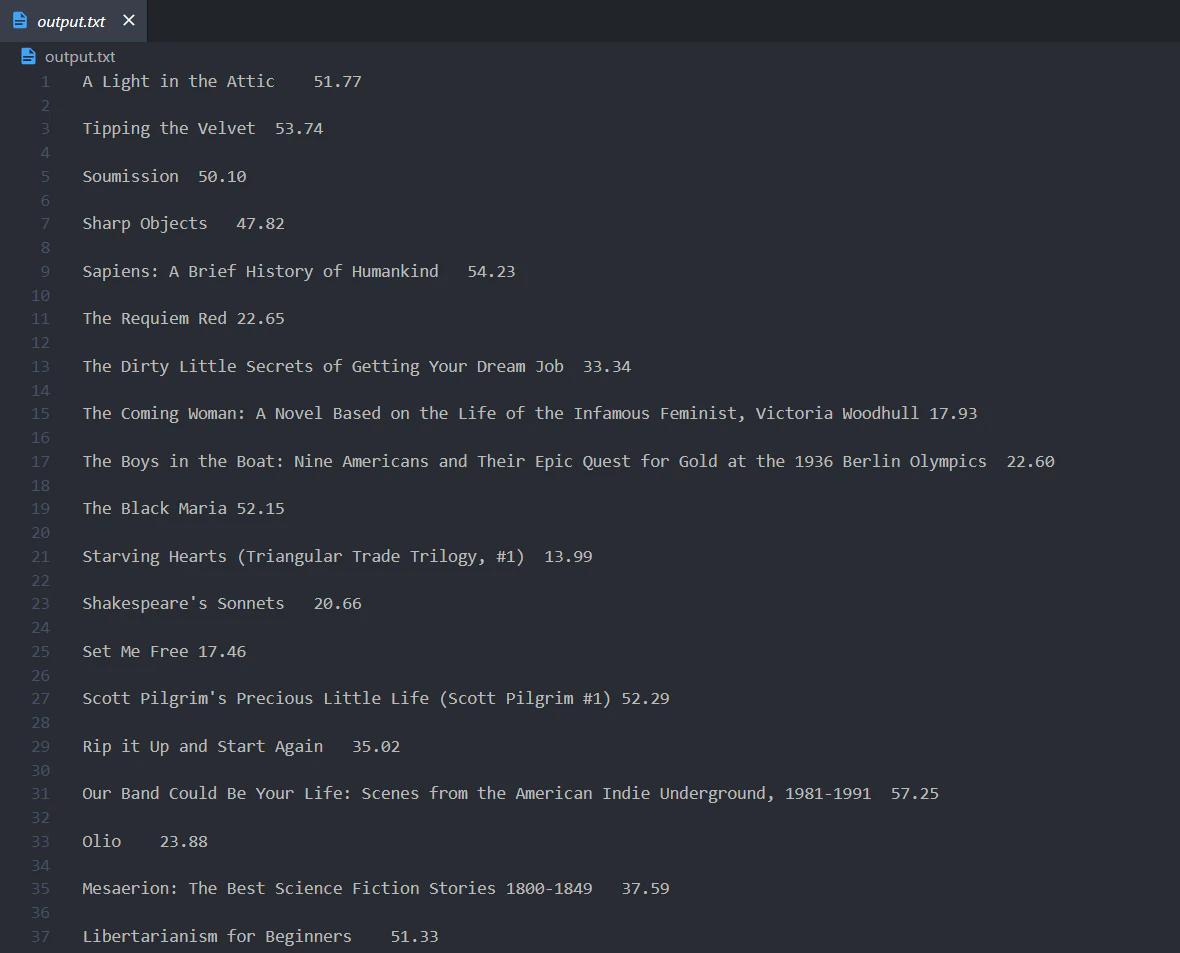
with open("output.txt", "w") as f:
for title, price in zip(titles_list, price_list):
f.write(title + "\t" + price + "\n")Putting everything together, this is the complete code that can be run by calling python demo.py:
# Importing the required libraries.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
# Requesting the HTML from the web page.
page = requests.get("https://books.toscrape.com/")
# Selecting the data.
soup = BeautifulSoup(page.content, "html.parser")
content = soup.find_all(class_="product_pod")
content = str(content)
# Processing the data using Regular Expressions.
re_titles = r'title="(.*?)">'
titles_list = re.findall(re_titles, content)
re_prices = "£(.*?)</p>"
price_list = re.findall(re_prices, content)
# Saving the output.
with open("output.txt", "w") as f:
for title, price in zip(titles_list, price_list):
f.write(title + "\t" + price + "\n")