-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Random wave spectra
This section describes the random wave spectra generation capabilities and associated parameters.
The Bretschneider spectrum is defined as [1]
where 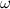



An alternative representation is
where 


The Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP) spectrum is defined as [3]
where
or
where

\sigma_a and \sigma_b indicate the width to the left and right side of the spectral peak, with typical values 0.07 and 0.09, respectively. For f \leq f_p, \sigma=\sigma_a and for f \gt f_p, \sigma = \sigma_b.
\gamma is the peak enhancement factor, defined as the ratio of maximum spectral density to the maximum of a corresponding Pierson-Moskowitz spectrum. Values can range from 1--7 with a typical value of 3.3 Goda (1985).
The Pierson-Moskowitz spectrum is defined as S(f) = \frac{\alpha g^2}{(2 \pi)^4 f^5} e^{-B/f^4},
where the Phillips Constant \alpha = 8.1 \times 10^{-3}, g is the gravitational constant, B=0.74 \left(\frac{g}{2 \pi U}\right)^4, and U is wind speed Sarpkaya (1981).


![S_j(\omega)=\frac{\alpha g^2}{\omega^5}\exp\left[-\frac{5}{4}\left(\frac{\omega_p}{\omega}\right)^4\right]\gamma^r,](http://mathurl.com/zdpaqfq.png)
![r=\exp\left[-\frac{(\omega-\omega_p)^2}{2\sigma^2\omega_p^2}\right],](http://mathurl.com/nkvzauy.png)

