-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 63
paths.scad
Polylines, polygons and paths. To use, add the following lines to the beginning of your file:
include <BOSL/constants.scad>
use <BOSL/paths.scad>
Usage:
- simplify2d_path(path, [eps])
Description: Takes a 2D polyline and removes unnecessary collinear points.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
path |
A list of 2D path points. |
eps |
Largest angle delta between segments to count as colinear. Default: 1e-6 |
Usage:
- simplify3d_path(path, [eps])
Description: Takes a 3D polyline and removes unnecessary collinear points.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
path |
A list of 3D path points. |
eps |
Largest angle delta between segments to count as colinear. Default: 1e-6 |
Usage:
- path3d_length(path)
Description: Returns the length of the path.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
path |
The list of points of the path to measure. |
Example:
path = [[0,0], [5,35], [60,-25], [80,0]];
echo(path_length(path));
Usage:
- path2d_regular_ngon(n, r|d, [cp], [scale]);
Description:
Returns a 2D open counter-clockwise path of the vertices of a regular polygon of n sides.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
n |
Number of polygon sides. |
r |
Radius of regular polygon. |
d |
Radius of regular polygon. |
cp |
Centerpoint of regular polygon. Default: [0,0]
|
scale |
[X,Y] scaling factors for each axis. Default: [1,1]
|
Example:
trace_polyline(path2d_regular_ngon(n=12, r=50), N=1, showpts=true);

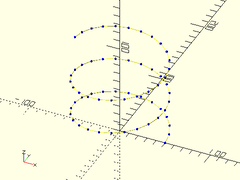
Usage:
- path3d_spiral(turns, h, n, r|d, [cp], [scale]);
Description: Returns a 3D spiral path.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
Height of spiral. |
turns |
Number of turns in spiral. |
n |
Number of spiral sides. |
r |
Radius of spiral. |
d |
Radius of spiral. |
cp |
Centerpoint of spiral. Default: [0,0]
|
scale |
[X,Y] scaling factors for each axis. Default: [1,1]
|
Example:
trace_polyline(path3d_spiral(turns=2.5, h=100, n=24, r=50), N=1, showpts=true);
Usage:
- points_along_path3d(polyline, path);
Description:
Calculates the vertices needed to create a polyhedron() of the
extrusion of polyline along path. The closed 2D path shold be
centered on the XY plane. The 2D path is extruded perpendicularly
along the 3D path. Produces a list of 3D vertices. Vertex count
is len(polyline)*len(path). Gives all the reoriented vertices
for polyline at the first point in path, then for the second,
and so on.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
polyline |
A closed list of 2D path points. |
path |
A list of 3D path points. |
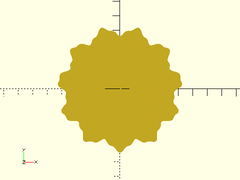
Description: Creates a 2D polygon circle, modulated by one or more superimposed sine waves.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
r |
radius of the base circle. |
sines |
array of [amplitude, frequency] pairs, where the frequency is the number of times the cycle repeats around the circle. |
Example:
modulated_circle(r=40, sines=[[3, 11], [1, 31]], $fn=6);
Description: Extrudes a 2D shape between the points pt1 and pt2. Takes as children a set of 2D shapes to extrude.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
pt1 |
starting point of extrusion. |
pt2 |
ending point of extrusion. |
convexity |
max number of times a line could intersect a wall of the 2D shape being extruded. |
twist |
number of degrees to twist the 2D shape over the entire extrusion length. |
scale |
scale multiplier for end of extrusion compared the start. |
slices |
Number of slices along the extrusion to break the extrusion into. Useful for refining twist extrusions. |
Example:
extrude_from_to([0,0,0], [10,20,30], convexity=4, twist=360, scale=3.0, slices=40) {
xspread(3) circle(3, $fn=32);
}

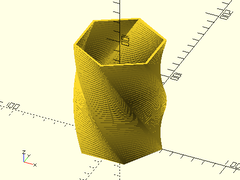
Description: Similar to linear_extrude(), except the result is a hollow shell.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
wall |
thickness of shell wall. |
height |
height of extrusion. |
twist |
degrees of twist, from bottom to top. |
slices |
how many slices to use when making extrusion. |
Example:
extrude_2d_hollow(wall=2, height=100, twist=90, slices=50)
circle(r=40, $fn=6);
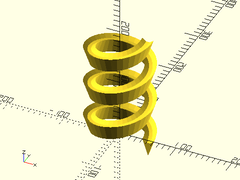
Description: Takes a closed 2D polyline path, centered on the XY plane, and extrudes it along a 3D spiral path of a given radius, height and twist.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
polyline |
Array of points of a polyline path, to be extruded. |
h |
height of the spiral to extrude along. |
r |
radius of the spiral to extrude along. |
twist |
number of degrees of rotation to spiral up along height. |
Example:
poly = [[-10,0], [-3,-5], [3,-5], [10,0], [0,-30]];
extrude_2dpath_along_spiral(poly, h=200, r=50, twist=1080, $fn=36);
Description:
Takes a closed 2D path polyline, centered on the XY plane, and extrudes it perpendicularly along a 3D path path, forming a solid.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
polyline |
Array of points of a polyline path, to be extruded. |
path |
Array of points of a polyline path, to extrude along. |
ang |
Angle in degrees to rotate 2D polyline before extrusion. |
convexity |
max number of surfaces any single ray could pass through. |
Example:
shape = [[0,-10], [5,-3], [5,3], [0,10], [30,0]];
path = concat(
[for (a=[30:30:180]) [50*cos(a)+50, 50*sin(a), 20*sin(a)]],
[for (a=[330:-30:180]) [50*cos(a)-50, 50*sin(a), 20*sin(a)]]
);
extrude_2dpath_along_3dpath(shape, path, ang=140);

Description: Extrudes 2D children along a 3D polyline path. This may be slow.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
path |
array of points for the bezier path to extrude along. |
convexity |
maximum number of walls a ran can pass through. |
clipsize |
increase if artifacts are left. Default: 1000 |
Example:
path = [ [0, 0, 0], [33, 33, 33], [66, 33, 40], [100, 0, 0], [150,0,0] ];
extrude_2d_shapes_along_3dpath(path) circle(r=10, $fn=6);
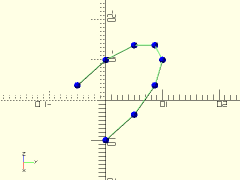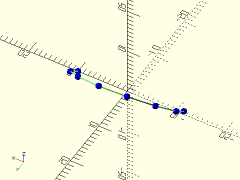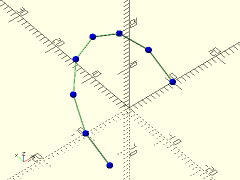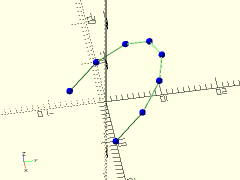
Description: Renders lines between each point of a polyline path. Can also optionally show the individual vertex points.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
pline |
The array of points in the polyline. |
showpts |
If true, draw vertices and control points. |
N |
Mark the first and every Nth vertex after in a different color and shape. |
size |
Diameter of the lines drawn. |
color |
Color to draw the lines (but not vertices) in. |
Example:
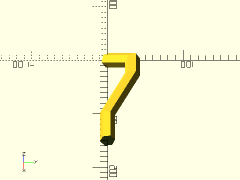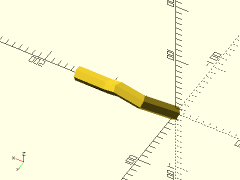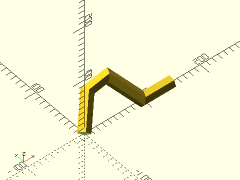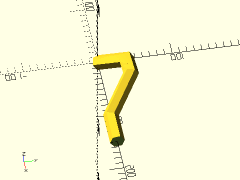
polyline = [for (a=[0:30:210]) 10*[cos(a), sin(a), sin(a)]];
trace_polyline(polyline, showpts=true, size=0.5, color="lightgreen");
Description:
A drop-in replacement for polygon() that renders and labels the path points.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
points |
The array of 2D polygon vertices. |
paths |
The path connections between the vertices. |
convexity |
The max number of walls a ray can pass through the given polygon paths. |
Example:
debug_polygon(
points=concat(
path2d_regular_ngon(r=10, n=8),
path2d_regular_ngon(r=8, n=8)
),
paths=[
[for (i=[0:7]) i],
[for (i=[15:-1:8]) i]
]
);
