An interactive visualization of straight skeletons and their construction.
A straight skeleton is a representation of a polygon by a skeleton. The edges of the polygon are moved inwards parallel to themselves at constant speed. This process is called shrinking. The straight skeleton is the set of lines traced out by moving vertices in this process.
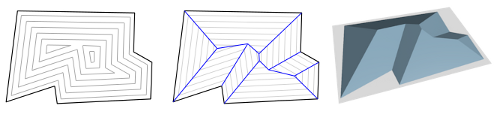
Given a polygon, we implement a shrinking algorithm that constructs the straight skeleton. An example starts with a polygon (left) and constructs the straight skeleton (middle). This can be applied to construciton of a roof with constant slope over a polygonal building (right):
- Clone repo
- Open index.html
This repository is not under active development by the authors, but we highly encourage contributions for multiple reasons:
- Simple Tech Stack: JS and P5
- Algorithmic development: I would take a different approach to the algorithm knowing what I know now. Visit the literature to understand straight skeletons.
- Course development: this was developed as an interactive visualization to educate our Computational geometry class on this topic.
Edge event: An edge shrinks to zero, making its neighboring edges adjacent
Split event: A reflex vertex runs to this edge and splits it, thus splitting the entire polygon. New adjacencies occur between the split edge and each of the two edges incident to the reflex vertex.
- Initialize polygon as list of lines (|V|,|E|)
- Define lambda, where lambda is the constant distance that each edge will shrink in every iteration
- direction = list of tuples of length |V|
- for each line: extract points and determine which direction to shrink
- while(not done): if(split event): break up into two polygons newpts = shrink(pts, direction) for each existing polygon
- create new lines from pts to newpts for each existing polygon
- Repeat 3-6 until all edges have edge event
The program will be a webpage where users will be able to draw a polygon on the screen with their mouse. This will be done by clicking the screen at the location where an edge of the polygon should start, moving the cursor to the location where it should end, and clicking again, which will generate the edge visually on the screen between those two points.
Once this is done, the point at the end of the first edge will be set as the start of the second edge, and the next place the user clicks will generate the second edge between those two points on the screen.
This process is repeated until the user generates a line which creates a full polygon.
Once the polygon is created, the program will then display the process of the construction of the straight skeleton. This will show the lines being created as the edges of the polygon move inward.