A flexible web view and analysis platform for solver log files of mathematical optimization software, backed by Elasticsearch.
This is a detailed description of how to set up Rubberband.
Java 8 is required to run Elasticsearch. For Ubuntu, you can install Java 8 this way.
sudo apt-get install python-software-properties
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
To confirm that Java is properly installed, check the version.
$ java -version
java version "1.8.0_101"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_101-b13)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.101-b13, mixed mode)
Now you're ready to install Elasticsearch. NOTE: Elasticsearch is rapidly developing software. Only 2.x versions of Elasticsearch are supported by Rubberband. Sadly, Elasticsearch is neither backwards- nor forwards-compatible. Here are the most current instructions for installing Elasticsearch with apt on Ubuntu.
wget -qO - https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
echo "deb http://packages.elastic.co/elasticsearch/2.x/debian stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elasticsearch-2.x.list
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install elasticsearch
General instructions for installing Elasticsearch can be found in the offical Elasticsearch documentation.
More information about running Elasticsearch as a service can be found here, though this shouldn't be required for a development setup.
Rubberband is built on tornado and IPET, an interactive performance evaluation tool that comes with a parsing library for benchmark files. To get Rubberband running locally, make sure you first have Elasticsearch installed and running.
sudo service elasticsearch start
Now clone this repository and set up a virtual environment.
virtualenv -p python3 --no-site-packages venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt
The first install command will clone and install IPET from github, you don't need to do this manually.
For a deployed version of Rubberband copy the configuration file in config/app.cfg into /etc/rubberband/, and edit the required variables. Rubberband has some sane defaults already configured, so this step isn't strictly required. However, if you want to connect Rubberband to a Gitlab instance, or to an SMTP server to send email, you will need to edit app.cfg.
NOTE: If you install Rubberband as a developer version, you don't need to do this.
To populate the database or run unit tests, first install Rubberband inside the virtualenv.
pip install -e .
Now take a look at the control script in bin/rubberband-ctl. Running the control script with no options will show the help. For first-time, create the index, and populate that index with data. This can be accomplished with the following two commands.
bin/rubberband-ctl create-index
bin/rubberband-ctl populate-index
The second command will need a few minutes to finish. If the commands complete sucessfully, stdout should look something like this:
WARNING:elasticsearch:HEAD /solver-results [status:404 request:0.005s]
INFO:elasticsearch:PUT http://127.0.01:9200/solver-results [status:200 request:0.107s]
INFO:elasticsearch:HEAD http://127.0.01:9200/solver-results [status:200 request:0.002s]
INFO:elasticsearch:PUT http://127.0.01:9200/solver-results/_mapping/file [status:200 request:0.041s]
INFO:elasticsearch:HEAD http://127.0.01:9200/solver-results [status:200 request:0.002s]
INFO:elasticsearch:PUT http://127.0.01:9200/solver-results/_mapping/testset [status:200 request:0.019s]
INFO:root:Loading additional configuration from /etc/rubberband/app.cfg
INFO:root:Setting up Elasticsearch connection.
INFO:rubberband.utils.importer:debug opened a connection to elasticsearch with the ResultClient
INFO:rubberband.utils.importer:Found 4 files. Beginning to parse.
INFO:urllib3.connectionpool:Starting new HTTP connection (1): 127.0.01
INFO:elasticsearch:GET http://127.0.01:9200/solver-results/testset/_search [status:200 request:0.057s]
INFO:rubberband.utils.importer:Adding SoluFile.
...
Cross your fingers and run the following command from your virtual environment.
python server.py
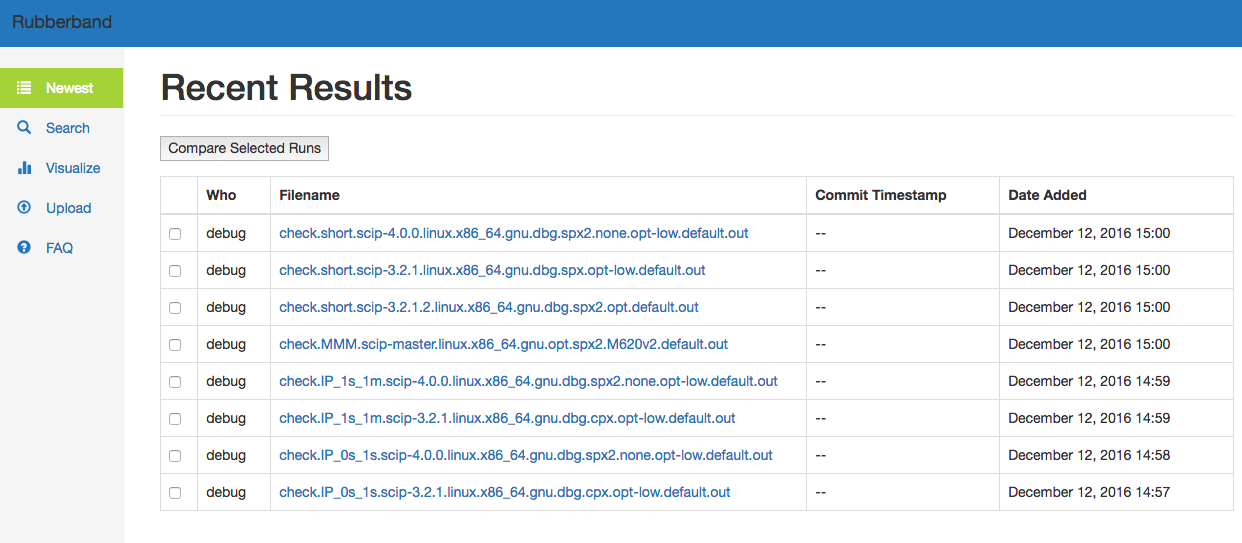
If everything went well, you should be able to open http://127.0.0.1:8888/ in your browser and see something that looks like this.
To build the documentation run the following commands from inside the virtualenvironment:
cd doc
make doc
Now you can view the documentation by opening doc/build/html/index.html in your favorite webbrowser.
Run the test suite.
py.test -v tests/
Tests will fail if Elasticsearch is not running, or if the index is empty or if you didn't configure authentication correctly.
Rubberband currently requires a connection to an Elasticsearch 2.x instance and (optionally) a Gitlab instance to run. To configure a Gitlab connection, edit the configuration variables in /etc/rubberband/app.cfg beginning with gitlab_. The Gitlab connection is used to look up information from the code base that your test set log is linked to. Examples of this type of information are git commit date and last committer. The visualize tab is disabled if no Gitlab connection information is provided.
There is no authentication built into Rubberband, though rubberband will authorize requests to the frontend using the X-Forwarded-Email header. Request made to the API require this header, as well as an X-Api-Token header. This is to say that authentication and setting the appropriate headers is the responsibility of the user/deployer. oauth2_proxy is a convenient proxy that, when properly hooked up to an OAuth provider, will set this header for you.
Rubberband is meant to be deployed behind a production webserver, such as a nginx or apache. See config/rubberband-oauth for a sample nginx configuration. This example shows an HTTPS deployment configured with Let's Encrypt.
Supervisor is a process monitor and manager, and great way to make sure Rubberband keeps running reliably in production.
See CONTRIBUTING.md.