This is a Laravel service provider for winzou/state-machine. It provides dependency injection for the StateMachineFactory. You can also use Laravel's service container to resolve class methods for the callbacks. A facade is also available for convenience.
You can install the package via composer. This package requires Laravel 7.0 or higher.
For previous Laravel versions, please check the compatibility table.
Then require the package using the command-line interface:
composer require sebdesign/laravel-state-machineIf you need to install this package in older Laravel installations, use the table below to find a compatible version.
| Package | Laravel | PHP |
|---|---|---|
| ^3.0 | ^7.0 - ^9.0 |
^7.2.5 |
| ^2.0 | 5.5.* - ^6.0 |
^7.0 |
| ^1.0 | 5.1.* - 5.8.* |
^5.5.9 | ^7.0 |
Since version 5.5, Laravel uses package auto-discovery, so you don't need to manually add the ServiceProvider and the facade. If you don't use auto-discovery or you are using an older version, add the service provider and the facade in config/app.php.
<?php
'providers' => [
Sebdesign\SM\ServiceProvider::class,
],
'aliases' => [
'StateMachine' => Sebdesign\SM\Facade::class,
],Publish the config file in config/state-machine.php.
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Sebdesign\SM\ServiceProvider"Please see the documentation of the StateMachineBundle for all the available options.
<?php
// Get the article
$article = App\Article::find($id);
// Get the state machine for this article, and graph called "simple"
// Using the facade
$stateMachine = StateMachine::get($article, 'simple');
// Or using the service container with dependency injection
public function method(SM\Factory\FactoryInterface $factory)
{
$stateMachine = $factory->get($article, 'simple');
}Now you can use the $stateMachine to interact with the state of the $article.
<?php
// Get the actual state of the object
$stateMachine->getState();
// Get all available transitions
$stateMachine->getPossibleTransitions();
// Check if a transition can be applied: returns true or false
$stateMachine->can('approve');
// Apply a transition: returns true or throws an SM\SMException
$stateMachine->apply('publish');
// Apply a transition without throwing an exception: returns true or false
$stateMachine->apply('publish', true);Callbacks are used to guard transitions or execute some code before or after applying transitions. This package adds the ability to use Laravel's service container to resolve callbacks.
E.g.:
You want to call the handle method on the MyService class to determine if the state machine can apply the submit_changes transition.
<?php
'callbacks' => [
// will be called when testing a transition
'guard' => [
'guard_on_submitting' => [
// call the callback on a specific transition
'on' => 'submit_changes',
// will call the method of this class
'do' => ['MyService', 'handle'],
// arguments for the callback
'args' => ['object'],
],
],
],You can specify callbacks in array format, e.g. ['Class', 'method'], or in @ delimited string format, e.g. Class@method.
If you don't want to use custom classes/methods for guarding, you can use Laravel's authorization gates or policies for determining if a transition can be applied.
Instead of specifying a do key, you must define a can key with the name of the ability you want to check. Since Laravel 5.5, you can also specify an array of abilities, and every one will be checked.
By default, the object instance will be passed as an argument to the gate. You can also override the arguments by specifying them in the args key.
In this example, we have defined a gate which will accept the $article as and argument. You are not required to define this parameter in your gate if you don't need it.
<?php
use App\User;
use App\Article;
Gate::define('approve', function (User $user, Article $article) {
//
});<?php
'callbacks' => [
'guard' => [
'guard_on_approving' => [
// call the gate on a specific transition
'on' => 'approve',
// will call Gate:allows('approve', $article)
'can' => 'approve',
],
],
],Say you have created an ArticlePolicy policy for your Article model, which has an approve method.
You should define approve in the can index. This will be the equivalent of calling $user->can('approve', $article).
You can also override the arguments that will be passed in the approved method, by specifying the args array. You must use object as the first argument in order for the policy class to be resolved. E.g.: 'args' => ['object', '"final_approval"'] would be the equivalent of calling $user->can('approve', [$article, 'final_approval']).
<?php
namespace App\Policies;
use App\User;
use App\Article;
class ArticlePolicy
{
public function approve(User $user, Article $article)
{
//
}
}<?php
'callbacks' => [
'guard' => [
'guard_on_approving' => [
// call the policy on a specific transition
'on' => 'approve',
// will call Gate:allows('approve', $article)
'can' => 'approve',
],
],
],When checking if a transition can be applied, the SM\Event\SMEvents::TEST_TRANSITION event is fired.
Before and after a transition is being applied, the SM\Event\SMEvents::PRE_TRANSITION and SM\Event\SMEvents::POST_TRANSITION events are fired respectively.
All the events receive a Sebdesign\SM\Event\TransitionEvent instance.
If you wish to listen to all the events with the same listener, you can use the winzou.state_machine.* wildcard parameter.
You can define your own listeners in your app's EventServiceProvider. E.g.:
<?php
use SM\Event\SMEvents;
/**
* The event listener mappings for the application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $listen = [
SMEvents::TEST_TRANSITION => [
\App\Listeners\CheckTransition::class,
],
SMEvents::PRE_TRANSITION => [
\App\Listeners\BeforeTransition::class,
],
SMEvents::POST_TRANSITION => [
\App\Listeners\AfterTransition::class,
],
'winzou.state_machine.*' => [
\App\Listeners\Transition::class,
],
];You can also pass additional data as an array when checking or applying transitions.
This array will be passed to the Sebdesign\SM\Event\TransitionEvent.
You can access the array using $event->getContext() in your event listeners or callbacks.
Example using an event listener:
<?php
// Reject the transition of the approval date is past
Event::listen(SMEvents::TEST_TRANSITION, function (TransitionEvent $event) {
$context = $event->getContext();
if ($context['approved_at']->isPast()) {
$event->setRejected();
}
});
// Check if a approve transition can be applied on some date
$stateMachine->can('approve', ['approved_at' => now()]);Example using a callback:
<?php
// Setup an callback after publishing
[
'callbacks' => [
'after' => [
'after_publishing' => [
'on' => 'publish',
'do' => [App\Actions\PublishArticleAction::class, 'execute'],
'args' => ['object', 'event'],
],
],
],
];
// Save the publish date in your action
class PublishArticleAction
{
public function execute(Article $article, TransitionEvent $event)
{
$context = $event->getContext();
$article->update(['published_at' => $context['published_at']]);
}
}
// Apply a publish transition on some date
$stateMachine->apply('publish', false, ['published_at' => now()]);You can optionally store metadata in graphs, states and transitions. The metadata are stored in associative arrays, and can be anything you want.
<?php
return [
'graphA' => [
'class' => App\Article::class,
'metadata' => [
'title' => 'Article State Machine',
],
'states' => [
[
'name' => 'pending_review',
'metadata' => ['title' => 'Pending Review'],
],
],
'transitions' => [
'ask_for_changes' => [
'from' => ['pending_review'],
'to' => 'accepted',
'metadata' => ['title' => 'Ask for changes'],
],
],
],
];The state machine object offers many flexible ways to fetch metadata, either as associative arrays, either specific values by keys. You can also pass default values or closures in case the specified key doesn't exist.
<?php
$stateMachine = StateMachine::get($article);
// ['title' => 'Article State Machine']
$stateMachine->metadata('graph');
$stateMachine->metadata()->graph();
// 'Article State Machine'
$stateMachine->metadata('title');
// 'Article State Machine'
$stateMachine->metadata('graph', 'title');
$stateMachine->metadata()->graph('title');
// null
$stateMachine->metadata('graph', 'invalid');
$stateMachine->metadata()->graph('invalid');
// 'default'
$stateMachine->metadata('graph', 'invalid', 'default');
$stateMachine->metadata()->graph('invalid', 'default');$stateMachine = StateMachine::get($article);
// ['title' => 'Pending Review']
$stateMachine->metadata('state', 'pending_review');
$stateMachine->metadata()->state('pending_review');
// 'Pending Review'
$stateMachine->metadata('state', 'pending_review', 'title');
$stateMachine->metadata()->state('pending_review', 'title');
// null
$stateMachine->metadata('state', 'pending_review', 'invalid');
$stateMachine->metadata()->state('pending_review', 'invalid');
// 'default'
$stateMachine->metadata('state', 'pending_review', 'invalid', 'default');
$stateMachine->metadata()->state('pending_review', 'invalid', 'default');<?php
$article->state = 'pending_review';
$stateMachine = StateMachine::get($article);
// ['title' => 'Pending Review']
$stateMachine->metadata('state');
// 'Pending Review'
$stateMachine->metadata('state', 'title');
// null
$stateMachine->metadata('state', 'invalid');
// 'default'
$stateMachine->metadata('state', 'invalid', 'default');<?php
$stateMachine = StateMachine::get($article);
// ['title' => 'Ask for changes']
$stateMachine->metadata('transition', 'ask_for_changes');
$stateMachine->metadata()->transition('ask_for_changes');
// 'Ask for changes'
$stateMachine->metadata('transition', 'ask_for_changes', 'title');
$stateMachine->metadata()->transition('ask_for_changes', 'title');
// null
$stateMachine->metadata('transition', 'ask_for_changes', 'invalid');
$stateMachine->metadata()->transition('ask_for_changes', 'invalid');
// 'default'
$stateMachine->metadata('transition', 'ask_for_changes', 'invalid', 'default');
$stateMachine->metadata()->transition('ask_for_changes', 'invalid', 'default');An artisan command for debugging graphs is included. It accepts the name of the graph as an argument. If no arguments are passed, the graph name will be asked interactively.
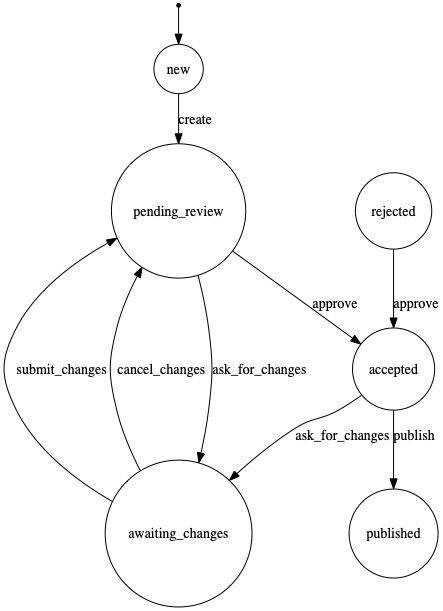
$ php artisan winzou:state-machine:debug simple
+--------------------+-----------------------+
| Configured States: | Metadata: |
+--------------------+-----------------------+
| new | |
| pending_review | title: Pending Review |
| awaiting_changes | |
| accepted | |
| published | |
| rejected | |
+--------------------+-----------------------+
+-----------------+------------------+------------------+
| Transition | From(s) | To |
+-----------------+------------------+------------------+
| create | new | pending_review |
+-----------------+------------------+------------------+
| ask_for_changes | pending_review | awaiting_changes |
| | accepted | |
+-----------------+------------------+------------------+
| cancel_changes | awaiting_changes | pending_review |
+-----------------+------------------+------------------+
| submit_changes | awaiting_changes | pending_review |
+-----------------+------------------+------------------+
| approve | pending_review | accepted |
| | rejected | |
+-----------------+------------------+------------------+
| publish | accepted | published |
+-----------------+------------------+------------------+
+---------------------+--------------------+------------------------+--------+
| Guard Callbacks | Satisfies | Do | Args |
+---------------------+--------------------+------------------------+--------+
| guard_on_submitting | On: submit_changes | MyClass::handle() | object |
| guard_on_approving | On: approve | Gate::check("approve") | |
+---------------------+--------------------+------------------------+--------+
+---------------------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------------+
| Before Callbacks | Satisfies | Do | Args |
+---------------------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------------+
| log_before_approval | On: approve | Log::info() | "approving article", object |
+---------------------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------------+
+----------------------+--------------+------------------------------+---------------+
| After Callbacks | Satisfies | Do | Args |
+----------------------+--------------+------------------------------+---------------+
| email_after_approval | To: accepted | SendApprovalMail::dispatch() | object, event |
+----------------------+--------------+------------------------------+---------------+
An artisan command for generating an image of a given graph is included. It accepts the name of the graph as an argument. It's taken from the corresponding bundle for Symfony: https://github.com/MadMind/StateMachineVisualizationBundle, so all credits goes to the original author.
If you want to run this command, you need to have installed dot - Part of graphviz package (http://www.graphviz.org/). In your mac, this is equal to having run brew install graphviz
php artisan winzou:state-machine:visualize {graph? : A state machine graph} {--output=./graph.jpg} {--format=jpg} {--direction=TB} {--shape=circle} {--dot-path=/usr/local/bin/dot}If you want to interact with the state machine directly within your models, you can install the laravel-statable package by iben12.
This package allows you to get the graph from the model, checking/applying transitions, as well as recording the state history in the database.
Please see CHANGELOG for more information what has changed recently.
$ composer testPlease see CONTRIBUTING for details.
If you discover any security related issues, please email info@sebdesign.eu instead of using the issue tracker.
The MIT License (MIT). Please see License File for more information.